



In the Carbiocial Project viable land management strategies were explored to optimize the level of carbon in soil and water, helping to maintain and/or improve ecosystem functions, under changing climatic conditions in the Southern Amazon and the Brazilian Cerrado. In the framework of this project, on-farm experiments were performed to enrich tropical agricultural soils in the medium term, with different types of organic matter (OM). In the experiment the effect of different types of OM amendments on soil carbon and macro-nutrients (N, P, and K), soil physical properties (waterholding capacity) and crop yield (soy biomass and grain production) were assessed. The amendments applied are locally available, and are either free (being waste materials) or considered cost-efficient.
The objective of this on-going experiment is to compare the impact of (i) the quality and quantity of OM applied, (ii) and the application methods (directly on the soil surface or incorporation by harrow) on soil chemical and physical properties. It is hypothesised that the addition of OM can enhance crop yields and, potentially, soil biodiversity. The effects of the different OM types, amounts and application methods were evaluated after one, two and three years. From the results, the aim is to provide recommendations for the development of soil OM-enrichment schemes and carbon-friendly landscape management programs for farmers, using local resources.
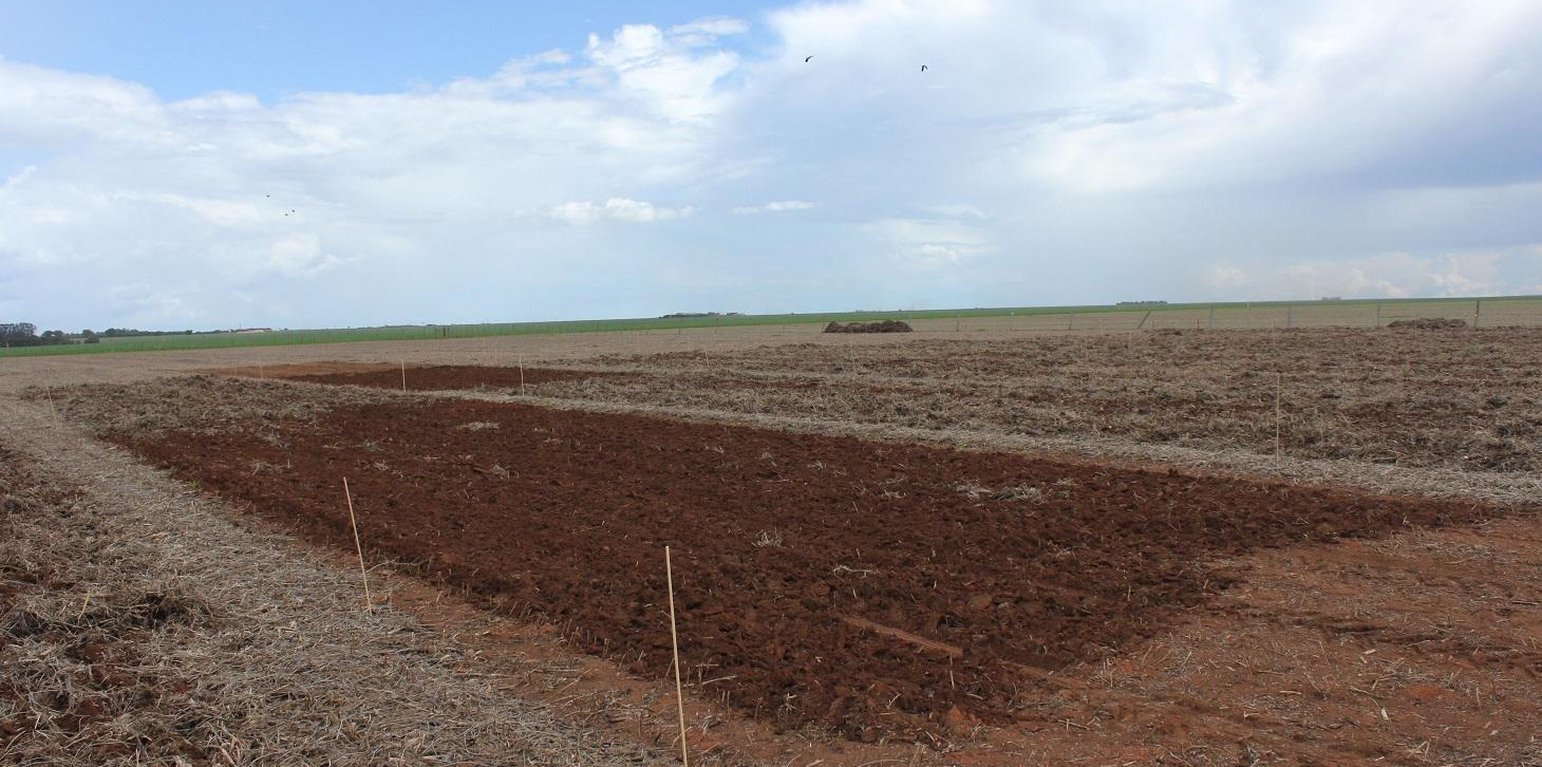
The experiment was established on an area of about one hectare on a ferrasol (red latosol) at the Rio Engano Farm, in the municipality of Campo Verde, Mato Grosso State. The farm has a total area of ca. 1500 ha, 830 ha of which are cultivated with soybean and maize rotation, under a zero-tillage system, which is typical of many farms in this region. It is located in the Brazilian Cerrado (savanna) biome at about 685 m a.s.l. This biome covers 2 million km2, which is 23% of the country area. It has a semi-humid climate with a pronounced dry season. The precipitation during the rainy season (September-April) varies between 800 and 2000 mm/year.
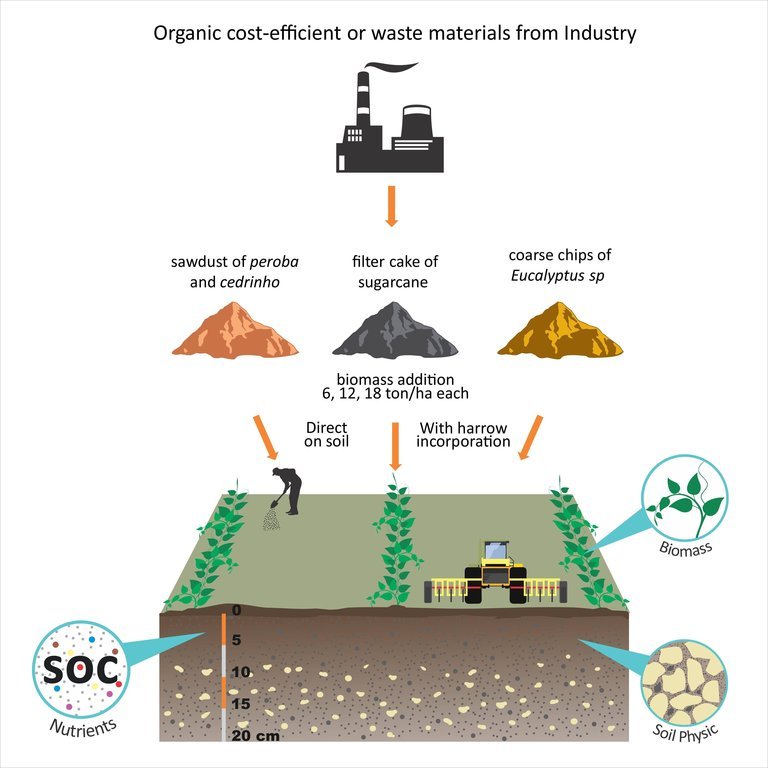
At the beginning of the experiment (February 2012), three different types of OM amendments were applied. They comprised (a) sugarcane filter cake (Saccharum officinarum from ethanol/sugar-production, (b) sawdust of peroba and cedrinho (Peroba jaune and Erisma uncinatum, respectively) and (c) coarse chips of Eucalyptus sp. Quantities applied were 0 (control), 6, 12 and 18 tonnes of each per hectare; using two methods: directly on the soil surface, and incorporated by harrow. There were three repetitions per treatment. The area was not fenced to allow the farmers to continue with their field routines on all plots. In February 2013, 2014 and 2015 soil samples were taken to analyze their chemical and physical properties. Soybean samples were also taken in February 2014 and 2015 to estimate biomass and grain production. From the initial results some conclusions can be drawn: 1) Organic amendment addition to ferrasols can significantly increase soil organic carbon, even in amounts as low as 6 t/ha. 2) Amendments should be reapplied every 2 years. 3) The amendment type and application method does not have a significant effect on increasing soil organic carbon. 4) The addition of OM amendments is a win-win situation as a solution for organic matter waste recycling, and simultaneously to improve soil quality.
The area was not fenced to allow the farmer to continue with their arable field routines on all treatment plots. In February 2013, 2014 and 2015 soil samples were taken to analyze their chemical and physical properties. Soy bean samples were also taken in February 2014 and 2015 to estimate biomass and grain production.
From our first results we can draw some conclusions:
1) Organic amendment addition to Ferrasol can increase significantly soil organic carbon (SOC) percentage, even in small amounts such as 6 ton/ha.
2) Amendment reapplication should be done in 2 years intervals.
3) The amendment type and disposition did not have a significant effect on increasing SOC.
4) The addition of OM amendments is a win-win situation as a solution for organic matter waste recycling and to improve soil quality.
Location: Campo Verde, Mato Grosso, Brazil
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (0.011544 km²)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: less than 10 years ago (recently)
Type of introduction








| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (BRL) | Total costs per input (BRL) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| labour | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| machine use | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| truck transport | ha | 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 170.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 42.5 | ||||
There is not specific machinery for organic matter application in large scale
In case the technology reduces the crop demand for chemical fertilization, nonetheless this effect has not been yet evaluated