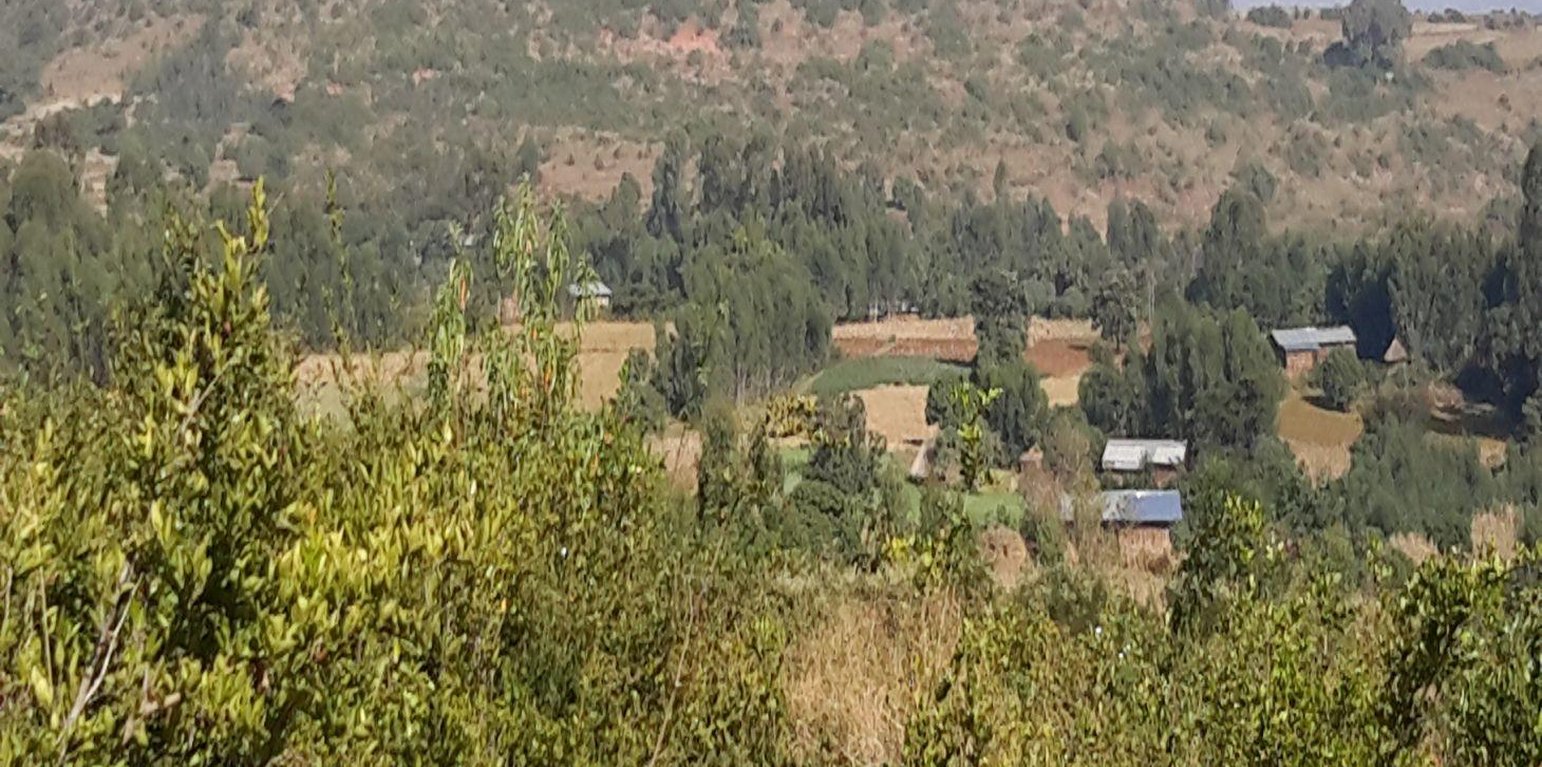




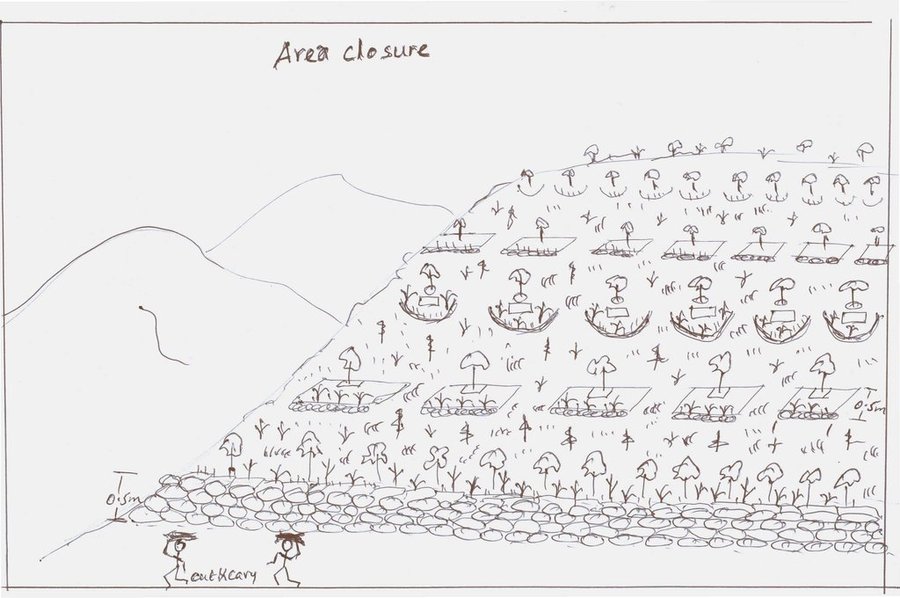
Area closure is a land management practice that helps to rehabilitate degraded lands, restore the biophysical conditions like soil, vegetation and hydrology by avoiding the interference of animals and human. Because of over grazing and erosion impact, areas delineated for closure are usually degraded shrub or pasture lands that served for grazing. First of all, implementing area closure requires continuous dialogue and discussion with community to reach consensus to close. The community wants to make sure they have benefited from the technology as the land was serving for grazing. They should take the responsibility and create sense of ownership to implement conservation measures, protect and maintain closure areas, and regulate utilization of benefits gained out of it. Questions raised from the community must be discussed thoroughly ahead of the implementation. What part of the degraded land? For what purpose the area is closed? Who are the users? Who are responsible to protect and manage the developed resourcess? How is the benefit sharing among identified users? Commonly, the shared benefits from area closures are hay for livestock through cut-and-carry system, timbers from plantations, and honey production.
Depending on the soil, rainfall and slope conditions different structural and vegetative measures are integrated to enhance the fast regeneration of plant species, restore the soil and increase water availability. It includes enrichment used to rehabilitate and increase the vegetation cover, vegetative and structural measures to retain the soil and water on its place. Structures such as hillside terrace often integrated with grass or shrub hedgerows is used to control soil erosion. In-situ water harvesting structures such as trenches or half moon or eye brow are used to harvest and infiltrate rain or runoff water to increase regeneration and survival of planted trees. Trees and/or shrub species that have high rehabilitation and multipurpose values are used as enrichment plantations. Closed areas need collective action to protect, maintain and manage the common resources. Collective user rights have to be entitled to bring equity on resource sharing and minimize social conflicts.
The purposes of area closure are: 1) rehabilitate degraded lands, 2) protect and restore the natural resource base, and 3) change into productive land and enhance economic and environmental functions of rehabilitated lands.
Implementation of area closure begins with the selection and demarcation of area through genuine participation of land users. After identifying the area to be closed, at establishment stage construction of ditches and terraces is made using stones combined with grasses or shrubs of multipurpose value such as Vetiver grass, Dinsho grass, Bana grass, susbania, etc. Depending on site conditions, enrichment tree species which have rehabilitation and soil restoration purposes are planted in the form of wood lot or scattered tree plantation. Among the common species, A. albida, A. saligna, A. decurrense, Gravilia robusta, etc. are used to rehabilitate and serve as fuel wood and timber. In moisture stress areas structures like trench, level bunds, and half moon should be constructed to increase survival rate of planted tree/shrub species whereas in areas having sufficient moisture these structures, depending on the landforms and soil drainage conditions, help to increase infiltration and recharging of ground water in downstream areas. Therefore, site selection and demarcation, construction of soil conservation and moisture conservation structures, and seedling management and plantation of multipurpose trees, shrubs and grasses are the activities accomplished at establishment stage of area closure. The required inputs are stones, seeds/seedlings, grass cuttings/splits, hand tools, and collective labor. For recurrent maintenance activities, seedlings and cuttings for re-plantation purpose or replace dead seedlings, stones to repair damage stone terraces and moisture conservation structures. Harvesting and transporting of area closure products such as grass and timber become a recurrent activity. Person days per hectare per year required for plantation (preparation of holes and planting) is 11.5, for harvesting and transporting harvested grass is 30, and for terrace construction is 26.5.
Area closure management is commonly practiced on degraded hills where soil is highly depleted, its water holding capacity is low, and vegetation is denuded. Usually degraded lands are used to serve for communal grazing system. The degree of land degradation becomes severe where there are high livestock and human population pressure. Management of closure area and the benefit sharing has to be regulated using agreed bylaws.
The living condition depends on subsistence crop-livestock mixed farming. On average households have 5-6 family size. Crop production is meant for home consumption with small surplus for local market. The services related to water supply, energy supply, and infrastructure are low. Besides it is an asset, animals often used to cope shocks during drought periods.
Location: Mecha / Yilmana Densa / Bahir Dar Zuria, Amhara National Regional State, Ethiopia
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. 1-10 km2)
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: less than 10 years ago (recently)
Type of introduction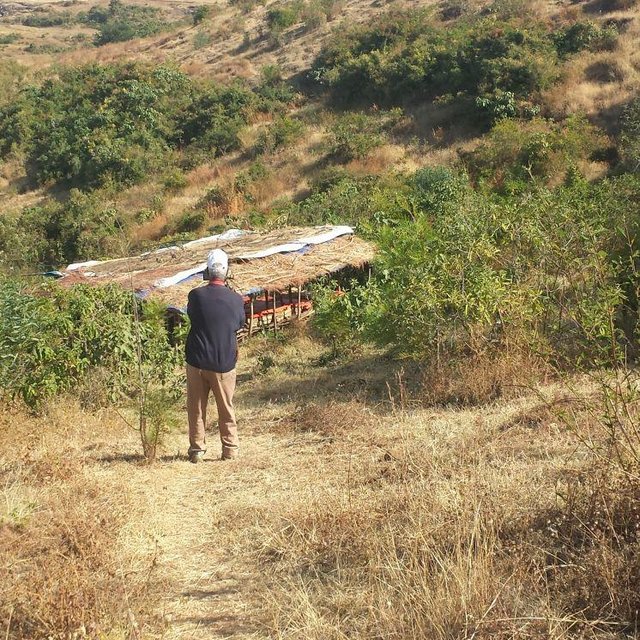









| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (ETB) | Total costs per input (ETB) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| labour | ha | 1.0 | 1766.0 | 1766.0 | 80.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| tools | ha | 1.0 | 300.6 | 300.6 | 50.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 405.6 | 405.6 | 100.0 |
| seeds | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | |||||
| stone | ha | 1.0 | 1300.0 | 1300.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 3'792.2 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 189.61 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (ETB) | Total costs per input (ETB) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| labour | ha | 1.0 | 624.0 | 624.0 | 29.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 874.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 43.7 | ||||
Mainly serve for grass harvest
Cut and carry improve the production
By improving the land use management, production area for pasture increased
People try to diverse apiculture production in closed areas
Labor requirement to harvest and transport fodder and pasture increase
Establishment of user groups and watershed users association
Increase the level of awareness that area closure can shortly reverse land degradation
Reduce conflict arise due to pasture shortage
Some rural unemployed youths get employed in apiculture production and fruit production
The livestock production is moderately improved due to increase in biomass/ pasture harvest
Quantity before SLM: End of Nov
Quantity after SLM: Mar-April
Because of high vegetation cover, the recharrging capacity improved resulting in prolonging the stream flow/baseflow