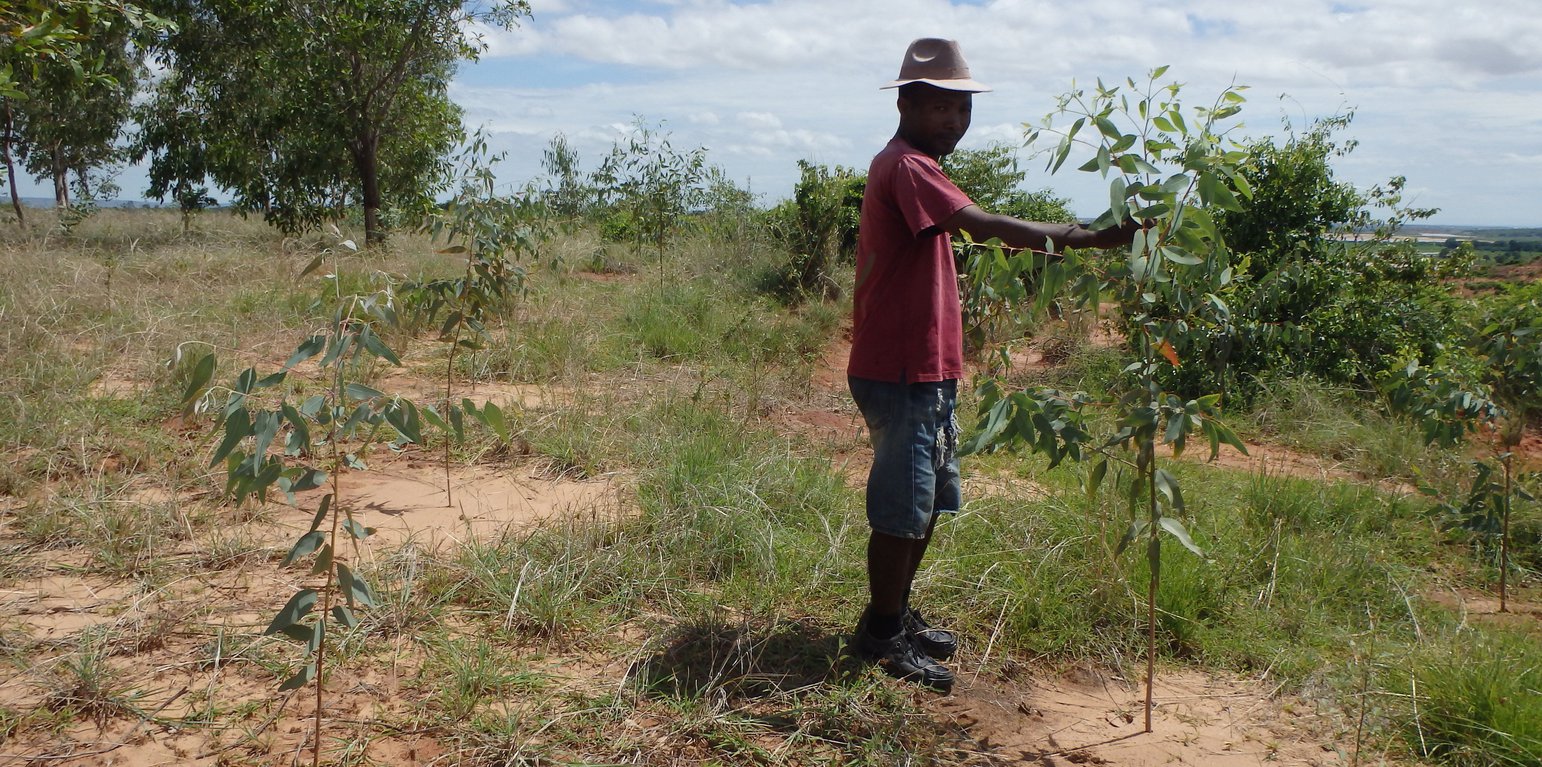




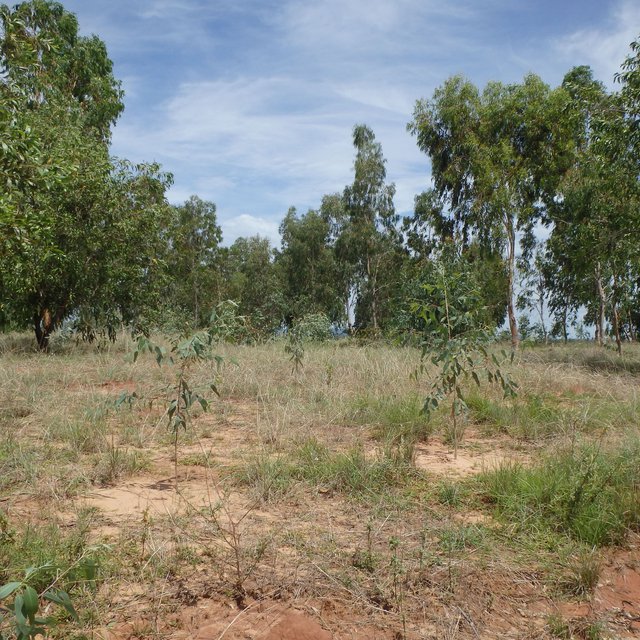
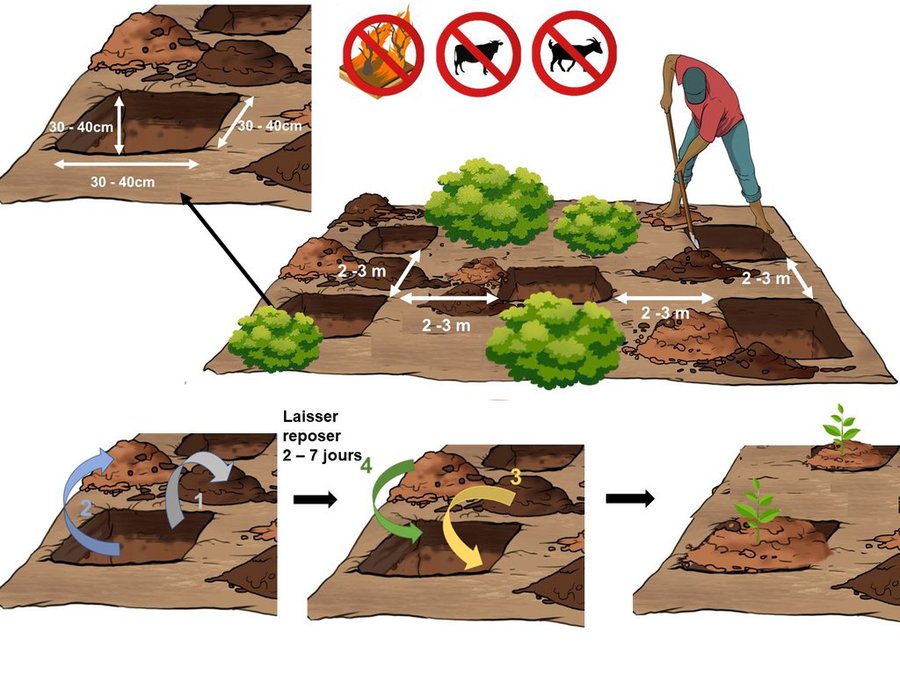
Crop exclosures are created on hilltops and steep slopes where cultivation is not recommended due to erosion risks. Passive crop exclusion comprises leaving a forested area uncultivated and encouraging the natural regeneration of the environment, while protecting it from fire and roaming livestock. Active exclosures, on the other hand, consists in supporting natural regeneration through restoration (enrichment and reforestation). When applying this technology, preference should be given to indigenous species (Harungana madagascariensis, Albizia lebbeck, etc.) over fast-growing species (Eucalyptus spp, Acacia spp) in order to maintain the biological diversity of the environment.
The various stages involved in establishing either passive or active crop exclosures are as follows:
- organisation of a general information meeting to raise awareness and canvas the concerns of the surrounding population;
- participatory delineation of the area to be protected (local authorities, owners and users concerned, etc.);
- creation of a management committee;
- preparation of a crop exclusion plans;
- public consultation and validation of the projects;
- formalization in the Fokontany and commune;
- implementation.
The development of surrounding areas and the installation of fascines (vegetative checkdams) to control gullying may also be incorporated into the clearing process, as per the agreed-upon local arrangement. Crop exclusion helps downstream areas from silting up, preserves soil fertility and regenerates degraded lands. It also improves infiltration and reduces erosion and soil loss.
The branches of regenerated trees can be sustainably harvested according to specific needs, such as fodder, wood, or organic matter for mulching purposes. Additionally, non-wood products can be gathered on these plots, including honey, medicinal plants, and species used for traditional knowledge-based or "ady gasy" products.
Location: Tsaramandroso, Antanambao Andranolava, Marovoay Banlieue, Manerinerina, Boeny, Madagascar
No. of Technology sites analysed: 2-10 sites
Spread of the Technology: evenly spread over an area (approx. < 0.1 km2 (10 ha))
In a permanently protected area?: No
Date of implementation: 2020; less than 10 years ago (recently)
Type of introduction







| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Ariary) | Total costs per input (Ariary) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Hole digging and seedling planting | man-days | 6.0 | 5000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | |||||
| Seedlings | number | 100.0 | 700.0 | 70000.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 100'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 23.26 | ||||
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit (Ariary) | Total costs per input (Ariary) | % of costs borne by land users |
| Labour | |||||
| Creation and maintenance of a firebreak | man-days | 26.0 | 5000.0 | 130000.0 | 100.0 |
| Pruning | man-days | 22.0 | 10000.0 | 220000.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 350'000.0 | ||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 81.4 | ||||