Bulk sales approach for farmer apex organisations (FaAO)
(Mali)
Approche de commercialisation groupée par des organisations paysannes faitières (OPF))
Description
Improve the income of family farms by setting up an organized trade mechanism that factors in market price fluctuations.
The objective of the practice is to improve the income of family farms by setting up an organized trade mechanism that factors in market price fluctuations. Structuring trade in this way puts producers in a stronger position in their value chains.
The FaAOs’ approach to trade is based, on the one hand, on purchase agreements for preservable produce (cereals, sesame, etc.) between the FaAO and its producers and, on the other, on sales contracts with one or several market operators/suppliers. The practice enables producers to sell their produce after the harvest at an attractive price, depending on market fluctuations. For the operator, it means a large quantity can be purchased over time, without the need for mobilising major pre-financing resources. As the intermediary, the FaAO benefits from a profit margin and charges levied on transactions.
Stages of implementation: 1) Estimating the areas of family farms that are members of the FaAO: Together with its producers, the FaAO calculates sown areas (of rice, for example) fairly speculatively, providing the first estimates of future outputs. 2) Estimating outputs: Prior to harvesting, the initial estimates made in stage 1 are further refined through crop inspections. 3) Evaluating the quantities for home consumption and for sale: After the harvest, FaAO producers assess what part of their output will be retained for home consumption and what will be sold. 4) Contracting between the family farms and FaAO: The FaAO enters into a contract with the producers for the part to be sold. 5) Contracting between the economic operator and FaAO: Research into economic operators; At a consultation day involving producers, FaAO and operators, a contract is negotiated between FaAO and the operators, who will factor in price increases up to the lean period. Operation: Introducing this approach requires a robust FaAO or family farm, a market analysis and good quality produce. The portion of the output for sale is transferred to the FaAO storage facility. The operator draws down this produce over an extended period. The price for each consignment varies according to the market rate prevailing at the time the produce is drawn down.
Producers provide, process and pack the produce, and enter into a contract with FaAO. The apex organisation researches economic operators, negotiates the sales contract on behalf of the economic operators, stores the produce, monitors sales and manages rebates. Operators draw down produce in line with the terms of the sales contract, and make payments accordingly. Support partners deliver training, provide advisory support and foster contacts.
Location
![]()
Location: Ségou, Sikasso, Mali, Mali
Geo-reference of selected sites
Initiation date: 2008
Year of termination: n.a.
Type of Approach
-
traditional/ indigenous
-
recent local initiative/ innovative
-
project/ programme based

Hulling fonio in San (HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation)
Approach aims and enabling environment
Main aims / objectives of the approach
The objective of the practice is to improve the income of family farms by setting up an organized trade mechanism that factors in market price fluctuations. Structuring trade in this way puts producers in a stronger position in their value chains.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: low income of family farms, market price fluctuations
Conditions enabling the implementation of the Technology/ ies applied under the Approach
Conditions hindering the implementation of the Technology/ ies applied under the Approach
-
Availability/ access to financial resources and services: low income of family farms
Treatment through the SLM Approach: setting up an organized trade mechanism that factors in market price fluctuations; purchase agreements for preservable produce (cereals, sesame, etc.) between the FaAO and its producers and sales contracts with one or several market operators/suppliers.
Participation and roles of stakeholders involved
Stakeholders involved in the Approach and their roles
| What stakeholders / implementing bodies were involved in the Approach? |
Specify stakeholders |
Describe roles of stakeholders |
| local land users/ local communities |
|
|
| SLM specialists/ agricultural advisers |
|
|
| NGO |
|
|
| local government |
|
|
| national government (planners, decision-makers) |
|
|
Involvement of local land users/ local communities in the different phases of the Approach
none
passive
external support
interactive
self-mobilization
Flow chart
The stages of the trading strategy
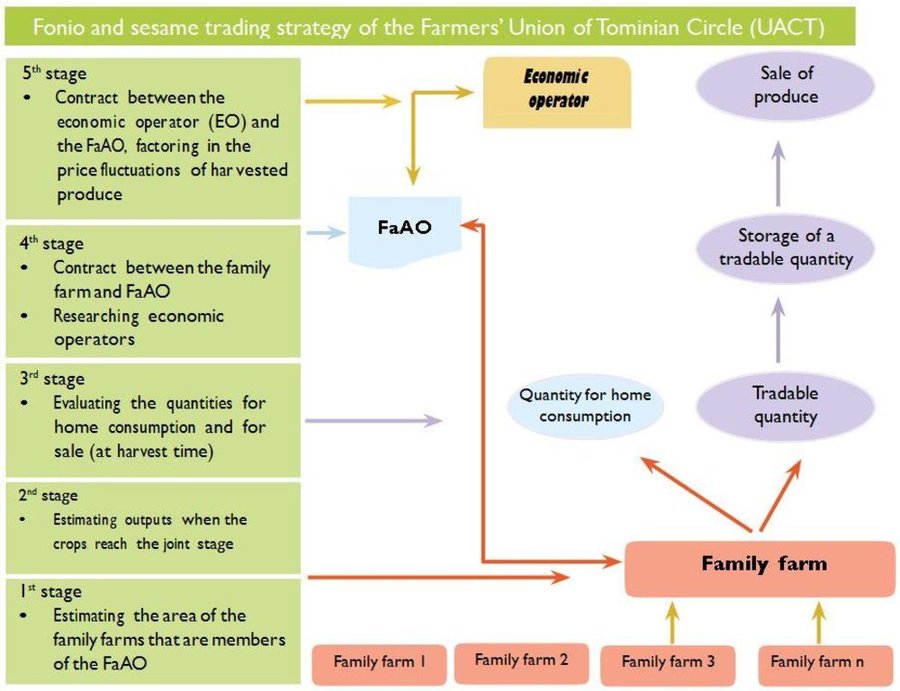
Author: HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation
Decision-making on the selection of SLM Technology
Decisions were taken by
-
land users alone (self-initiative)
-
mainly land users, supported by SLM specialists
-
all relevant actors, as part of a participatory approach
-
mainly SLM specialists, following consultation with land users
-
SLM specialists alone
-
politicians/ leaders
Decisions were made based on
-
evaluation of well-documented SLM knowledge (evidence-based decision-making)
-
research findings
-
personal experience and opinions (undocumented)
Technical support, capacity building, and knowledge management
The following activities or services have been part of the approach
-
Capacity building/ training
-
Advisory service
-
Institution strengthening (organizational development)
-
Monitoring and evaluation
-
Research
Capacity building/ training
Training was provided to the following stakeholders
-
land users
-
field staff/ advisers
Form of training
-
on-the-job
-
farmer-to-farmer
-
demonstration areas
-
public meetings
-
courses
Subjects covered
Support partners deliver training, provide advisory support and foster contacts.
Institution strengthening
Institutions have been strengthened / established
-
no
-
yes, a little
-
yes, moderately
-
yes, greatly
Describe institution, roles and responsibilities, members, etc.
Type of support
-
financial
-
capacity building/ training
-
equipment
Further details
Improve the income of family farms by setting up an organized trade mechanism that factors in market price fluctuations. Structuring trade in this way puts producers in a stronger position in their value chains.
Monitoring and evaluation
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff, land users through observations
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements
management of Approach aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff through observations
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation
Research
Research treated the following topics
-
sociology
-
economics / marketing
-
ecology
-
technology
Financing and external material support
Annual budget in USD for the SLM component
-
< 2,000
-
2,000-10,000
-
10,000-100,000
-
100,000-1,000,000
-
> 1,000,000
Precise annual budget: n.a.
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international non-government: 100.0%
The following services or incentives have been provided to land users
-
Financial/ material support provided to land users
-
Subsidies for specific inputs
-
Credit
-
Other incentives or instruments
Impact analysis and concluding statements
Impacts of the Approach
No
Yes, little
Yes, moderately
Yes, greatly
Did the Approach help land users to implement and maintain SLM Technologies?
The approach offers producers greater opportunities to access enhanced seeds and inputs (credibility among service providers).
Did the Approach empower socially and economically disadvantaged groups?
When prices become more lucrative, producers are less inclined to sell off their harvest; the risk of slumps in prices is minimal.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
Implementation locations: Ségou and Sikasso. 12,750 beneficiaries are applying this approach in 14 apex organisations.
Main motivation of land users to implement SLM
-
increased production
-
increased profit(ability), improved cost-benefit-ratio
-
reduced land degradation
-
reduced risk of disasters
-
reduced workload
-
payments/ subsidies
-
rules and regulations (fines)/ enforcement
-
prestige, social pressure/ social cohesion
-
affiliation to movement/ project/ group/ networks
-
environmental consciousness
-
customs and beliefs, morals
-
enhanced SLM knowledge and skills
-
aesthetic improvement
-
conflict mitigation
Sustainability of Approach activities
Can the land users sustain what hat been implemented through the Approach (without external support)?
Conclusions and lessons learnt
Strengths: land user's view
Strengths: compiler’s or other key resource person’s view
-
Bank loans guaranteed as a result of retained stocks and management tools
-
Guaranteed revenues for small-scale producers
-
Improved post-harvest management
-
As revenues grow, producers seek to maximise their cropping schedules in order to earn more money. The approach offers producers greater opportunities to access enhanced seeds and inputs (credibility among service providers). When prices become more lucrative, producers are less inclined to sell off their harvest; the risk of slumps in prices is minimal. Incomes are stabilised, which improves living conditions and social cohesion. Communities are better able to pay taxes and more receptive to formalised contracts.
-
Price stabilisation (to prevent produce from being sold-off) and improved producer incomes (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: A thorough market analysis must be conducted to enable market price fluctuations to be accurately predicted and the best times for sale to be pinpointed. Client relationships must be professional and contractual. Informal commitments often fall through. The FaAO must have committed and business-minded leaders. It is wise to stay vigilant when it comes to the governance of these organisations, as they can fall prey to corrupt practices and the embezzlement of collective funds.)
Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks: land user's viewhow to overcome
Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks: compiler’s or other key resource person’s viewhow to overcome
References
Date of documentation: Sept. 24, 2014
Last update: June 21, 2017
Resource persons
-
Dieter Nill (dieter.nill@giz.de) - SLM specialist
-
Maïga Rosaline Dacko (rosaline.dacko@helvetas.org) - SLM specialist
-
Lassana Keita (lassana.keita@helvetas.org) - SLM specialist
-
Idrissa Guindo (idrissa.guindo@helvetas.org) - SLM specialist
Full description in the WOCAT database
Documentation was faciliated by
Institution
- Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - Germany
- HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)
Project
Key references
-
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel. Experiences from Mali. Published by GIZ in 2014.: http://star-www.giz.de/starweb/giz/pub/servlet.starweb
-
HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation: annual report 2010-2011 for the San Hub (Pôle de San) :
-
HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation (2013): JIGIYA programme evaluation report:





