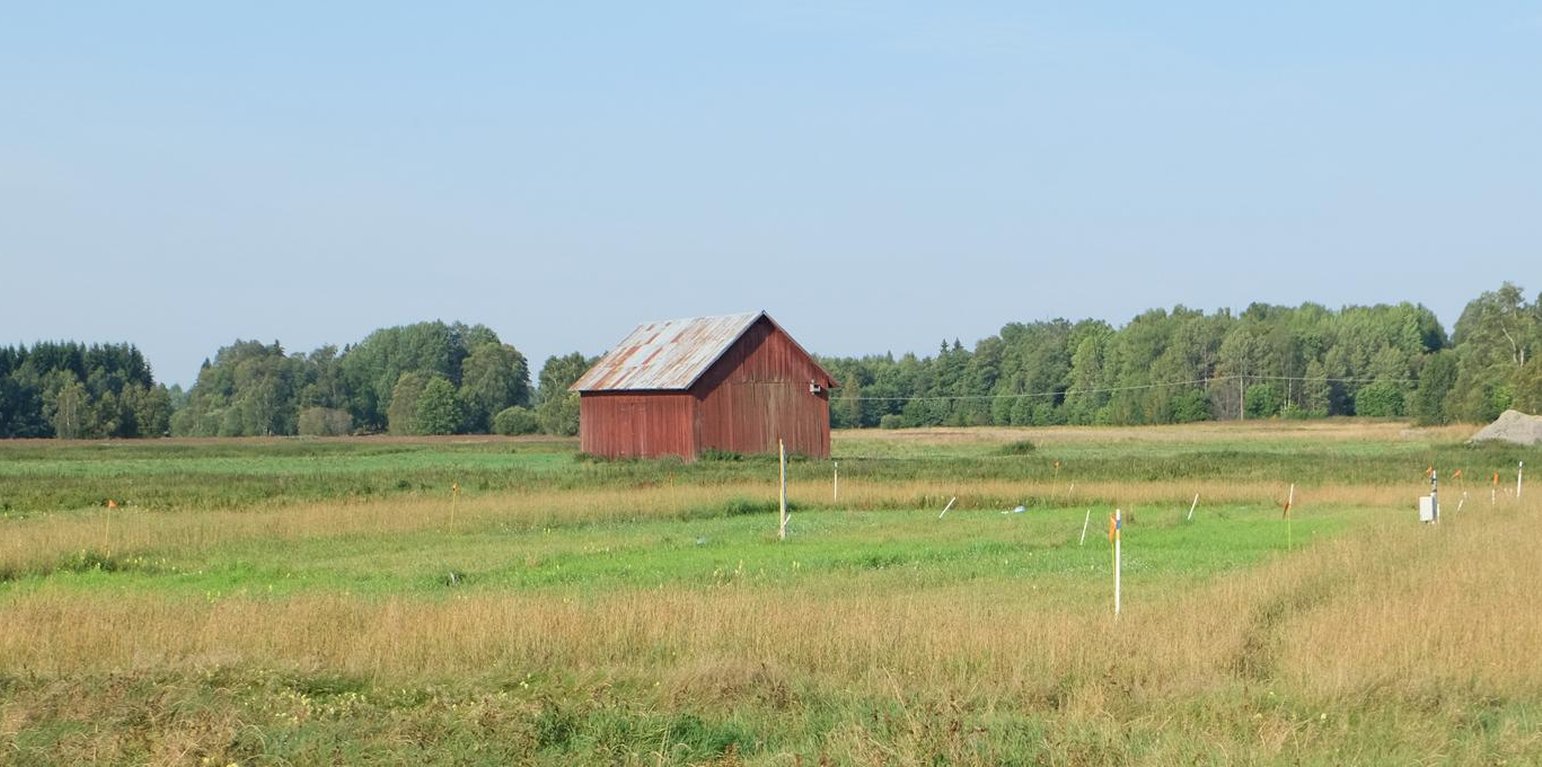
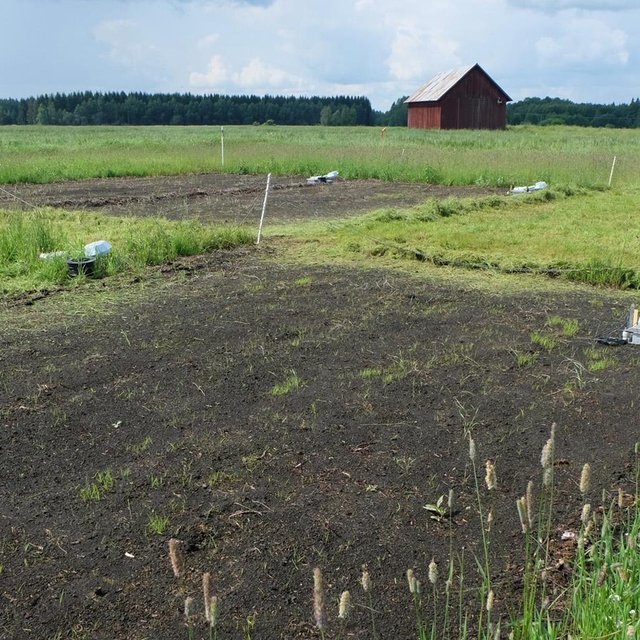

Field trial with different grasses (Thimoty, Reed canary grass, Tall fescue) (Örjan Berglund (SLU, dep. of soil and environment. Box 7014, 75007 Uppsala, Sweden))


Subsiding peat soils will suffer from rising ground water tables.
Purpose of the Technology: To find crops that can withstand a high groundwater table and still have a high yield.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Fertilisation, harvests.
Natural / human environment: Cultivated field
Location: Uppsala, Uppsala län, Sweden
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology:
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: less than 10 years ago (recently)
Type of introduction





