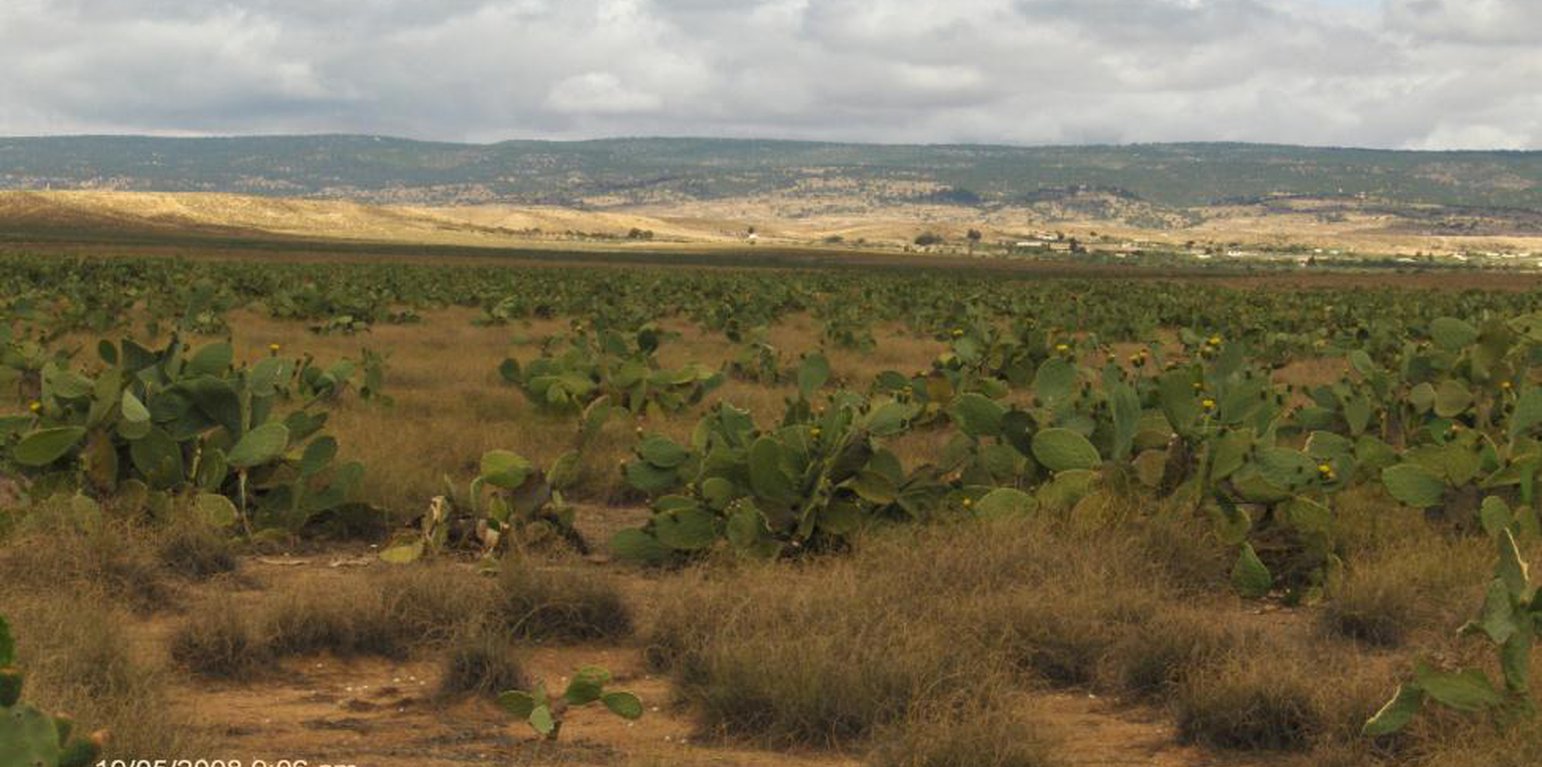




Les principaux arbustes fourragers utilisés au Centre – Sud de la Tunisie sont : Acacia cyanophylla, Atriplex nummularia et A. halimus, Opuntia ficus indica var. inermis si l’on peut considérer comme arbuste. Ces espèces ont donné des résultats spéctaculaires au Centre du pays elles ont par contre échoué dans le Sud en raison de l’aridité extrême. Ce n’est que ces dernières années que le recours aux espèces locales, plus adaptées aux conditions difficiles, comme Periploca angustifolia, Rhus tripartitum, Retama raetam a pris de l’ampleur.
Dans les parcours collectifs, les services forestiers se chargent à travers des chantiers de l’irrigation et de l’entretien des plantations. Au niveau des par-cours privés, l’Office d’Elevage et des Pâturages se charge d’apporter les plants et fournir des subventions au bénéficiaire qui se charge de toutes les opérations d’entretien et de protection.
L’exploitation par pacage direct ou recolte (cas du cactus) se fait après 3 à 4 ans pendant les périodes de soudure et de sécheresse.
Location: Kasserine, Tunisia
No. of Technology sites analysed: single site
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. 0.1-1 km2)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction






| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (n.a.) | Total costs per input (n.a.) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| 20.0 | 10.0 | 200.0 | |||
| Plant material | |||||
| 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | |||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 500.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 500.0 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (n.a.) | Total costs per input (n.a.) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||
| 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | |||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 300.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 300.0 | ||||