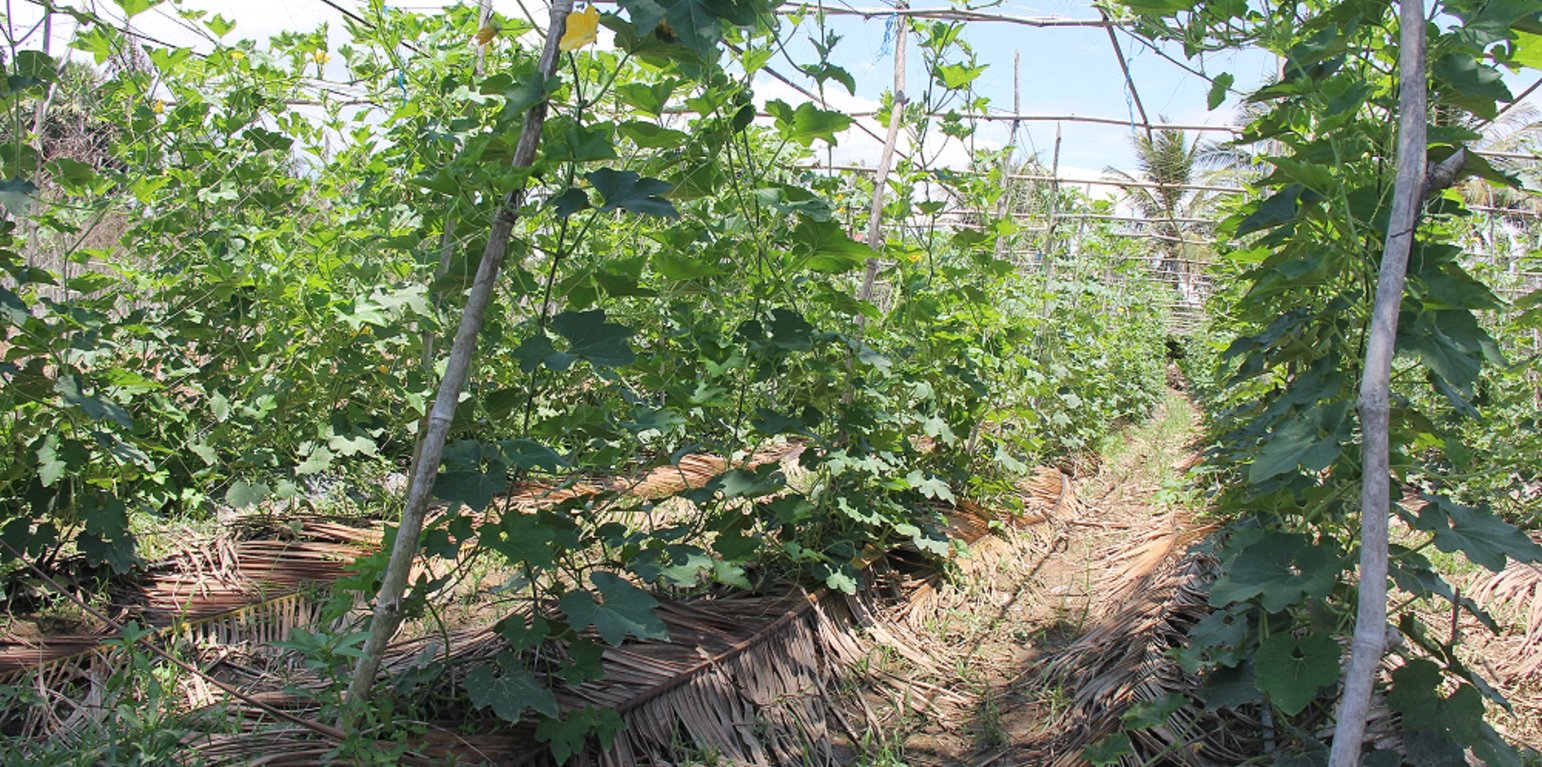




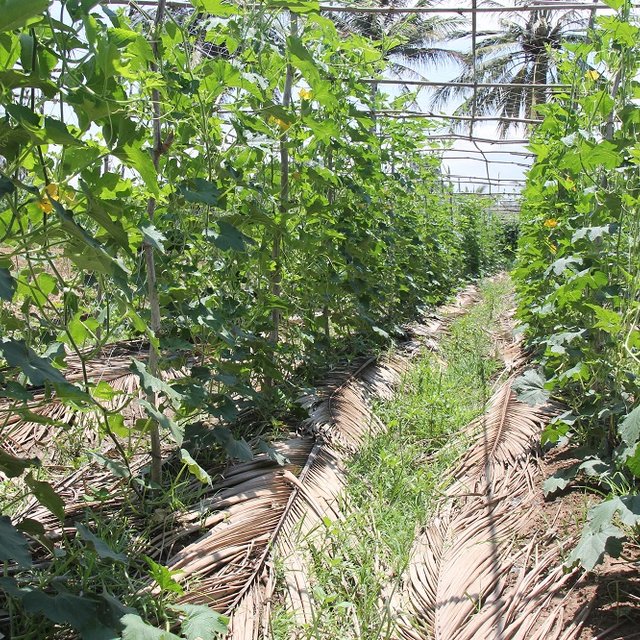
Coconut leaves mulching is the process of covering the soil around plant root area using green/ dry coconut leaves to help keep the soil moisture longer and reduce evaporation and temperatures, especially during the dry season. Beside this, the use of coconut leaves mulch for covering rows of winter melons helps to prevent soil erosion, improves soil fertility, reduces weed growth, and increases soil fertility following the decomposition of the plant residues. The soils best suited to winter melon cultivation are loamy and sandy loam soils with a soil pH of between 5.0 and 6.3 and soils along the low-land areas. If the pH soil is lower than 5.0, the melon growth is not good and may accelerate the ripening of the fruit before the appropriate time, with the fruit plants sometimes dying due to lack of nutrients (TSTD, 2012). The roots of the winter melon are able to grow in soil with a depth of between 65 and 100 cm, particularly sandy soils. This crop is not suitable for cultivation in areas which are wind prone because of increased moisture loss through plant evapotranspiration. Such areas are also sometimes prone to high temperatures which are also unsuitable for winter melon.
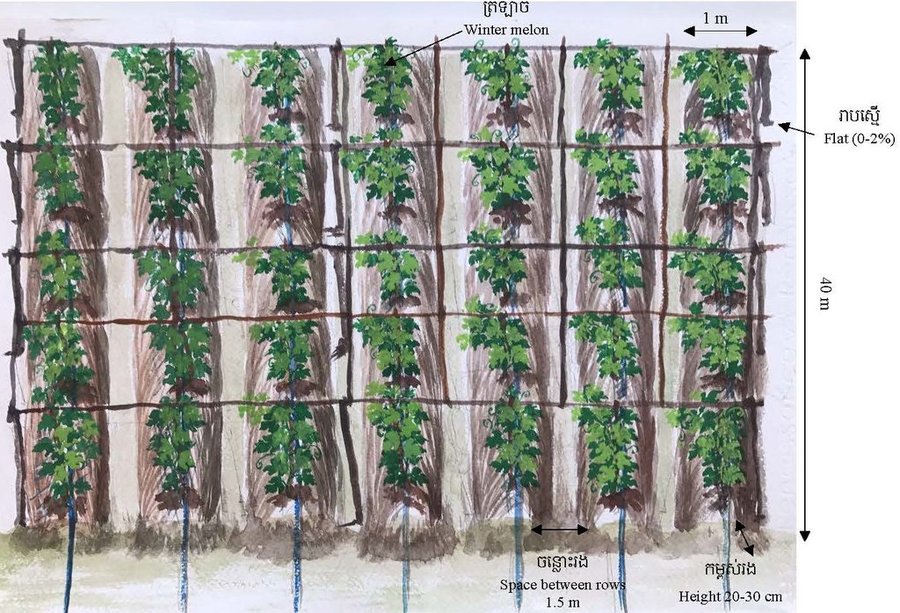
The implementation area for this study was 280 squares meters, with a row height of 20-30 centimeters, a row width of 1 meter, row length of 40 meters, and row spacing of 1.5 meters. There were a total of 8 planted rows, with 40 melon stems being planted into each row. The crop stems and the intercrop space between the rows is covered with coconut leaves by laying the leaves along the slopes of the melon crop, with 5 or 6 coconut leaves as mulch along the two sides of the crop. In order to save time and water, farmers used drip irrigation using a pipe irrigation system that could provide water at a rate of about 6 liters per house, twice daily (in the morning and evening). Irrigation was provided over 20 minute periods at a rate of 100 ml per minute (although this was reduced during the rainy season). The watering technique is not required to fill the basal area of the stem of growing winter melon plants. Water is generally not provided at noon or late evening as watering at this time can cause problems, such as rotting of roots. If the soil around the stem becomes dry, more water should be applied at short notice without waiting for the soil to dry out. This is particularly important in the period immediately after planting of the seedlings, when water and nutrients are important for initial plant growth. Also, during the flowering and fruiting phases of melon plant growth, water needs have to be closely monitored. As the soil had previously been used for sugarcane cropping, the nutrient status of the soil was low, so farmers have improved the soil nutrient status by adding some organic fertilizer (cow manure) and some chemical fertilizers in an appropriate manner. In addition, some pesticides have been used as well.
In general, the advantage of this technique is the low cost materials which are locally available, such as coconut leaves, and materials which can be purchased in the local market, such as drip pipe, black plastic string, etc. However, the important aspects of the adoption of this technique, besides improving soil quality and maintaining a stable environment, is that it provides practical and potential economic benefits to farmers of about 800,000 (US$ 200) Riel per season.
Location: Chamkar Ou village, Trapeang chorng commune, Bakan district, Pursat province, Cambodia
No. of Technology sites analysed: 10-100 sites
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 2013
Type of introduction







| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Riel) | Total costs per input (Riel) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Seedling preparation | person-day | 1.0 | 25000.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| Soil preparation | person-day | 5.0 | 30000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| Building of the pole support | person-day | 2.0 | 25000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Installment of the irrigation system | pieces | 2.5 | 27500.0 | 68750.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| Hoe | set | 2.0 | 7000.0 | 14000.0 | 100.0 |
| Scissors | set | 5.0 | 2500.0 | 12500.0 | 100.0 |
| Hacksaw | set | 1.0 | 12000.0 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| Axe | set | 1.0 | 12000.0 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| Watering can | pair | 2.0 | 25000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Floral hoe | set | 3.0 | 15000.0 | 45000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| Pesticide | bottle | 2.0 | 2500.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| DAP | bottle | 2.0 | 25000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Cali | kg | 50.0 | 2400.0 | 120000.0 | 100.0 |
| UREA | kg | 50.0 | 1800.0 | 90000.0 | 100.0 |
| Cow manure | bag | 1.0 | 25000.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | |||||
| Black string for building pole support | kg | 5.0 | 47000.0 | 235000.0 | 100.0 |
| Irrigation pipes | pieces | 2.5 | 90000.0 | 225000.0 | 100.0 |
| Valve | number | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | |||||
| Create rows by hilling up soil | person-day | 2.0 | 25000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 1'259'250.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 314.81 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Riel) | Total costs per input (Riel) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Thinning the branches | Person-day | 1.0 | 25000.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fixing the irrigation pipes | Person-day | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| Irrigation pipes | kg | 8.0 | 4700.0 | 37600.0 | 100.0 |
| Black strings for pole support | kg | 7.0 | 4700.0 | 32900.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 115'500.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 28.88 | ||||
The farmer used the coconut leaves mulch keeps good soil moisture and increase soil nutrient, thus increasing the crop production.
Farmer used raw material (coconut leaves) around her home that does not require any cost.
This technology improves soil moisture and soil nutrient, with less expense on the inputs as the coconut leaves are available around the house, thus the farm income increases.
After the farmer applied this technology, she was able to better secure food consumption in her house, and as well she was able to sell the winter melons at the market to get more income for buying food.
The farmer grew winter melon without any chemical use. She ate healthy vegetable that improved the health situation accordingly.
Farmer knows how to conserve soil moisture and preserves the soil from erosion, and increases crop productivity through implementing this SLM technology as before her land was not good for planting vegetable. She tried to convert her land from infertile to fertile soil using animal manure (cow dung) mixed with topsoil from the hill.
The technology area decreased the evaporation by using the coconut mulch as it keeps the soil moisture during the dry period.
The soil moisture is still remain even it dried for 3 days.
The conversion from infertile to fertile soil using animal manure mixed with topsoil increased the amount of soil organic matter.
The improved soil moisture let the winter melon plant survive even at drought events of one week.