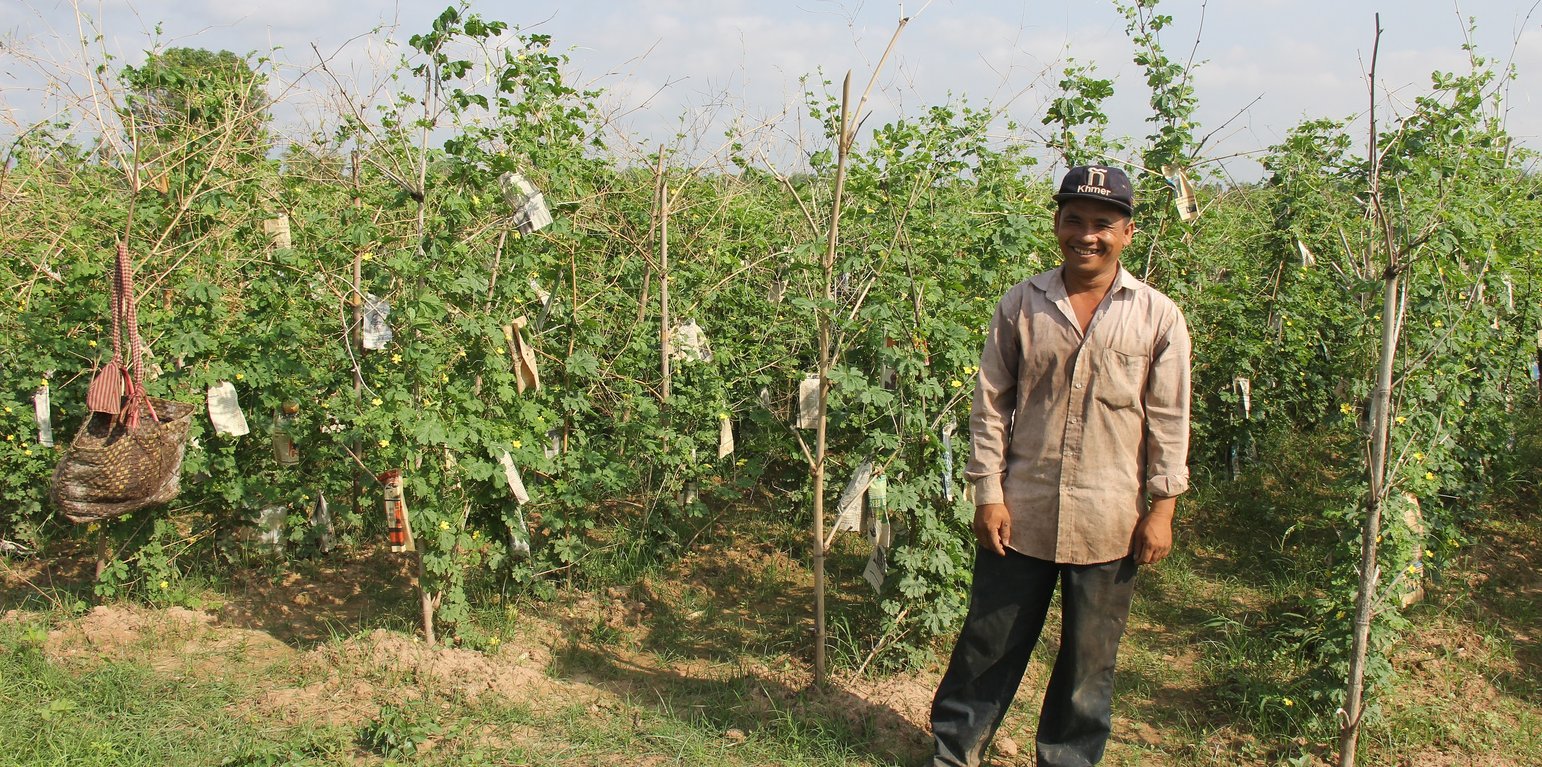




Bitter gourd is a crop that can be supported by trellises and it is possible to plant it throughout the year. However it is not recommended to grow it in areas with strong winds because then it takes longer to grow. Bitter gourd requires more fertile soil than other varieties in the Cucurbitaceae family. It needs to be well-saturated or loamy soil with a pH of 6 to 6.8. The most suitable land can be found along river banks, streams, and lakes with high silt content. Bitter gourds are susceptible to be damaged by pests and diseases. In order to protect the fruit from pests, plastic, paper or other materials are wrapped around the fruit. Additionally, the crop needs nets for climbing, which can be quite expensive (Agritoday, 2016).
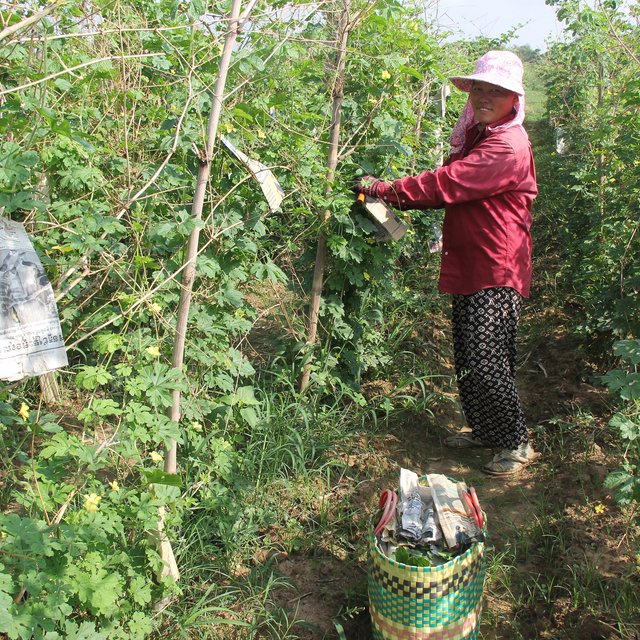
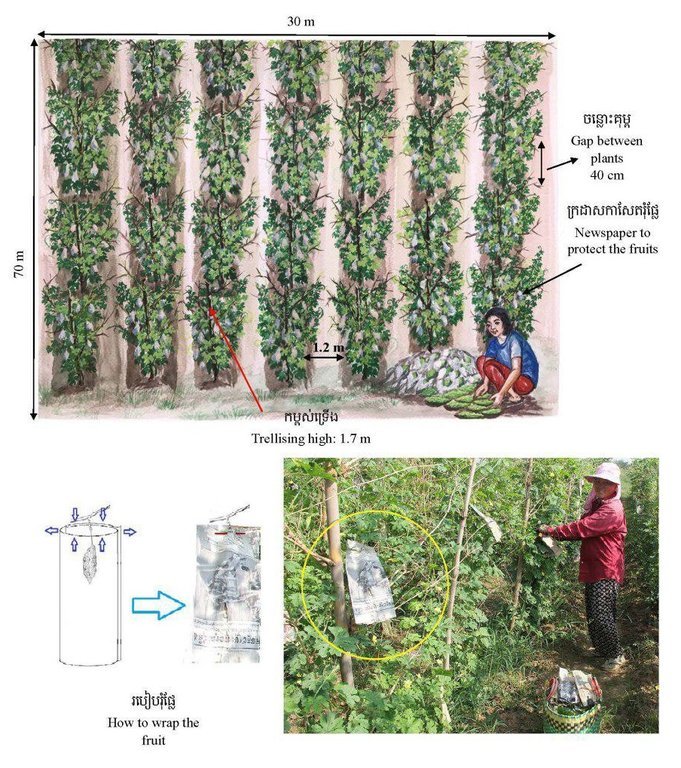
In this case study the farmer plants bitter gourds by using bamboo sticks to construct the trellis for plant climbing. And he wraps up the fruits with old newspapers. This growing technique is less expensive than using nets for plant climbing and medium A4 sized brown paper envelopes to protect the fruit. The bamboo sticks can be used for two years, and during this period the farmer is able to make use of them three to four times a year. The newspapers that have been bought to protect the fruit can be used two or three times, so as not only to reduce the cost but also to reduce the environmental impact. Covering the fruit with newspapers is better than using plastic bags or pages from books, because plastic bags can easily become too hot, and pages are particularly vulnerable to rain or water. The main purpose of wrapping up the bitter gourd with newspapers is to protect them from insects, especially the fruit fly. However it also protects them from the heat of the sun makes the fruit whiter, and acts as a protection against pesticides as this would otherwise be directly sprayed onto the fruit. Insecticides normally last an average of 7 to 10 days and plants will then have to be sprayed again to prevent the return of the insects. Farmers are able to harvest the bitter gourd about 15 days after pinned with newspaper.
As the area is flooded by the Mekong River during the months of August - October, it is not possible to plant bitter gourd in the rainy season. After the water has receded the soil should be ploughed and dried by the sun for 15 days. After this the soil should be plowed again, and then the field needs to be harrowed evenly and the soil left to dry for three more days. Fertilizers should not be added whilst ploughing. Planting is done by firstly using a hoe to scratch a central trench in the field. Further parallel lines to this trench should be 1.2 meters apart and the bitter gourd seeds should then be planted along the lines, at 40 centimeter intervals. Once the seeds are in the ground manure, cow or buffalo compost should be applied over the top and then watered. Before growing, it should be soaked for 2 hours and then covered with cloth. Afterwards they should be left to soak in a steady flow of water for 4 to 5 days until the shoots begin to grow. After when the developing bitter melon is 15 days old a bamboo pole with bamboo sticks of about 1.7 meters height and 10 cm from the plants has to be placed. A further 15 days after having put up the poles, the soil should be loosen up again and then the fish head fertilizer mixed with a little bit of UREA is applied. The fertilizer should be spread about 30 to 40 cm from plants, or it can be added between the bitter gourd clumps, which can also be combined with manure and UREA. Watering should be done twice a day, once in the morning and once in the evening. The irrigation system involves pumping water from a nearby lake. Even though pesticides are used regularly, if paper is not used to protect the fruits, they can still be affected by pests. Once affected the fruit falls down, becomes stunted, grows into irregular shapes, the color becomes dull. In case the fruit were directly affected by the poison it could be harmful to people’s health. Any combination of these physical symptoms can be identified very easily and monitored by the farmers themselves. Since the use of this technique the farmer’s income has increased because they are able to grow a product of good quality and high output.
Location: Floodplain which is flooded from August until September, Preaek Roka village, Saob commune, Preaek Prasap district, Kratie province, Cambodia
No. of Technology sites analysed: single site
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (0.0021 km²)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction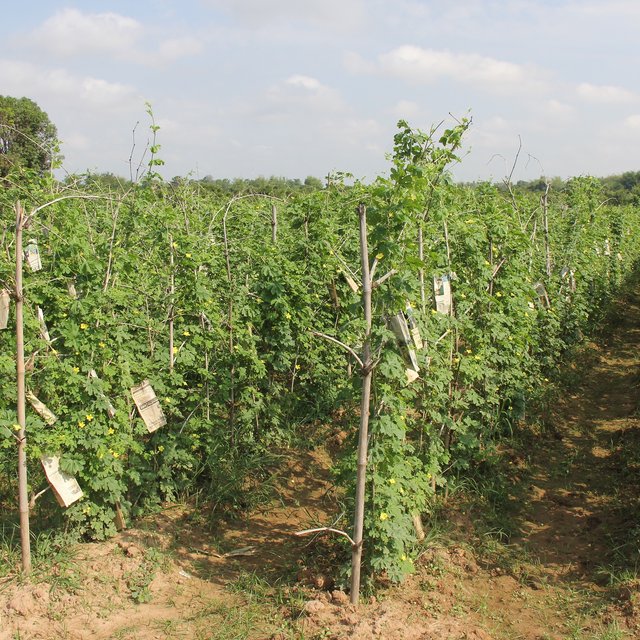






| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Riel) | Total costs per input (Riel) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Nursery and watering | peson-day | 3.5 | 20000.0 | 70000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plowing 2 times | peson-day | 3.75 | 20000.0 | 75000.0 | 100.0 |
| Draw the line and planting | peson-day | 8.0 | 20000.0 | 160000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| Pumping machine | piece | 1.0 | 1600000.0 | 1600000.0 | 100.0 |
| Spade | piece | 2.0 | 20000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 |
| Knife | piece | 2.0 | 20000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 |
| Large basket | pair | 1.0 | 5000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| Seeds | seed | 3000.0 | 60.0 | 180000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| Fish head fertilizer, compost and urea | kg | 200.0 | 2500.0 | 500000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | |||||
| Bamboo branches | piece | 100.0 | 5000.0 | 500000.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | |||||
| Newspaper | kg | 40.0 | 1000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 |
| Spraying tank | piece | 1.0 | 80000.0 | 80000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 3'290'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 822.5 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Riel) | Total costs per input (Riel) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Making the soil to be soft, adding more soil at bottom of plants, and trellising | person-day | 8.0 | 20000.0 | 160000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| Urea (46-0-0)) | kg | 6.0 | 2500.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| Pesticide | bottle | 2.0 | 15000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| Fish head | kg | 50.0 | 600.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| Other | |||||
| Gasoline to pumping for irrigation (3 months) | liter | 45.0 | 3200.0 | 144000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 379'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 94.75 | ||||
Using newspaper to wrap up is making the bitter melon healthier.
The expenses on agricultural inputs are reduced due to less use of chemical fertilizer (little use of mixture of urea, animals manure and fish head fertilizer) and less expenses as instead of expensive nets he uses bamboo sticks and also he uses cheaper newspaper for fruit protection.
The income is increased due to reduction of insects damaging.
It is increased a bit because he has to wrap up all fruits.
This newspaper wrap up technique controls only pest.
Reused of newspaper and bamboo branches for optimizing.