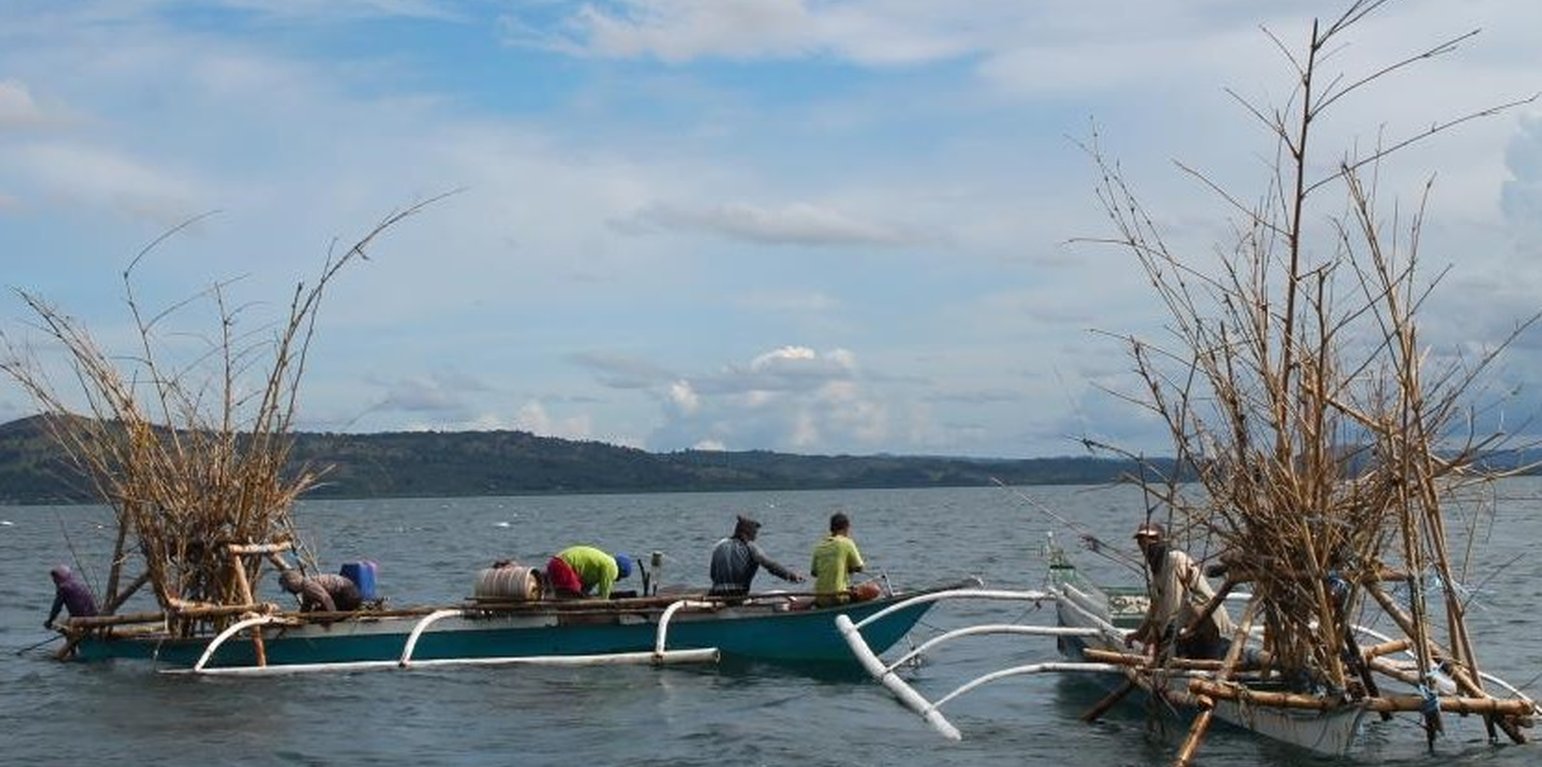




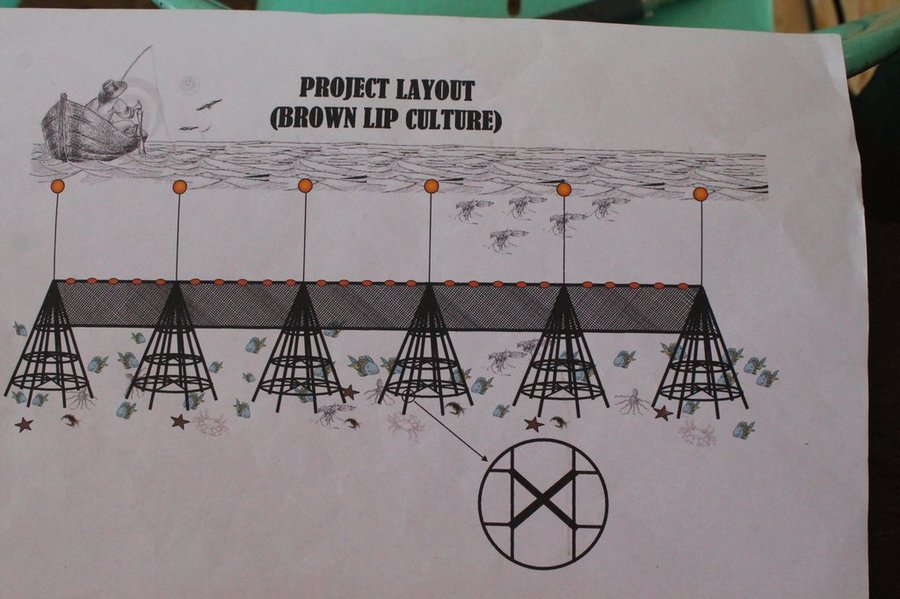
The fishers of Bohol have been using Artificial Reef over a long period of time. This is a fish aggregating device but at the same time, used for brown lip culture. Aside from the above mentioned functions of Artificial Reef, the Island of Bilangbilangan East in Bien Unido, Bohol installed this technology around the buffer zone of the marine sanctuary because the floater will serve as indicator of the marine protected area.
Artificial Reef Technology is a project of Bilangbilangan East Fishers Association (BEFA) from Brgy. Bilangbilangan East, Bien Unido, Bohol; Calituban Fisherfolks Association (CFO) from Brgy. Calituban, Talibon, Bohol and Nasingin Fisherfolks and Mangrove Planters Association (NasFiMPA) from Brgy. Nasingin, Getafe. This technology is owned and managed by the People's Organization found in these three island barangays namely BEFA, CFO and NasFiMPA.
Artificial Reef if is primarily made of bamboo with a life span of 3 to 5 years. For stability, it is anchored in the four corners using a cemented container tied to every end of its corners. For markings, floaters are placed in the sea surface but Nasingin and Calituban fishers preferred not to use floaters for the security of their installed artificial reefs, rather, they used terrestrial points to identify the location.
This technology was installed within the municipal waters (15 kilometers from the shoreline) to help minimize fishing cost and avoid the hazards of sudden change in weather condition. The PO are now vigilant because they already installed Artificial Reefs before but were destroyed by the dynamite fishers. This encouraged the PO members to practice safe and legal forms of fishing in order to sustain their project. Above all, artificial reef will enhance fish spawning and provide alternative shelter to fishes during hot season.
Location: Brgy. Bilangbilangan East, Municipality of Bien Unido; Brgy. Calituban, Municipality of Talibon; Brgy. Nasingin, Municipality of Getafe, Bohol, Philippines
No. of Technology sites analysed: 2-10 sites
Spread of the Technology: applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 2017
Type of introduction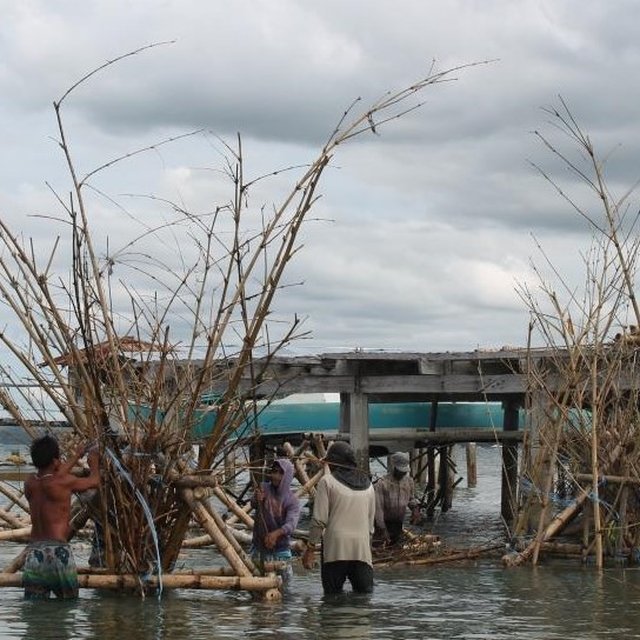



| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Philippine Peso) | Total costs per input (Philippine Peso) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Equipment | |||||
| motorboat rental | piece | 2.0 | 300.0 | 600.0 | |
| Construction material | |||||
| Bamboo Pole | piece | 10.0 | 120.0 | 1200.0 | |
| Spiny Bamboo | piece | 4.0 | 50.0 | 200.0 | |
| Nylon #10 | kilo | 10.0 | 120.0 | 1200.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 3'200.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 62.75 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Philippine Peso) | Total costs per input (Philippine Peso) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| monitoring | persons-day | 2.0 | 250.0 | 500.0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 500.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 9.8 | ||||
By installing artificial reefs the fishers are not obliged to go further.
decrease in fuel consumption
The fishers can catch fish even if there is gale warning.
The technology will not be affected directly or indirectly by the effects of gale warning and typhoon.