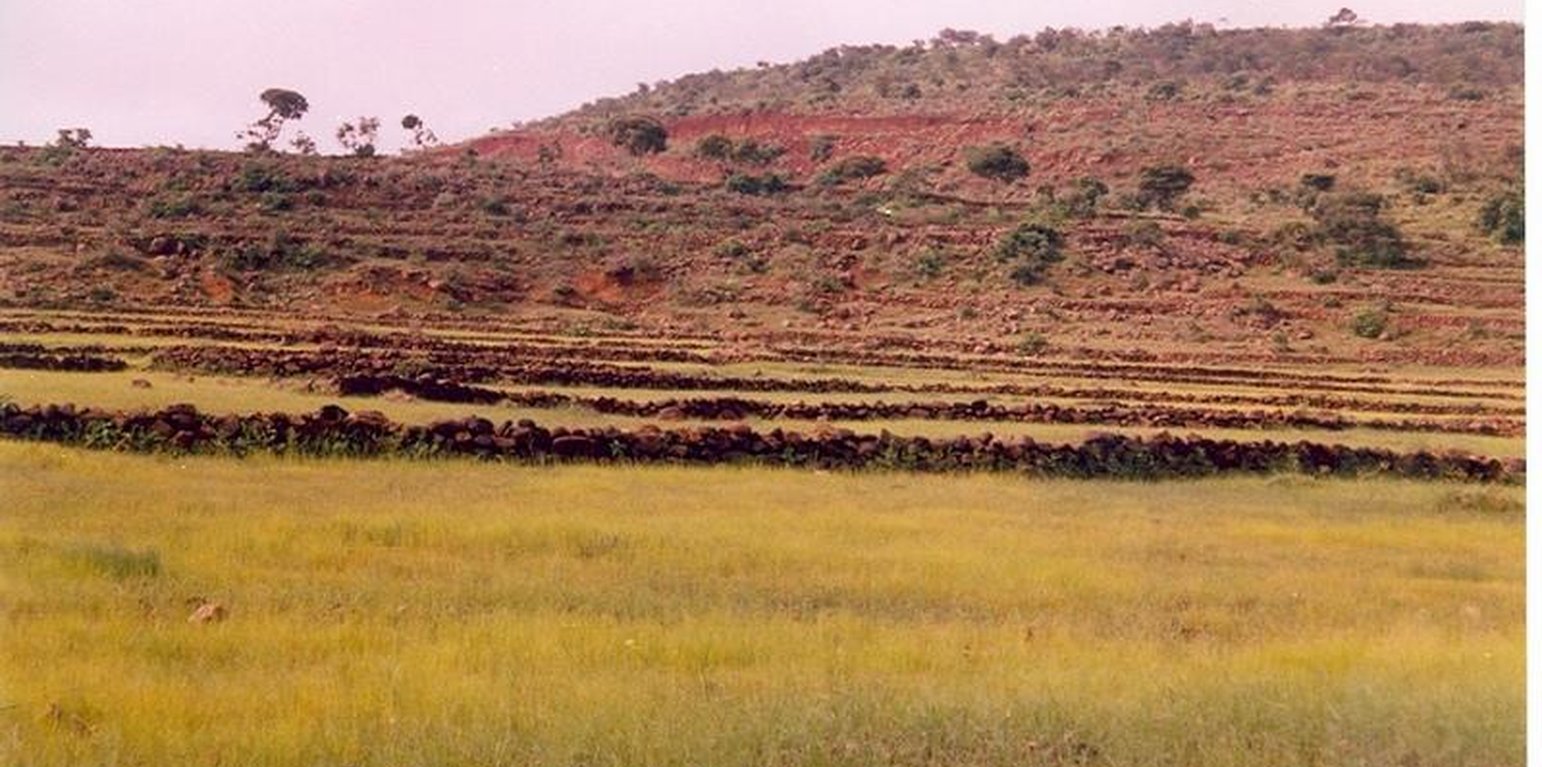




Description: digging of foundation, stone wall constructionof 60-80 m, digging of trench along the contour Purpose: decrease soil erosion, moisture harvesting, decrease slope length, reduce runoff velocity and increase productivity per unit area Establishment/Maintenance: planting of fodder trees and integrate with biological measures Environment: enhance to grow natural grasses and vegetation, minimize desertification, recharge ground water and improve local climate
Location: Adet Naedir, Tigray, Ethiopia
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Spread of the Technology:
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation: more than 50 years ago (traditional)
Type of introduction








| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Birr) | Total costs per input (Birr) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 118.0 | 118.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| Animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Tools | ha | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | |||||
| Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 6.25 | 6.25 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | |||||
| Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 33.75 | 33.75 | 100.0 |
| Other | |||||
| Other cost | ha | 1.0 | 17.5 | 17.5 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 197.5 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 24.69 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Birr) | Total costs per input (Birr) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1.0 | 10.5 | 10.5 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 10.5 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 1.31 | ||||
Can lead to waterlogging