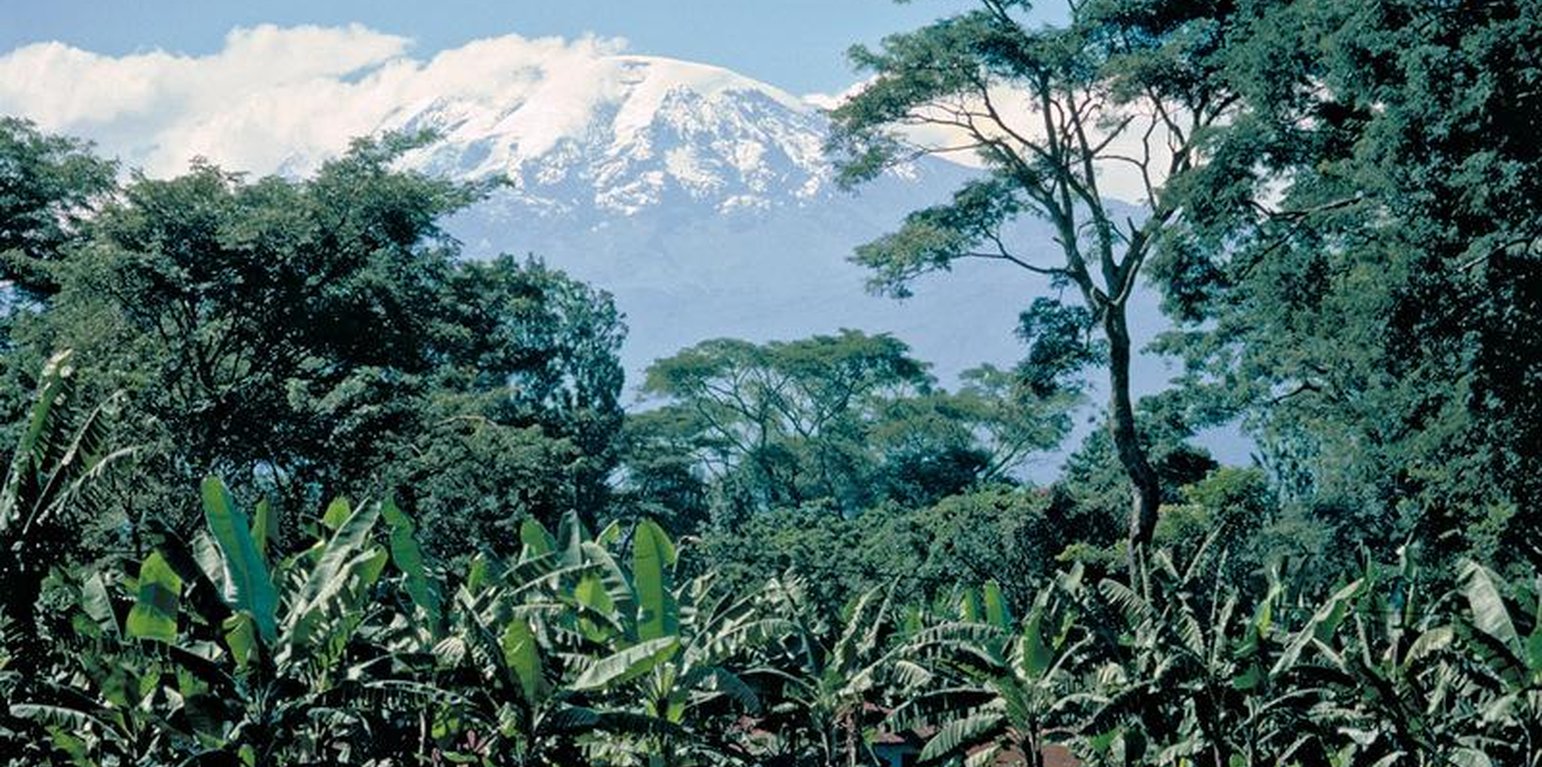




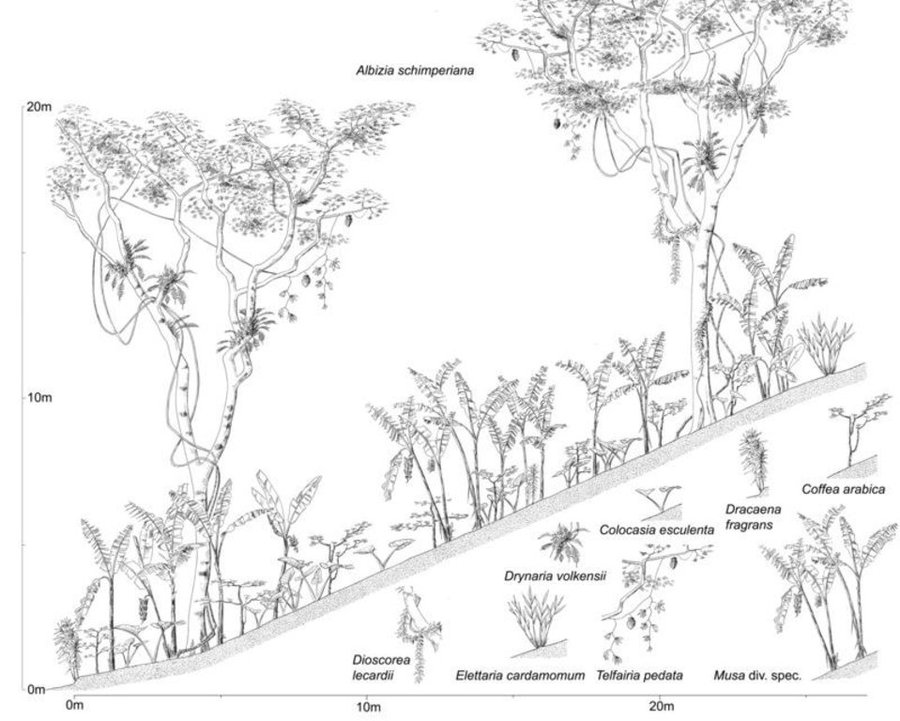
The complex multicropping system evolved over several centuries through a gradual transformation of the natural forest on the footslopes of Kilimanjaro. A Chagga homegarden has an average size of 0.68 ha and integrates numerous multipurpose trees and shrubs with food crops, and stall-fed animals, without a specific spatial arrangement. However, vertically, the following 4 stories/canopies can be distinguished: (1) food crops: taro, beans, vegetables and fodder herbs / grasses; (2) coffee: 500-1,400 plants/ha; (3) banana: primary crop; 50% cover; 330-1,200 clumps/ha; and (4) Trees, such as Cordia abyssinica, Albizia schimperiana and Grevillea robusta. The trees provide shade for coffee, act as live fences, provide medicines, firewood, fodder, mulching material, bee forage; and some have pesticidal properties (e.g. Rauwolfia caffra). This multilayer system maximizes the use of limited land in a highly populated area, making sustained production possible with a minimum of external inputs, minimizes risk (less production failure, increased resistance against droughts and pests) and ensures at the same time environmental protection. The large species diversity provides both subsistence and cash crops. Parts of the homegarden area are irrigated and drained by a network of over 1000 canals and furrows tapping runoff from the montane forest. However, many systems are now in disrepair.
Natural / human environment: Starting in the 1930s when coffee took more space from the food production, it became necessary to expand food production to the lowlands. Today, the Chagga highland homegarden works only in combination with a lowland field where maize, millet, beans, sunflower and groundnuts are grown to ensure food security.
Location: Mt. Kilimanjaro Region, Tanzania, United Republic of
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology:
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: more than 50 years ago (traditional)
Type of introduction






| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (USD) | Total costs per input (USD) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Planting, tending and harvesting | unit | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| Tools | unit | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| Compost / manure | unit | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 445.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 445.0 | ||||
Fuelwood production 1.5-3 m3/ha/year
185 kg beans/ha; 410 kg coffee/ha; 400 bunches of banana /ha; ca. 30 kg honey/ha
increased labour efficiency
for breeding programmes to improve crop varieties for multistorey cropping systems
over 500 plant species including 400 non-cultivated plants
? land use change from natural forest to agroforest