Vertical growing of potatoes in pits, by the gradual addition of further layers of soil.
(Tajikistan)
Description
Vertical growing of potatoes in pits, by the gradual addition of further layers of soil.
The technology is used in areas that have extreme climatic conditions and a high water deficit. The technology is quite simple; compost or enriched soil is placed into the bottom of a 50x50x50cm pit. Then, one or two potatoes are planted into the base of the pit, and covered with soil. As the potato grows, the pit is gradually filled up with soil to keep it covered. It is also watered regulary.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of this technology is to improve the potato yield, and therefore to increase farm income under these climatic conditions. The technology is well adapted to this arid area with only a little irrigation water available, because the method improves access to water.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The technology is quite simple and not cost intensive. Costs are mainly connected to the purchase of high-quality seeds and compost production. Labour is needed to dig the pits, and fill and maintain them.
Natural / human environment: The technology can be used under any agricultural conditions, such as on Dehkan farms as well as in kitchen gardens
Location
Location: Khatlon District, Nosiri Husrav region, Tajikistan, Tajikistan
No. of Technology sites analysed:
Geo-reference of selected sites
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. < 0.1 km2 (10 ha))
In a permanently protected area?:
Date of implementation:
Type of introduction
-
through land users' innovation
-
as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
-
during experiments/ research
-
through projects/ external interventions
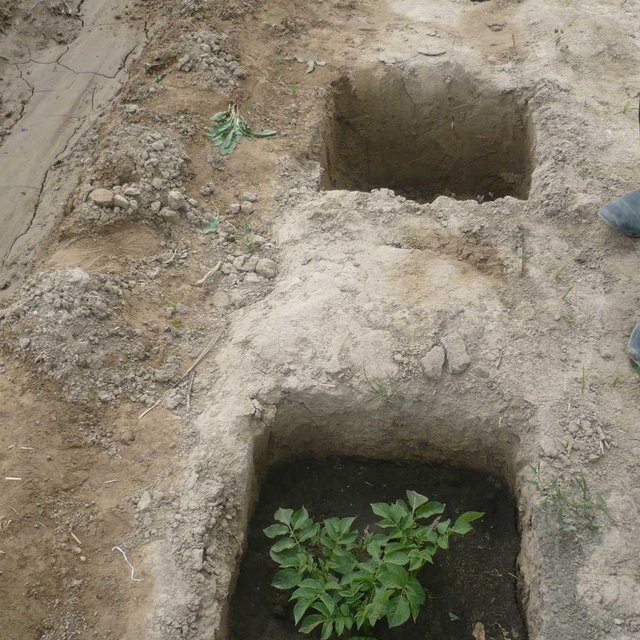

Showing the pits where the potatoes are planted. (Kalandarov R. (Dushanbe, 3 Herzin street))
Classification of the Technology
Main purpose
-
improve production
-
reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
-
conserve ecosystem
-
protect a watershed/ downstream areas – in combination with other Technologies
-
preserve/ improve biodiversity
-
reduce risk of disasters
-
adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
-
mitigate climate change and its impacts
-
create beneficial economic impact
-
create beneficial social impact
Land use
-
Cropland
- Annual cropping: root/tuber crops - potatoes
Number of growing seasons per year: 2
Water supply
-
rainfed
-
mixed rainfed-irrigated
-
full irrigation
Purpose related to land degradation
-
prevent land degradation
-
reduce land degradation
-
restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
-
adapt to land degradation
-
not applicable
Degradation addressed
-
chemical soil deterioration - Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content (not caused by erosion)
-
physical soil deterioration - Pk: slaking and crusting, Pi: soil sealing
SLM group
-
irrigation management (incl. water supply, drainage)
SLM measures
-
agronomic measures - A2: Organic matter/ soil fertility, A6: Residue management
Technical drawing
Technical specifications
A drawing showing the pit's lower part, which is filled with compost and rich soil as the potato grows.
Location: South of Tajikistan. Husrav, Khatlon
Date: 11.05.2011
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing)
Relay cropping
Material/ species: potato seeds
Remarks: digging pits
Manure / compost / residues
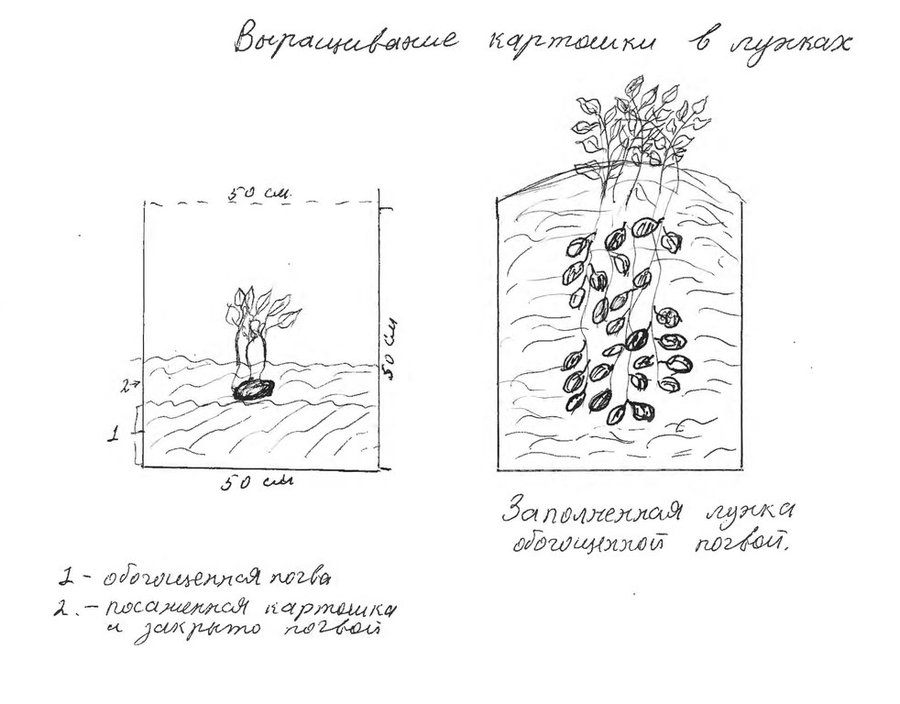
Author: Kalandarov R., Dushanbe, 3 Herzin street
Establishment and maintenance: activities, inputs and costs
Calculation of inputs and costs
- Costs are calculated:
- Currency used for cost calculation: USD
- Exchange rate (to USD): 1 USD = n.a 450
- Average wage cost of hired labour per day: 5
Most important factors affecting the costs
Digging the pits is the most determinate factor as it requires a lot of labour.
Establishment activities
-
Digging holes (Timing/ frequency: None)
Establishment inputs and costs
| Specify input |
Unit |
Quantity |
Costs per Unit (USD) |
Total costs per input (USD) |
% of costs borne by land users |
|
Labour
|
| Digging holes |
ha |
1.0 |
8.0 |
8.0 |
100.0 |
|
Equipment
|
| Tools |
pieces |
1.0 |
5.0 |
5.0 |
100.0 |
|
Plant material
|
| Seeds |
kg |
200.0 |
0.45 |
90.0 |
1.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology |
103.0 |
|
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD |
103.0 |
|
Maintenance activities
-
Filling pits with soil (Timing/ frequency: человек ден)
-
заполнение лунок почвой (Timing/ frequency: человек/день)
Maintenance inputs and costs
| Specify input |
Unit |
Quantity |
Costs per Unit (USD) |
Total costs per input (USD) |
% of costs borne by land users |
|
Labour
|
| Filling pits with soil |
Persons/day |
0.1 |
5.0 |
0.5 |
100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology |
0.5 |
|
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD |
0.5 |
|
Natural environment
Average annual rainfall
-
< 250 mm
-
251-500 mm
-
501-750 mm
-
751-1,000 mm
-
1,001-1,500 mm
-
1,501-2,000 mm
-
2,001-3,000 mm
-
3,001-4,000 mm
-
> 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
-
humid
-
sub-humid
-
semi-arid
-
arid
Specifications on climate
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Slope
-
flat (0-2%)
-
gentle (3-5%)
-
moderate (6-10%)
-
rolling (11-15%)
-
hilly (16-30%)
-
steep (31-60%)
-
very steep (>60%)
Landforms
-
plateau/plains
-
ridges
-
mountain slopes
-
hill slopes
-
footslopes
-
valley floors
Altitude
-
0-100 m a.s.l.
-
101-500 m a.s.l.
-
501-1,000 m a.s.l.
-
1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
-
1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
-
2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
-
2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
-
3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
-
> 4,000 m a.s.l.
Technology is applied in
-
convex situations
-
concave situations
-
not relevant
Soil depth
-
very shallow (0-20 cm)
-
shallow (21-50 cm)
-
moderately deep (51-80 cm)
-
deep (81-120 cm)
-
very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil)
-
coarse/ light (sandy)
-
medium (loamy, silty)
-
fine/ heavy (clay)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface)
-
coarse/ light (sandy)
-
medium (loamy, silty)
-
fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter content
-
high (>3%)
-
medium (1-3%)
-
low (<1%)
Groundwater table
-
on surface
-
< 5 m
-
5-50 m
-
> 50 m
Availability of surface water
-
excess
-
good
-
medium
-
poor/ none
Water quality (untreated)
-
good drinking water
-
poor drinking water (treatment required)
-
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
-
unusable
Water quality refers to:
Is salinity a problem?
Occurrence of flooding
Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation
-
subsistence (self-supply)
-
mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
-
commercial/ market
Off-farm income
-
less than 10% of all income
-
10-50% of all income
-
> 50% of all income
Relative level of wealth
-
very poor
-
poor
-
average
-
rich
-
very rich
Level of mechanization
-
manual work
-
animal traction
-
mechanized/ motorized
Sedentary or nomadic
-
Sedentary
-
Semi-nomadic
-
Nomadic
Individuals or groups
-
individual/ household
-
groups/ community
-
cooperative
-
employee (company, government)
Age
-
children
-
youth
-
middle-aged
-
elderly
Area used per household
-
< 0.5 ha
-
0.5-1 ha
-
1-2 ha
-
2-5 ha
-
5-15 ha
-
15-50 ha
-
50-100 ha
-
100-500 ha
-
500-1,000 ha
-
1,000-10,000 ha
-
> 10,000 ha
Scale
-
small-scale
-
medium-scale
-
large-scale
Land ownership
-
state
-
company
-
communal/ village
-
group
-
individual, not titled
-
individual, titled
Land use rights
-
open access (unorganized)
-
communal (organized)
-
leased
-
individual
Water use rights
-
open access (unorganized)
-
communal (organized)
-
leased
-
individual
Access to services and infrastructure
employment (e.g. off-farm)
drinking water and sanitation
Impacts
Socio-economic impacts
demand for irrigation water
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
Livelihood and human well-beeing
Cost-benefit analysis
Benefits compared with establishment costs
Short-term returns
very negative
very positive
Benefits compared with maintenance costs
Short-term returns
very negative
very positive
Climate change
Gradual climate change
annual temperature increase
not well at all
very well
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
not well at all
very well
not well at all
very well
not well at all
very well
not well at all
very well
Other climate-related consequences
not well at all
very well
Adoption and adaptation
Percentage of land users in the area who have adopted the Technology
-
single cases/ experimental
-
1-10%
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have done so without receiving material incentives?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
Number of households and/ or area covered
NA
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
To which changing conditions?
-
climatic change/ extremes
-
changing markets
-
labour availability (e.g. due to migration)
Conclusions and lessons learnt
Strengths: land user's view
Strengths: compiler’s or other key resource person’s view
-
New agricultural technology
-
Growing in pits promotes an increase in crop yield
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good yields are possible with the use of required agrotechnology
-
Water saving technology
How can they be sustained / enhanced? Individual irrigation
-
The technology can be used on small land plots and is therefore well adapted for the use in kitchen gardens
How can they be sustained / enhanced? The technology is able to provide one family with enough food for their use.
Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks: land user's viewhow to overcome
Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks: compiler’s or other key resource person’s viewhow to overcome
-
Technology is applicable to a small land area.
not taken into account due to specific characteristics of the technology
-
Problems during harvesting period
References
Reviewer
-
Alexandra Gavilano
-
David Streiff
-
Joana Eichenberger
Date of documentation: May 4, 2011
Last update: Nov. 2, 2021
Resource persons
-
Rustam Kalandarov - SLM specialist
-
Sa'dy Odinashoev - SLM specialist
Full description in the WOCAT database
Documentation was faciliated by
Institution
- NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Kyrgyzstan
- Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan (Youth Ecological Center, Tajikistan) - Tajikistan
Project
- Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)










