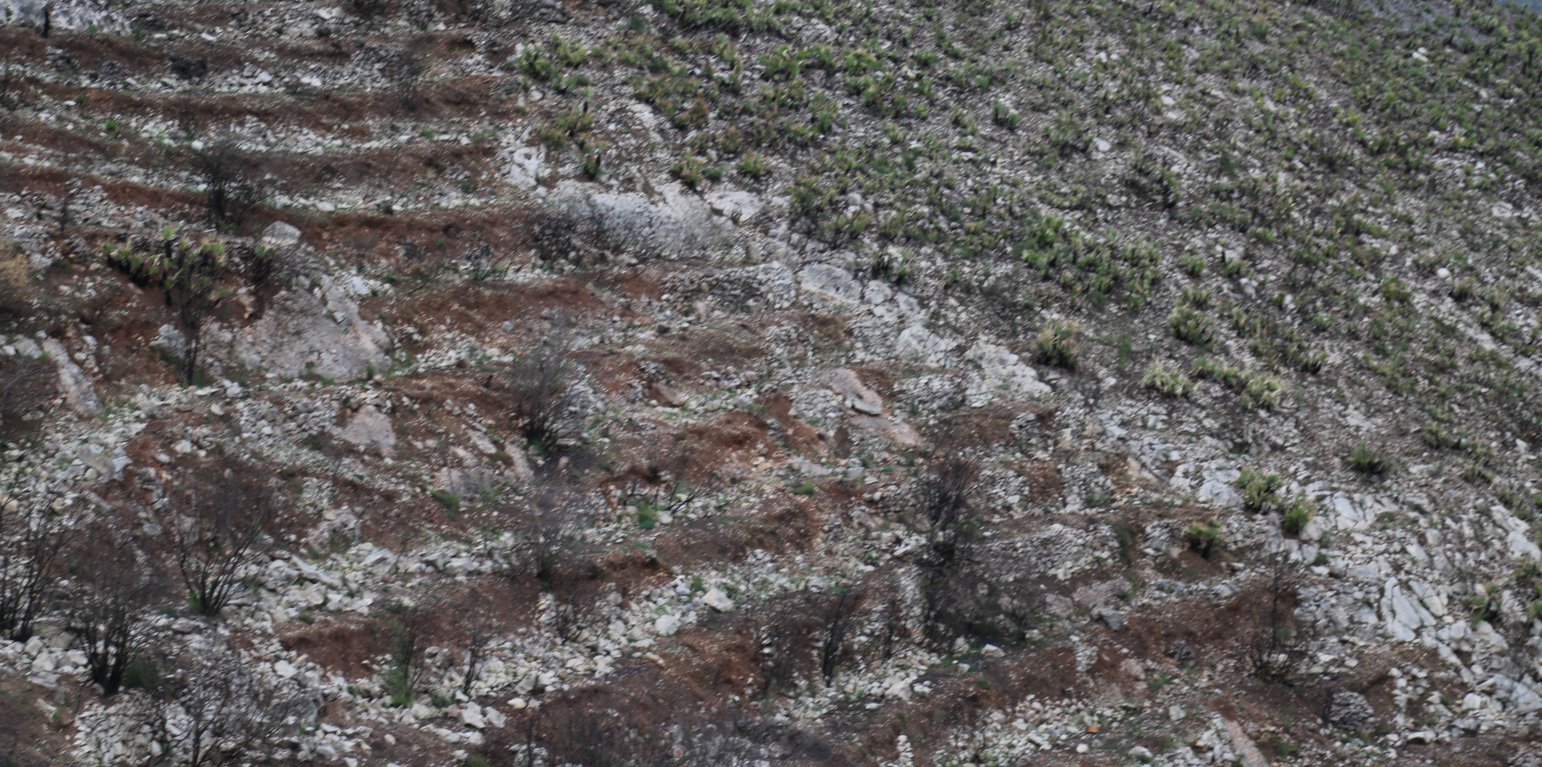




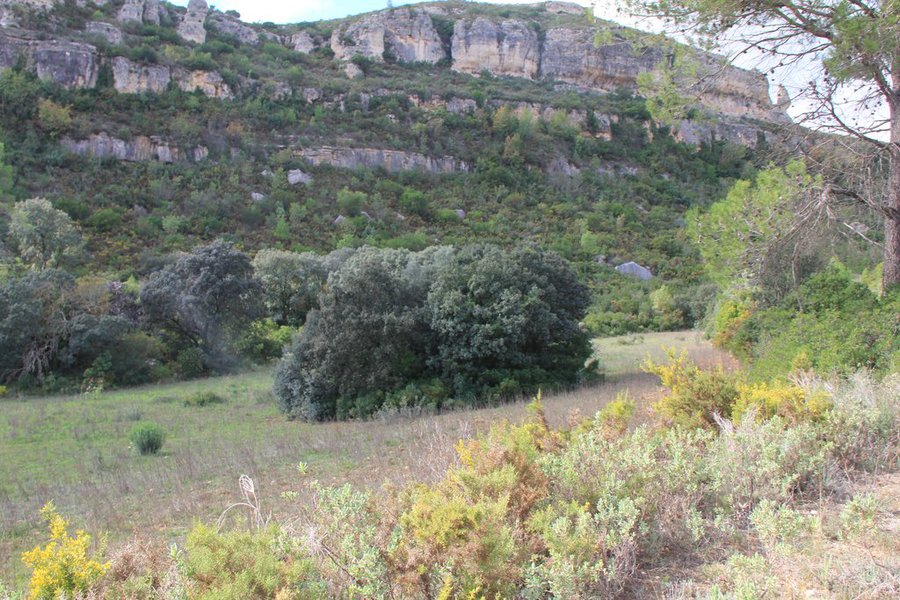
A wildfire is expected for summer 2015 in the Caroig mountain range. The area was afforested with Aleppo pines during the 20th century and nowadays the landscape is composed by mature Aleppo pines at different stages of development with shrub vegetation in the understorey.
Purpose of the Technology: The post-fire area is expected to be reforested with local shrubs species and Aleppo pines.
Perturbation by machinery when reforesting is expected to increase soil erosion.
The research team of the University of Valencia will implement an experiment based on the sediment fences technique to capture and measure post-fire soil losses in a reforested burned landscape.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Maintenance activity deals with the plantation scheme which includes man-power, machinery, access to remote areas and cost of plants, as main expenses.
Natural / human environment: The Aleppo pine trees in the region are typically planted as monoculture for wood production. The landscape reflects a long history of intense land management, with a mosaic of (semi-) natural and man-made agricultural (terraces) and afforested lands. Since the 1970´s, however, wildfires have increased dramatically in frequency and extent, driven primarily by socio-economic changes.
Location: Valencia, Spain, Spain
No. of Technology sites analysed: single site
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. 10-100 km2)
Date of implementation: less than 10 years ago (recently)
Type of introduction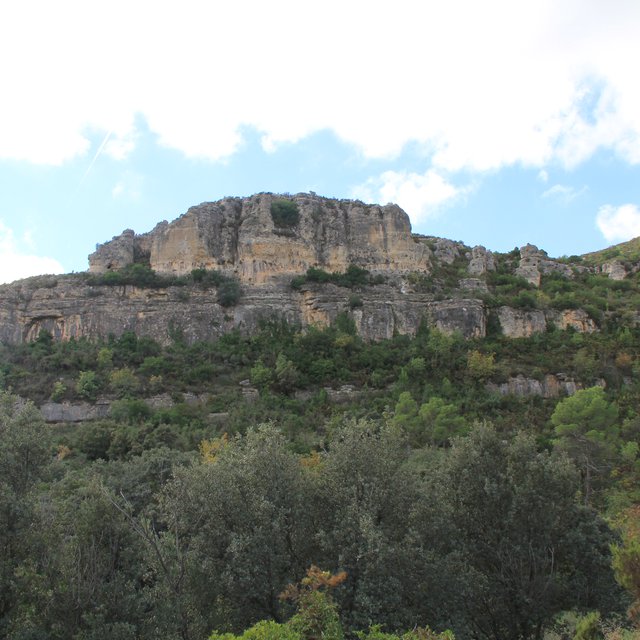







| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (US Dollars) | Total costs per input (US Dollars) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| abandonment | Person days | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (US Dollars) | Total costs per input (US Dollars) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| visits to the field | € | 1.0 | |||