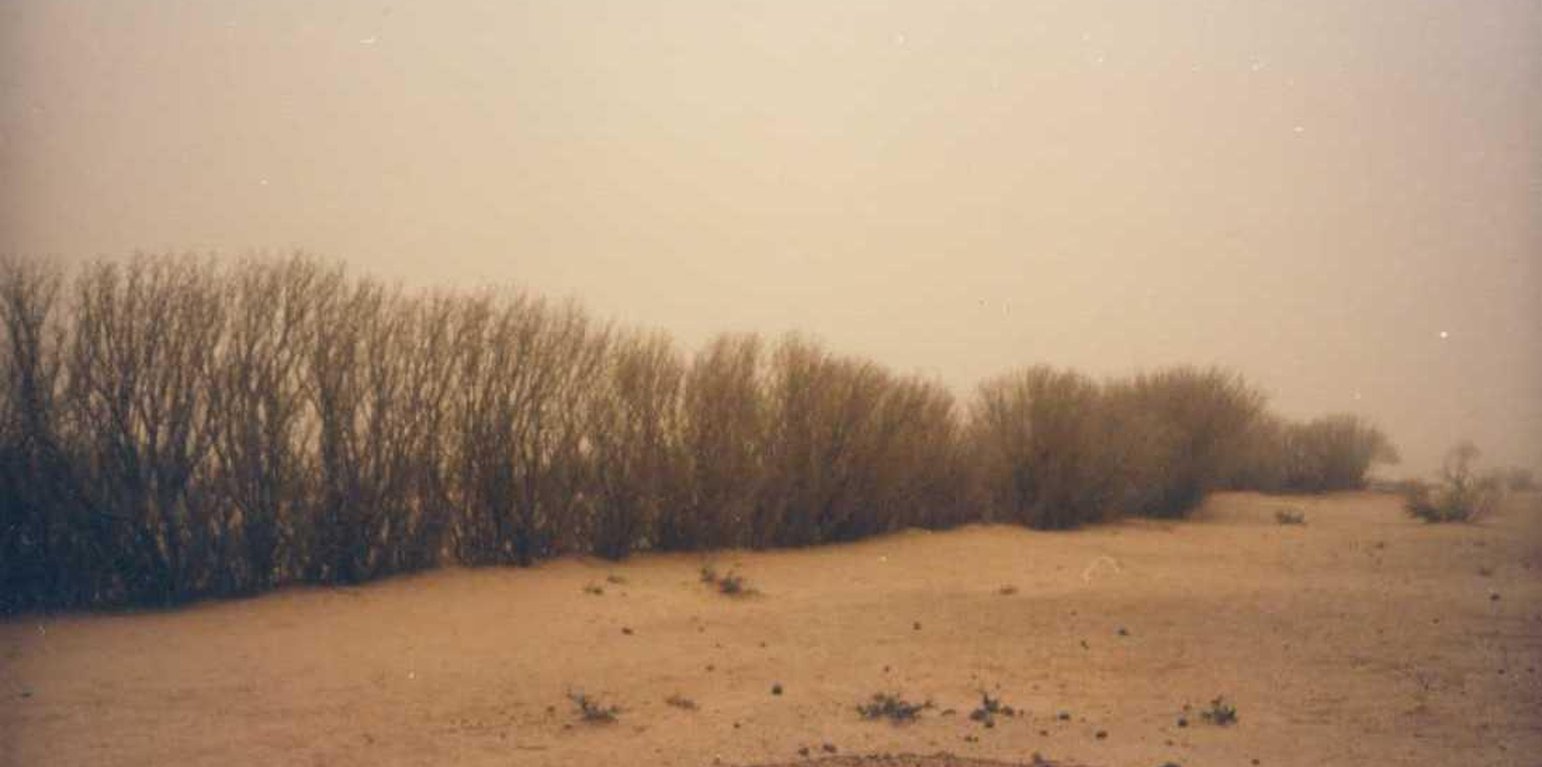




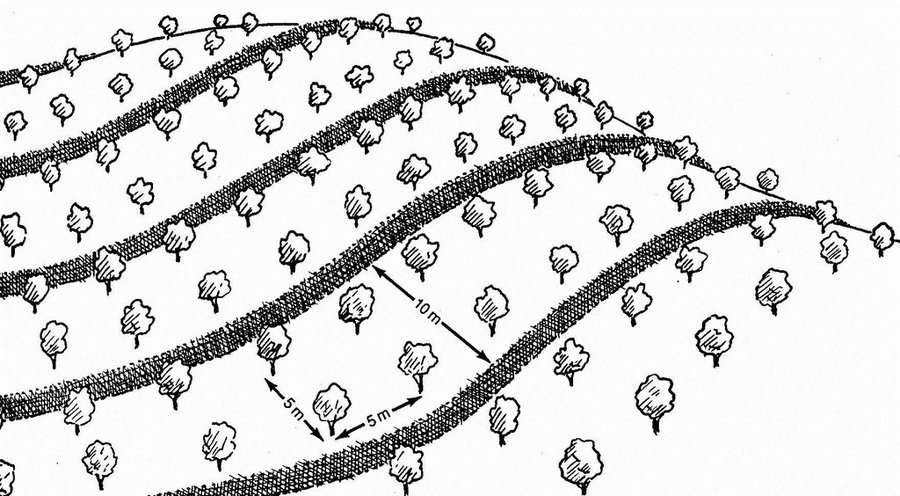
This measure is used to stabilise sand dunes in locations and villages where there is a risk of sand covering cropland or infrastructure (buildings, roads, irrigation systems, etc.). Dune stabilisation is achieved by setting up windbreaks arranged in a checkerboard pattern, with each side measuring between 10 and 15 m. The windbreaks are formed by palisades made from millet stalks or other plant material or by hedges and trees (Leptadenia pyrotechnica, Euphorbia balsamifera, Acacia raddiana, Acacia senegal, Balanites aegyptiaca, Prosopis juliflora, etc.).
Purpose of the Technology: They provide protection from wind erosion and reduce the amount of sand blown onto cropland, dwellings and other infrastructure which can prevent extensive damage. Grass and shrubs are planted in strips in the fenced-off areas to further stabilise the soil. The palisades and vegetation provide shade that lowers soil temperatures and the organic matter and waste improves the soil structure.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Specific experience is required to assess the degraded area as a whole and choose the most appropriate techniques, the right species to plant and the most suitable locations. Sometimes, the protected area is rehabilitated, particularly when land use pressure is high in neighbouring areas.
The protected dunes must be closely monitored and rigorously maintained for at least three years. It is therefore necessary to ensure good community organisation and take the action required to enforce the rules established and impose fines. Partial use of the area for grazing is sometimes allowed (one day a fortnight). Some projects prefer to fence off the sites with wire fencing to ensure that they are completely protected.
The success of this measure depends to a large extent on climatic conditions. A rainy year after the windbreaks have been erected creates favourable conditions for the species planted to become established.
Natural / human environment: With increasingly stronger winds and the accelerated degradation of the natural vegetation growing on sand dunes, it is very likely that the problems caused by shifting dunes will worsen in the future. Techniques to stabilise shifting sand dunes will therefore become more important.
Location: Niger, Niger
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (1.8 km²)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction





| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (CFA Franc) | Total costs per input (CFA Franc) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 96.45 | 96.45 | |
| Plant material | |||||
| Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 212.2 | 212.2 | |
| Other | |||||
| Transport | ha | 1.0 | 115.75 | 115.75 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 424.4 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 0.81 | ||||
Restrictions for grazing in the first three years
Sometimes, the protected area is rehabilitated, particularly when land use pressure is high in neighbouring areas. They provide protection from wind erosion and reduce the amount of sand blown onto cropland, dwellings and other infrastructure which can prevent extensive damage.