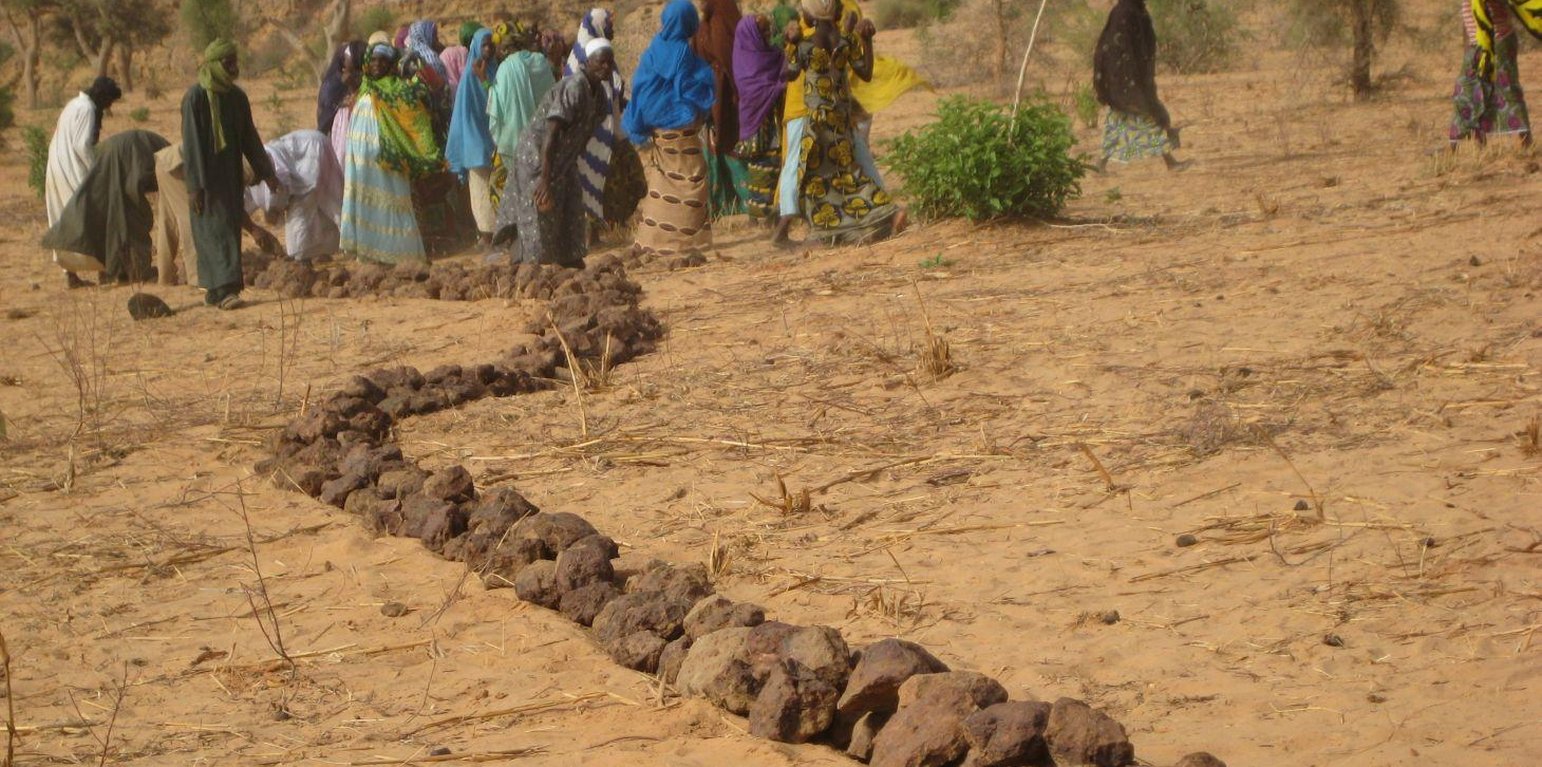




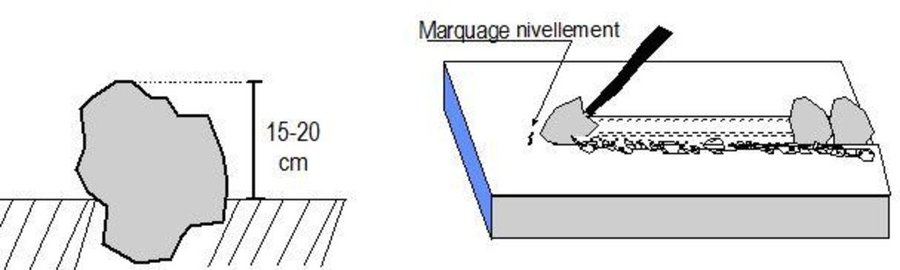
Contour stone bunds are erosion control structures built with quarry rock or stones in series of two or three. They are constructed in lines along the natural contour of the land after 10-15 cm of the soil has been removed from the line where they are to be built. They should be built to a height of 20-30 cm from the ground and spaced 20 to 50 m apart depending on the inclination of the terrain.
The best results are achieved when contour stone bunds are used in combination with biological measures (planting of grass, trees and hedges) and the use of organic fertiliser and mulching.
Purpose of the Technology: Contour stone bunds protect the land against sheet erosion caused by runoff. They form a barrier that slows down runoff and spreads it more evenly over the land. By slowing the flow of water over the land, it can seep into the soil and prevents the loss of rainwater. The bunds also act as a filter, trapping fine waterborne particles of soil and manure, resulting in a build-up of sediment and the formation of terraces. The seeds of grasses and shrubs are also trapped by the bunds, favouring the establishment of natural vegetation along the structure. This further stabilises the soil and the bunds and contributes to conserving the biodiversity of plants and small wild animals (monitor lizards, birds, snakes and other reptiles). If good vegetation cover is developed on the stone bunds, they also lower soil temperature and provide protection against wind erosion. Excess water filters through the bunds and infiltrates into the soil. When rainfall is erratic, the stone bunds contribute to conserving more moisture in the soil for longer, which helps to alleviate water stress during dry spells. There is evidence that bunds that have been in place for over 15 years have positive effects on yields.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A minimum amount of upkeep is required, which essentially involves replacing stones dislodged by animals or water flow. The lifespan of a stone bund is over 20 years.
In order to optimise the positive effects of stone bunds, it is important to ensure that they are constructed closely following the natural contour of the land and in accordance with the established technical standards.
The means of transport required depends on the proximity of a quarry or a supply of stones (cart or lorry).
Natural / human environment: This technique is designed for cropland, but can also be used on forest/rangeland. It is suitable for areas in the Sahel and the Sudan with rainfall ranging between 300 and 900 mm/year and low-to-medium gradient terrain.
When rainfall is high, they protect the land in the event of heavy rain, a phenomenon that tends to increase with climate change.
Location: Regions of Tillabéri, Filingué, Ouallam, Téra and Tahuoa, Niger, Mali, Burkina Faso, Chad, Niger
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. > 10,000 km2)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction









| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (USD) | Total costs per input (USD) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Levelling and construction of bunds | ha | 1.0 | 19.32 | 19.32 | |
| Equipment | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1.0 | 1.95 | 1.95 | |
| Other | |||||
| Transport of stones | ha | 1.0 | 15.07 | 15.07 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 36.34 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 36.34 | ||||
There is evidence that 15 year old bunds still maintain their positive effects on yields. 40 % higher grain yields were measured on such bunds and there is no evidence to suggest that yields decline with time. In dry years, while unimproved land produces nothing, land protected by stone bunds can still produce a harvest. Higher crop production improves household food security in proportion to the area of a farm improved with bunds. Under the PASP in Niger, an average of 16% of the area of a farm was improved with stone bunds, resulting in an increase of between 8% and 33% in annual output with no other additional measures.