



Irrigation is very important for increasing crop yields in arid, semi-arid and dry sub-humid climates. The area of irrigated land has increased more than twice in the last decades in the study areas. In recent years, the considerable reduction of winter and autumn rainfall has caused a serious lack of water resources. The production of the various crops is substantially reduced if water is not provided during the summer period.
The high demands for water consumption or other economic activities have increased the price of water, forcing up the cost of agricultural production. In addition, in many cases, low quality (with high electrical conductivity) water is used for irrigation. The need for intensification of agriculture to meet the high cost of production, the use of poor quality of water, the lack of drainage systems are in many cases responsible for soil degradation resulting from water logging, salinization, alkalinization, and soil erosion.
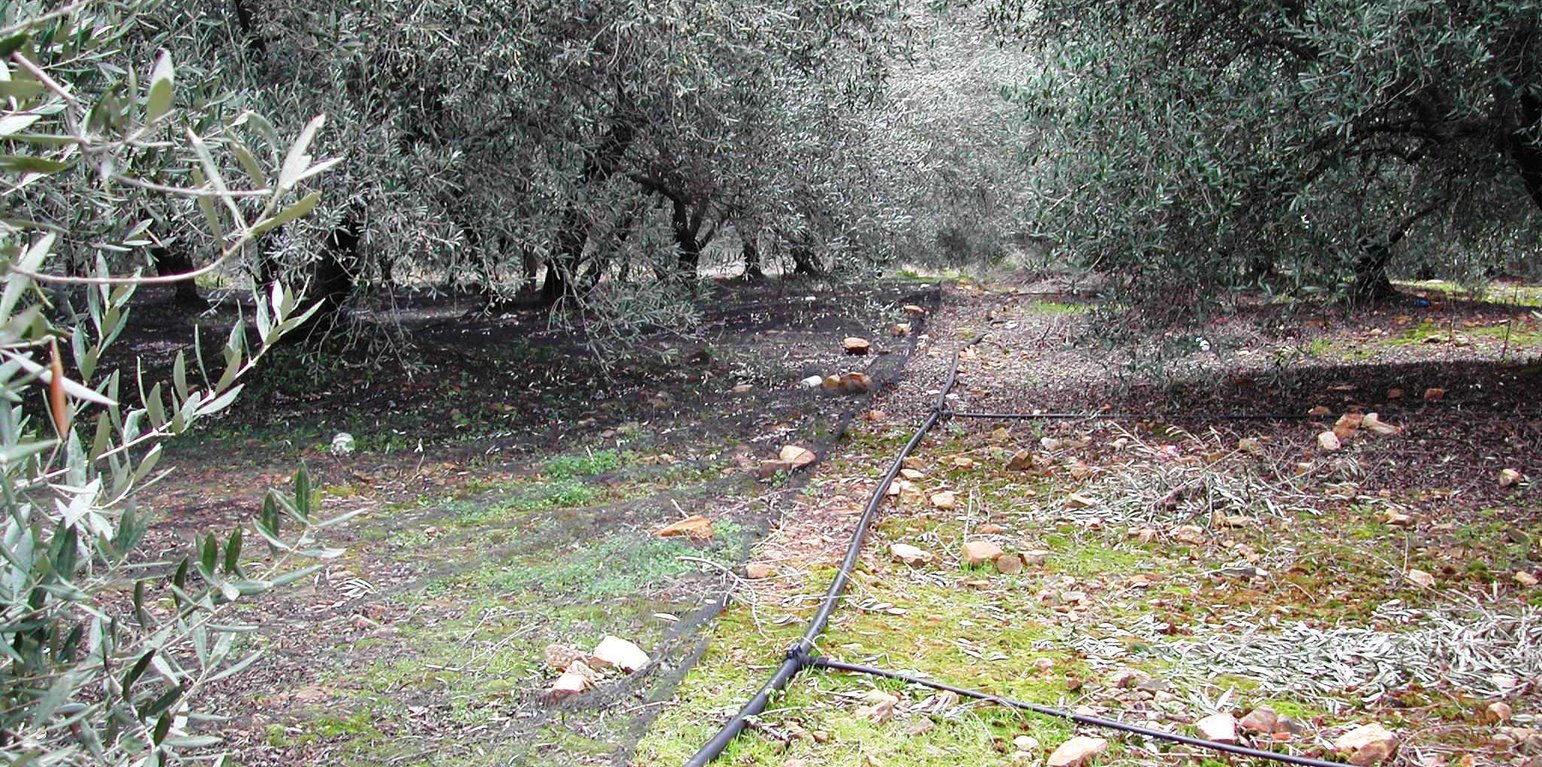
Purpose of the Technology: Drip or trickle irrigation achieves the highest irrigation efficiency since about 90% of the applied water is available to the plants. This SWC technology is especially suitable for watering trees or other large plants keeping strips among trees dry. Application of water by drip irrigation can be considered more as more efficient method using low quality of irrigation water. Irrigation water of high salt content can be applied in higher quantities in spots leaching salts to deeper soil layers. Drip irrigation can be applied in any type of soil from coarse- and fine-textured and without any limitation to slope gradient requiring little labour during installation.
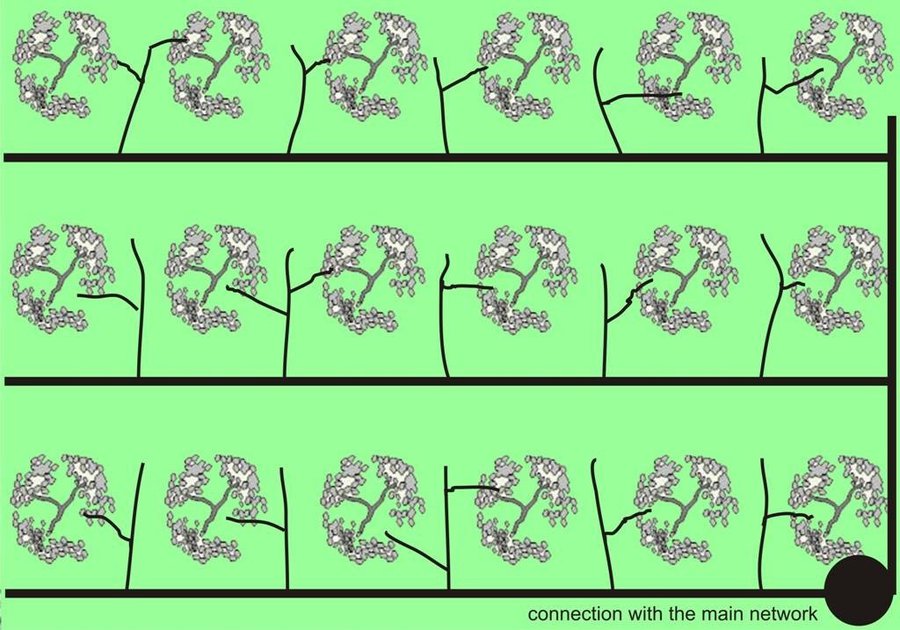
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In the study area of Chania trickle irrigation system includes mainly three branches from the outlet of main water network transportation system to the application in the trees. The last branch consists of plastic tube 12 to 32 mm in diameter that lies either on or just below the soil surface and applies the water either through small holes in the line or through emitter nozzle.
Natural / human environment: In recent years the increasing awareness of farmers on issues relating to the sustainability of the environment and conservation of water by promoting SWC technologies has led to widespread of use of drip irrigation in the area of Crete and in many other parts of the Country. The categorization of the specific SWC technology according to the WOCAT questionnaire is defined as: CtWtA3.
Location: Chania Crete, Kidonia, Greece
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology:
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation:
Type of introduction




| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (n.a.) | Total costs per input (n.a.) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| >Installation | ha | 1.0 | 350.0 | 350.0 | |
| Equipment | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1.0 | 1650.0 | 1650.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 2'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 2'000.0 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (n.a.) | Total costs per input (n.a.) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | |
| Equipment | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 60.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 60.0 | ||||
Quantity before SLM: 1500 kg/ha
Quantity after SLM: 2000 kg/ha
Cultivation of the land is hindered by the irrigation network
Quantity before SLM: 4500 euro/ha
Quantity after SLM: 5800 euro/ha
Significant environmental benefit from the rational use of irrigation water
environmental pollution due to presence of plastics not easily recycled