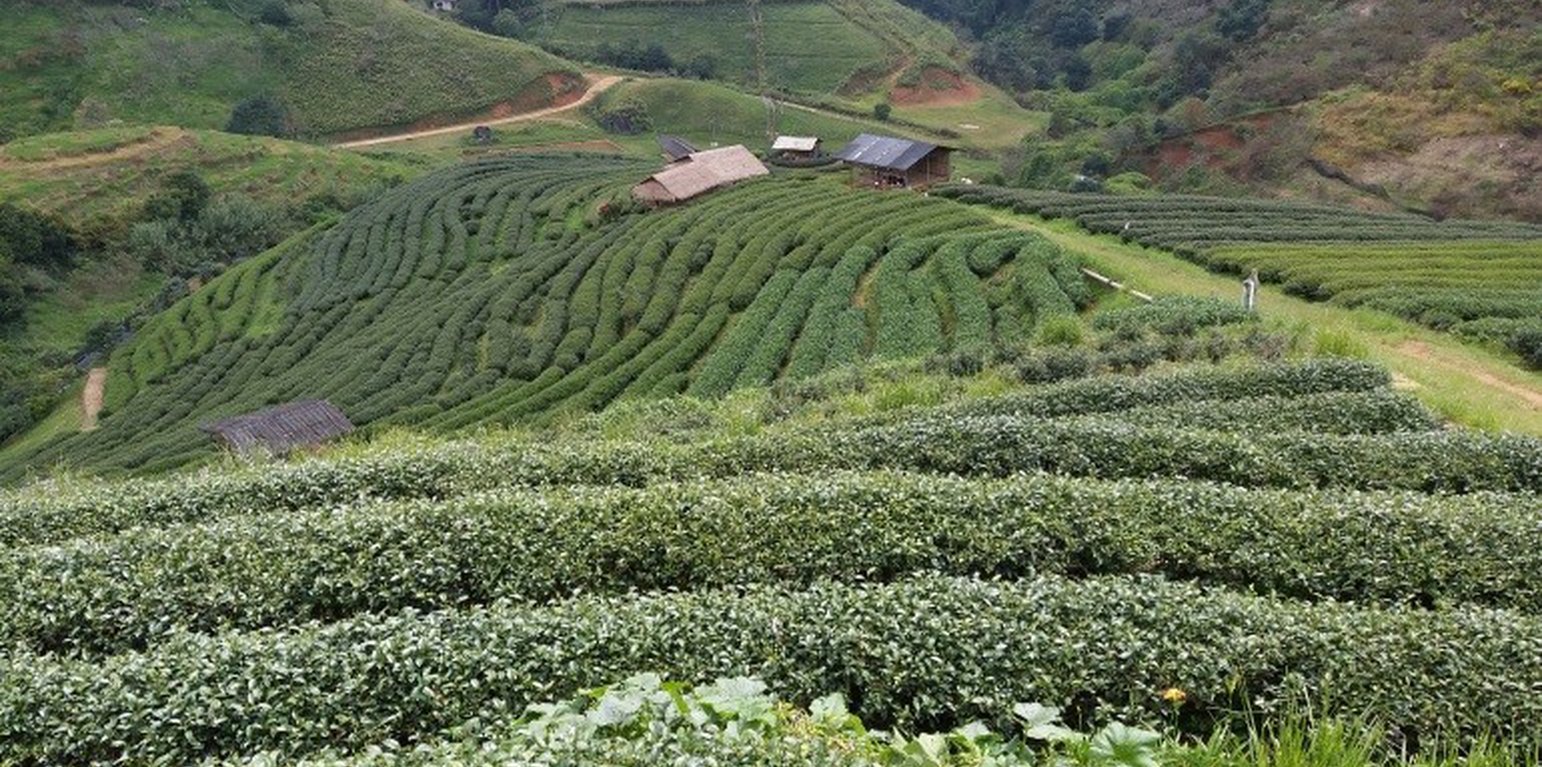




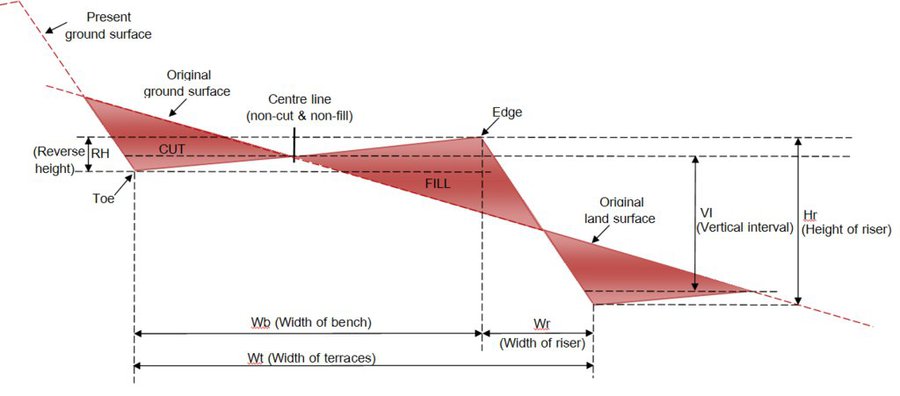
The continuous bench terrace (forward-sloping terrace) as soil and water conservation measure in the high landscape at Angkhang Royal Agricultural Station, Moo 5, Mae Ngon subdistrict, Fang district, Chiang Mai province was constructed in 1999 in the area of former winter fruit plantation plot of the station. Land Development Department had surveyed, designed and constructed the 3 meters wide of continuous bench terrace, which it is suitable for the tea cultivation and total area is approximately 100 rai. The Angkhang Royal Agricultural Station had selected 50 households of Palaung hill tribe who have more ability and aptitude to grow Chinese tea to participate in the Chinese tea development and promotion project in 2000 and named this area as "Plot 2000". The overview of this area is complex mountainous terrain with slope range 16-30 percent, and average attitude is 1,400 meters above sea level. The soil texture is silty loam and very deep (more tan 1.2 meter), almost well drained soil. The soil organic matter is moderate around 1-3 percent. Moreover, the data of Doi Ang Khang Meteorological Station (Station Code 48302) is located at average attitude 1,529 meters above the sea level, and average temperature throughout the year is 22.9 Celsius with the highest temperature is 32.1 Celsius (during May) and the lowest temperature is 3.9 Celsius (during December), and average annual rainfall is 1,925.3 mm, with rain starting from April to October.
In the past, the watershed areas in northern Thailand have been disturbed by natural disasters, climate change, and human threats. The hill tribe people had invaded the forest to grow opium and shifting cultivation continuously. These condition caused the serious problem in soil erosion, runoff with soil surface, lose of topsoil and plant nutrients, decreasing in soil fertility and productivity with the extremely damage to upstream forest ecosystem. Until in the year 1969, Angkhang Royal Agricultural Station was established from the initiative of His Majesty King Rama 9, which aimed to conduct research on the planting of winter economic crops as an example for hill tribe to plant those crops as their career instead of opium cultivation, and also stop cutting and shifting cultivation. Nowadays there are more than 50 species of economic plants in this project and generating more income for land users, more than that this slopping area is the sustainable in land use and land management under organization of the Royal Project Foundation.
The benefits this technology is important in sustainable utilization of land resources in this area, and all land users around the Angkhang Royal Agricultural Station have stable and more income because they can grow Chinese tea and also other winter economic crops on this highland throughout the year. Moreover, this continuous bench terrace is more convenient for land users in fertilizer application, soil improvement, machines operation, tea harvesting and also yield transportation from cultivated plots to local processing factory.
The impact of implementation continuous bench terrace with 3 meters based:
1. The obvious economic and social impacts of land users are the stability of income from the production of Chinese tea, which are produced throughout the year. This conservation is more convenient for land users to implement in their plot and also transport from cultivated plots to local processing factory. The local officers from Angkhang Royal Agricultural Station and others government agencies closely advised and guided breeding, planting, soil management, harvesting and price guarantee.
2. The environmental and ecological impact is to reduce the amount of runoff and soil sediment, increase soil moisture, preserve soil nutrients and fertility, encourage biodiversity in the area of Plot 2000.
3. The society and culture impact is all ethnic groups are given the opportunity to receive the allocation of arable land according to the group of plants that they are comfortable and want to produce. Thus respecting the use of land in zoning as allocated from the station, including right to use water. These caused the strength of community institutions, where they have various crop production groups, organic fertilizer production Group and others. They are all member of the cooperative of the community.
Location: Extension area for Chinese tea plantation (Plot 2000) at Angkhang Royal Agricultural Station, Mae Ngon Subdistrict, Fang District, Chiang Mai ProvincePlot, Ban Thap Sub-District, Mae Chaem District, Chiang Mai Province, 50270, Thailand
No. of Technology sites analysed: single site
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. 0.1-1 km2)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 1999; 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction





| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Baht) | Total costs per input (Baht) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| site survey 1 day | man | 0.5 | 175.82 | 87.91 | |
| set up contour line 1 day | man | 4.0 | 175.82 | 703.28 | |
| vetiver planting (400 slips x 8 rows) | slip | 3200.0 | 1.65 | 5280.0 | |
| man power (2.4 cu.m./m.) | cu.m. | 88.0 | 100.88 | 8877.44 | |
| Equipment | |||||
| machine power (2.4 cu.m./m.) | cu.m. | ||||
| pin wood | unit | 100.0 | 5.0 | 500.0 | |
| Plant material | |||||
| vetiver slip (LDD supported) | 3200.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 15'448.63 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1.0 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Baht) | Total costs per input (Baht) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| man power to repair the terrace | man | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 500.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 0.03 | ||||
They have cooperative activity to support investment and production costs such as fertilizers, bio-pesticides, pesticides and others.
In former time land users use shifting cultivation for corn and upland rice. After organic tea farming had set up at Plot 2000 their products and income were increased and can harvest throughout the year.
They have advised from stations' staff and promote varieties, planting, production, harvest, purchase, insurance price. There are tea processing factories in the market, making tea production sustainable (integrated)
this area can not extend.
After this system has been allocated for organic tea in the Plot 2000, where soil conservation measure and soil management is need.
This system need more water continuously.
This system need to maintain the terrace and more work to take care tea tree.
They have more income from tea product continuously.
They have equal opportunities in earning their life.
They have more workload almost daily and continuously because they need to intensive care on terrace construction and tea tree.
This system had set up zoning system for some crop by Angkhak Station, and also management in right to water utilization.
They have strong cooperatives and all members are the land users in this area. There are various crop production groups and organic fertilizer production group.
Almost land users in this area know very well about soil erosion in hillside with slopping area. and realizing that bench terrace can solve these problem and make it sustainable condition.
Every ethnic group has been given the opportunity to receive the allocated land according to their experience and knowledge in each crop.
This system can reduce amount of water runoff and store some water into the soil..
This system can store more water into the soil, and soil moisture are in soil layer longer.
The system would have more ground cover crops.
The bench terrace is very effective in prevention of soil erosion and water storage.
In the upper part almost soil are accumulated in the bench terrace, that means soil fertility and nutrient still stay in the slopping area.
The system makes more crops covered soil surface throughout the year.
The system improve small animals and insects in soil such as earthworms, bees, dragonflies, spiders, ladybugs and others.
They emphasized in organic farming, so they need to have more technical advised in natural products for pest and insect control.
The system can reduce in both of amount of runoff and soil sediment to the lower part.
-
-