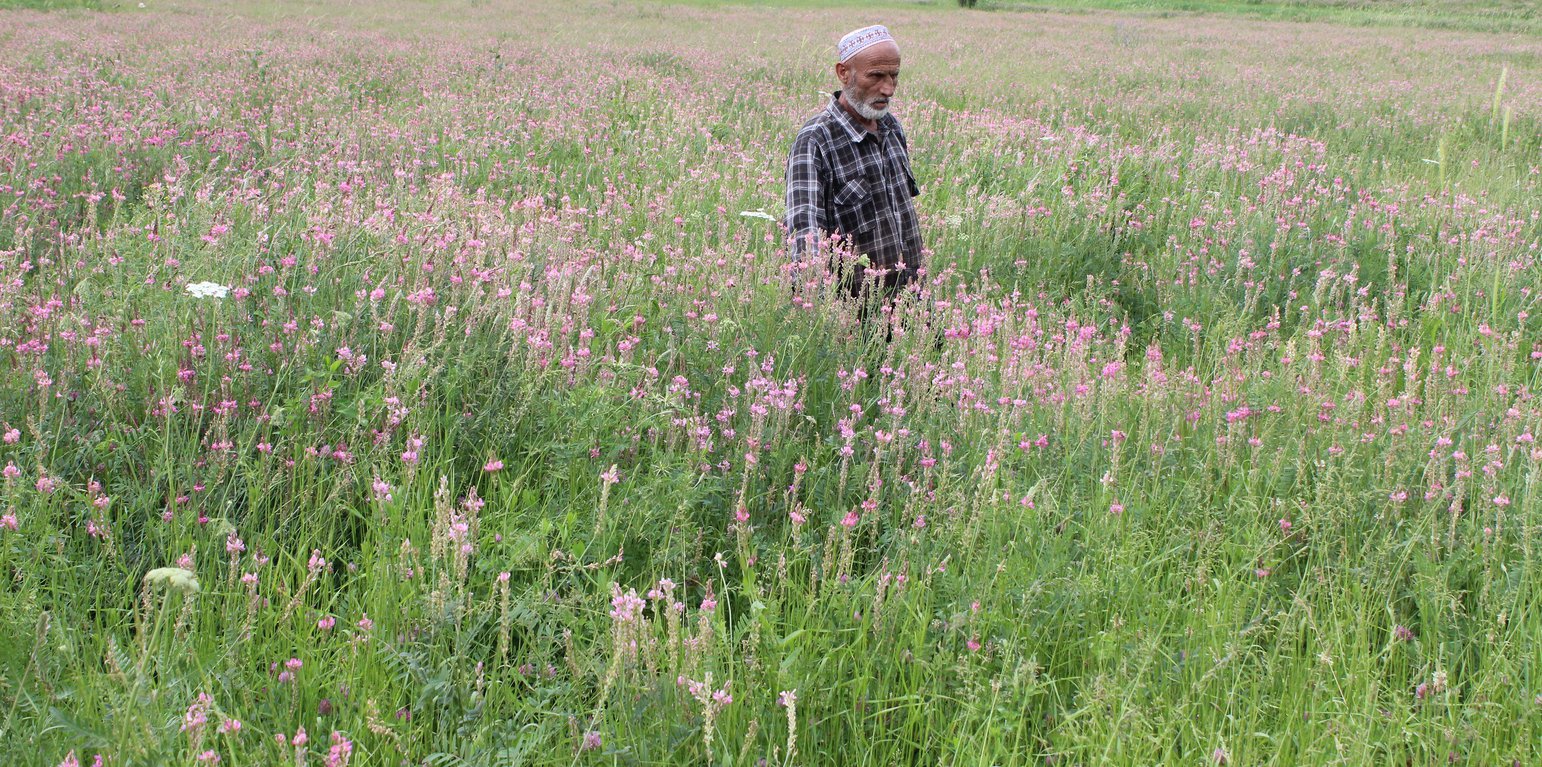
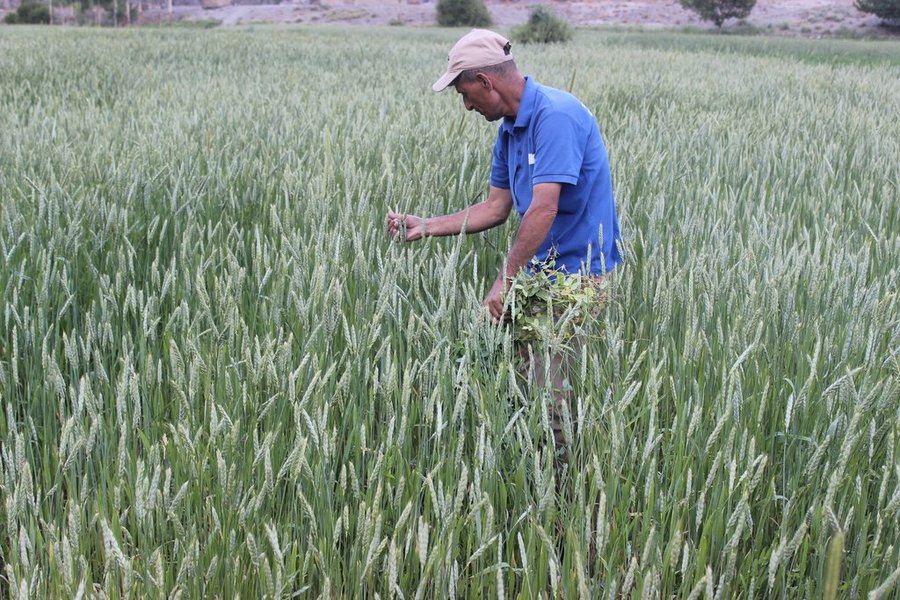
(Tajikistan)
Location
Location: Tajikistan
No. of Technology sites analysed: single site
Geo-reference of selected sites
Spread of the Technology: applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: 10-50 years ago
Type of introduction
-
through land users' innovation
-
as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
-
during experiments/ research
-
through projects/ external interventions

-
Classification of the Technology
Main purpose
-
improve production
-
reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
-
conserve ecosystem
-
protect a watershed/ downstream areas – in combination with other Technologies
-
preserve/ improve biodiversity
-
reduce risk of disasters
-
adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
-
mitigate climate change and its impacts
-
create beneficial economic impact
-
create beneficial social impact
Land use
-
Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Water supply
-
rainfed
-
mixed rainfed-irrigated
-
full irrigation
Purpose related to land degradation
-
prevent land degradation
-
reduce land degradation
-
restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
-
adapt to land degradation
-
not applicable
Degradation addressed
-
soil erosion by water - Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
-
soil erosion by wind - Et: loss of topsoil
-
physical soil deterioration - Pc: compaction
-
biological degradation - Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition/ diversity decline
SLM group
-
integrated crop-livestock management
-
improved ground/ vegetation cover
-
surface water management (spring, river, lakes, sea)
SLM measures
-
agronomic measures - A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
-
vegetative measures - V2: Grasses and perennial herbaceous plants
-
management measures - M2: Change of management/ intensity level, M3: Layout according to natural and human environment
Technical drawing
Technical specifications
Establishment and maintenance: activities, inputs and costs
Calculation of inputs and costs
- Costs are calculated: per Technology area
- Currency used for cost calculation: USD
- Exchange rate (to USD): 1 USD = 9.2
- Average wage cost of hired labour per day: n.a
Most important factors affecting the costs
n.a.
Establishment activities
-
(Timing/ frequency: None)
-
(Timing/ frequency: None)
-
(Timing/ frequency: None)
Establishment inputs and costs
| Specify input |
Unit |
Quantity |
Costs per Unit (USD) |
Total costs per input (USD) |
% of costs borne by land users |
|
Labour
|
|
|
1.0 |
22.0 |
22.0 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
22.0 |
22.0 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
30.0 |
30.0 |
|
|
Equipment
|
|
|
2.0 |
21.7 |
43.4 |
|
|
Plant material
|
|
|
80.0 |
1.3 |
104.0 |
|
|
|
150.0 |
0.27 |
40.5 |
|
|
Fertilizers and biocides
|
|
|
250.0 |
0.54 |
135.0 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
0.54 |
54.0 |
|
|
Other
|
|
|
200.0 |
0.7 |
140.0 |
|
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology |
610.9 |
|
Maintenance activities
-
(Timing/ frequency: None)
-
(Timing/ frequency: None)
-
(Timing/ frequency: None)
-
(Timing/ frequency: None)
Maintenance inputs and costs
| Specify input |
Unit |
Quantity |
Costs per Unit (USD) |
Total costs per input (USD) |
% of costs borne by land users |
|
Labour
|
|
|
1.0 |
22.0 |
22.0 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
22.0 |
22.0 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
20.0 |
20.0 |
|
|
|
1.0 |
30.0 |
30.0 |
|
|
Equipment
|
|
|
2.0 |
21.7 |
43.4 |
|
|
Plant material
|
|
|
80.0 |
1.3 |
104.0 |
|
|
|
150.0 |
0.27 |
40.5 |
|
|
Fertilizers and biocides
|
|
|
250.0 |
0.54 |
135.0 |
|
|
|
100.0 |
0.54 |
54.0 |
|
|
Other
|
|
|
2.0 |
21.7 |
43.4 |
|
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology |
514.3 |
|
Natural environment
Average annual rainfall
-
< 250 mm
-
251-500 mm
-
501-750 mm
-
751-1,000 mm
-
1,001-1,500 mm
-
1,501-2,000 mm
-
2,001-3,000 mm
-
3,001-4,000 mm
-
> 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
-
humid
-
sub-humid
-
semi-arid
-
arid
Specifications on climate
Average annual rainfall in mm: 1500.0
Slope
-
flat (0-2%)
-
gentle (3-5%)
-
moderate (6-10%)
-
rolling (11-15%)
-
hilly (16-30%)
-
steep (31-60%)
-
very steep (>60%)
Landforms
-
plateau/plains
-
ridges
-
mountain slopes
-
hill slopes
-
footslopes
-
valley floors
Altitude
-
0-100 m a.s.l.
-
101-500 m a.s.l.
-
501-1,000 m a.s.l.
-
1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
-
1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
-
2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
-
2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
-
3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
-
> 4,000 m a.s.l.
Technology is applied in
-
convex situations
-
concave situations
-
not relevant
Soil depth
-
very shallow (0-20 cm)
-
shallow (21-50 cm)
-
moderately deep (51-80 cm)
-
deep (81-120 cm)
-
very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil)
-
coarse/ light (sandy)
-
medium (loamy, silty)
-
fine/ heavy (clay)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface)
-
coarse/ light (sandy)
-
medium (loamy, silty)
-
fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter content
-
high (>3%)
-
medium (1-3%)
-
low (<1%)
Groundwater table
-
on surface
-
< 5 m
-
5-50 m
-
> 50 m
Availability of surface water
-
excess
-
good
-
medium
-
poor/ none
Water quality (untreated)
-
good drinking water
-
poor drinking water (treatment required)
-
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
-
unusable
Water quality refers to:
Is salinity a problem?
Occurrence of flooding
Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation
-
subsistence (self-supply)
-
mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
-
commercial/ market
Off-farm income
-
less than 10% of all income
-
10-50% of all income
-
> 50% of all income
Relative level of wealth
-
very poor
-
poor
-
average
-
rich
-
very rich
Level of mechanization
-
manual work
-
animal traction
-
mechanized/ motorized
Sedentary or nomadic
-
Sedentary
-
Semi-nomadic
-
Nomadic
Individuals or groups
-
individual/ household
-
groups/ community
-
cooperative
-
employee (company, government)
Age
-
children
-
youth
-
middle-aged
-
elderly
Area used per household
-
< 0.5 ha
-
0.5-1 ha
-
1-2 ha
-
2-5 ha
-
5-15 ha
-
15-50 ha
-
50-100 ha
-
100-500 ha
-
500-1,000 ha
-
1,000-10,000 ha
-
> 10,000 ha
Scale
-
small-scale
-
medium-scale
-
large-scale
Land ownership
-
state
-
company
-
communal/ village
-
group
-
individual, not titled
-
individual, titled
Land use rights
-
open access (unorganized)
-
communal (organized)
-
leased
-
individual
Water use rights
-
open access (unorganized)
-
communal (organized)
-
leased
-
individual
Access to services and infrastructure
employment (e.g. off-farm)
drinking water and sanitation
Cost-benefit analysis
Benefits compared with establishment costs
Short-term returns
very negative
very positive
Long-term returns
very negative
very positive
Benefits compared with maintenance costs
Short-term returns
very negative
very positive
Long-term returns
very negative
very positive
Adoption and adaptation
Percentage of land users in the area who have adopted the Technology
-
single cases/ experimental
-
1-10%
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have done so without receiving material incentives?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
To which changing conditions?
-
climatic change/ extremes
-
changing markets
-
labour availability (e.g. due to migration)
Conclusions and lessons learnt
Strengths: land user's view
Strengths: compiler’s or other key resource person’s view
Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks: land user's viewhow to overcome
Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks: compiler’s or other key resource person’s viewhow to overcome
References
Reviewer
-
Farrukh Nazarmavloev
-
Alexandra Gavilano
Date of documentation: June 9, 2018
Last update: Aug. 20, 2019
Full description in the WOCAT database
Documentation was faciliated by
Institution
Project
- Environmental Land Management and Rural Livelihoods (ELMAR)
- Mountain Societies Development Support Programme, Tajikistan















