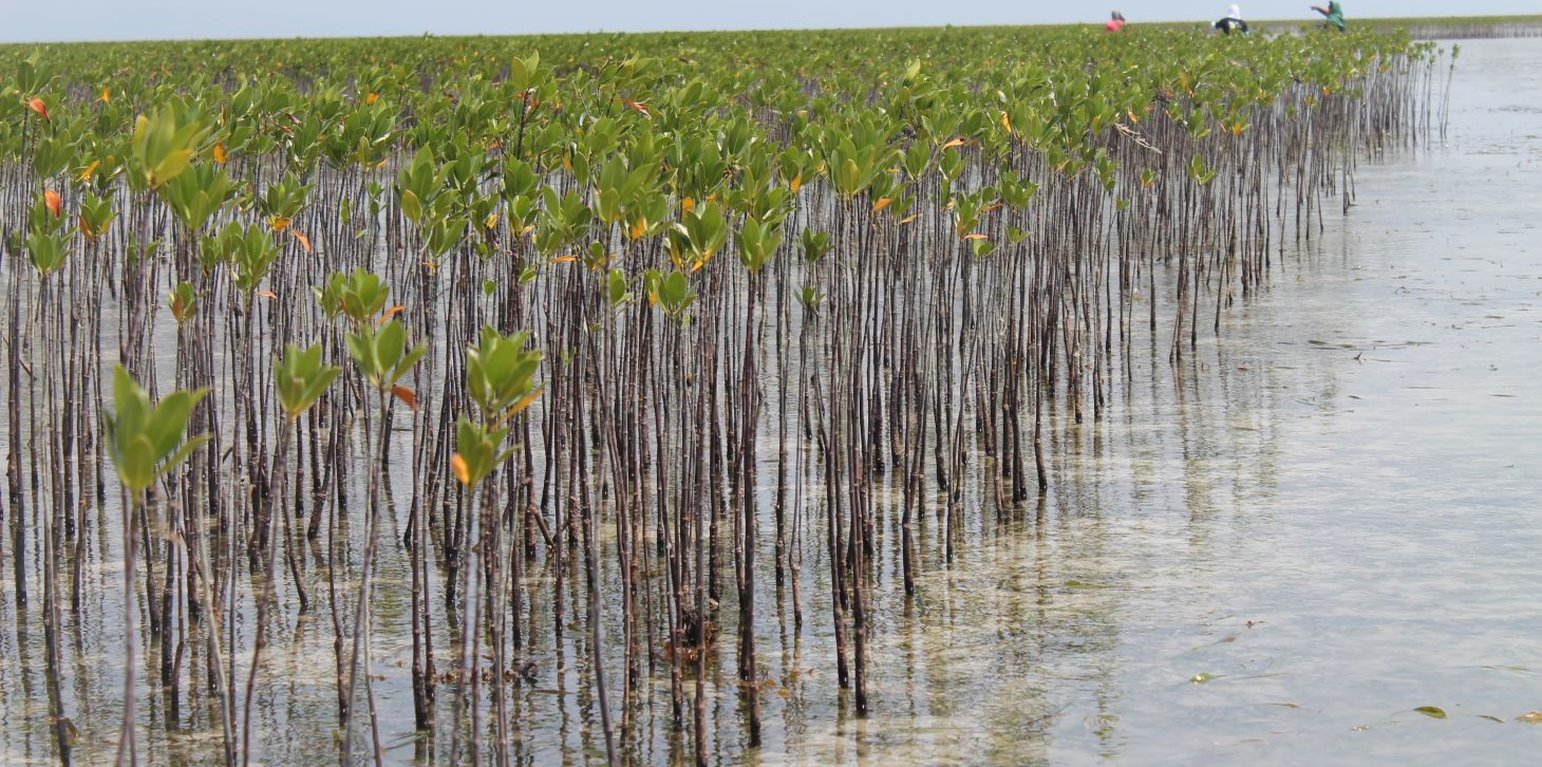




Mangrove plantation in the island of Banacon which is 10.91 kilometers away from the municipality of Getafe, Bohol in Central Visayas started in 1957.The most common specie grown is the “Bakauan” under the Rhizophoracea family.
Mangroves contribute in protecting the coast against natural hazards such as storms, tsunamis and coastal erosion. It weakens the impact of typhoons that bring strong winds, continuous high waves and storm surges. A dense cluster of bakauans obstruct the entry of winds and waves when passing through the mangroves minimizes the force of wind sand waves. According to the residents of the island, they were spared from total destruction of properties during onset of typhoons because of the presence of the bakauans. Mangroves were utilized also by the Banacon residents as source of poles for houses, fishpens and charcoals for cooking. The dense roots of the trees bind the soils thus preventing erosion. The tree roots serve as spawning ground for fishes and other variety of sea species that lead to an increase in harvest of sea foods in the area. The mangrove plantation was also developed into ecotourism site.
Site evaluation is the pre-requisite in the establishment of mangrove area. An ideal area is with sand dune during low tide. It is followed by site lay out using the planting design that is adopted, and direct planting of propagules in the soil. Planting materials used are the cigar-shaped mature propagules harvested from the Bacauan- Lalake specie of mangroves. The direct seeding planting is the ideal method of planting in establishing a mangroves plantation. Mangrove propagules must be planted after collection. It should not be exposed to direct sunlight to prevent moisture loss.
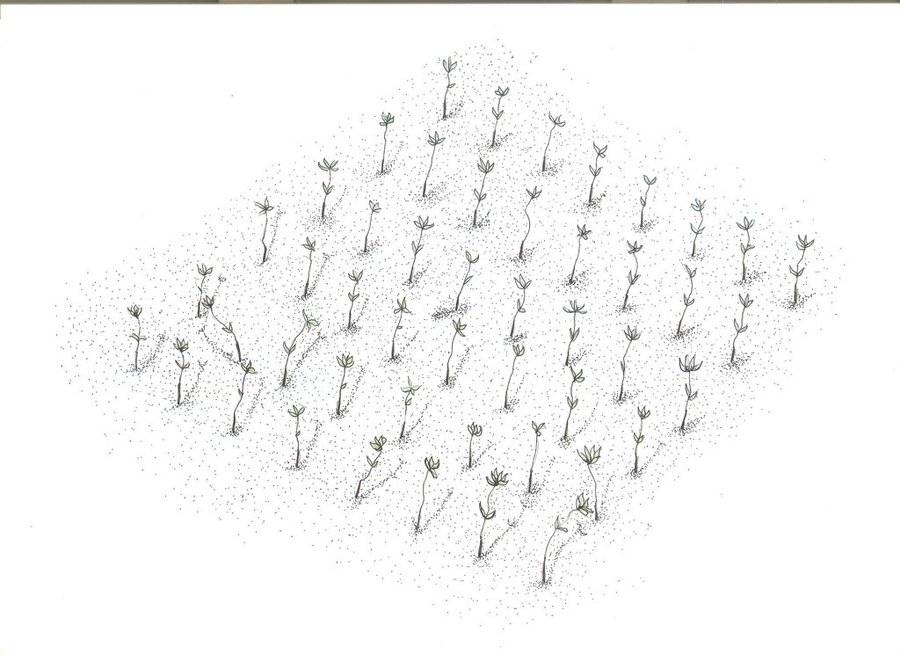
There are (3) planting designs used in the establishment of the mangroves. First, the high density planting of propagules with no lay out to be followed. This planting design can accommodate 30,000 pcs of propagules per hectare. Second, design has a spacing of 1 meter by 1 meter planted in rows and can hold 10,000 pieces of propagules per hectare. Third is the block/cluster design in which each cluster was planted with 750 pieces of propagules with a distance of 30 centimeters apart per propagules. The spacing between the blocks or cluster is 10 meters and can contain 5,000 pieces of propagules per hectare. Maintenance includes monitoring of the crop status, replanting of missing hills and weeding by removing sea weeds, barnacles and sea debris.
Location: Banacon Island, Getafe, Bohol, Philippines
No. of Technology sites analysed: single site
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. 1-10 km2)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: more than 50 years ago (traditional)
Type of introduction






| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Philippine peso) | Total costs per input (Philippine peso) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Person day/ hectare | 10.0 | 250.0 | 2500.0 | ||
| Plant material | |||||
| mangrove propagules | pieces | 5000.0 | 1.0 | 5000.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 7'500.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 150.0 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Philippine peso) | Total costs per input (Philippine peso) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| labour | person day | 3.0 | 250.0 | 750.0 | |
| Plant material | |||||
| propragules | pieces | 250.0 | 1.0 | 250.0 | |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 1'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 20.0 | ||||
Establishment of beach forest
Formation of Peoples Organization.