Conversion of stony slopes into an irrigated apricot orchard [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Pjotr M Sosin
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: David Streiff
Табдил додани замини сангоб ба зардолу бог
technologies_1055 - Tajikistan
- Full summary as PDF
- Full summary as PDF for print
- Full summary in the browser
- Full summary (unformatted)
- Conversion of stony slopes into an irrigated apricot orchard: March 20, 2017 (inactive)
- Conversion of stony slopes into an irrigated apricot orchard: July 22, 2017 (inactive)
- Conversion of stony slopes into an irrigated apricot orchard: Aug. 21, 2019 (inactive)
- Conversion of stony slopes into an irrigated apricot orchard: Nov. 2, 2021 (public)
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Tajik Soil Insitute (Tajik Soil Institute) - TajikistanName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Tajik Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Tajik Academy of Agricultural Sciences) - Tajikistan1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
03/05/2011
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Conversion of a stony plot of land into an apricot orchard and use for production of fodder.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
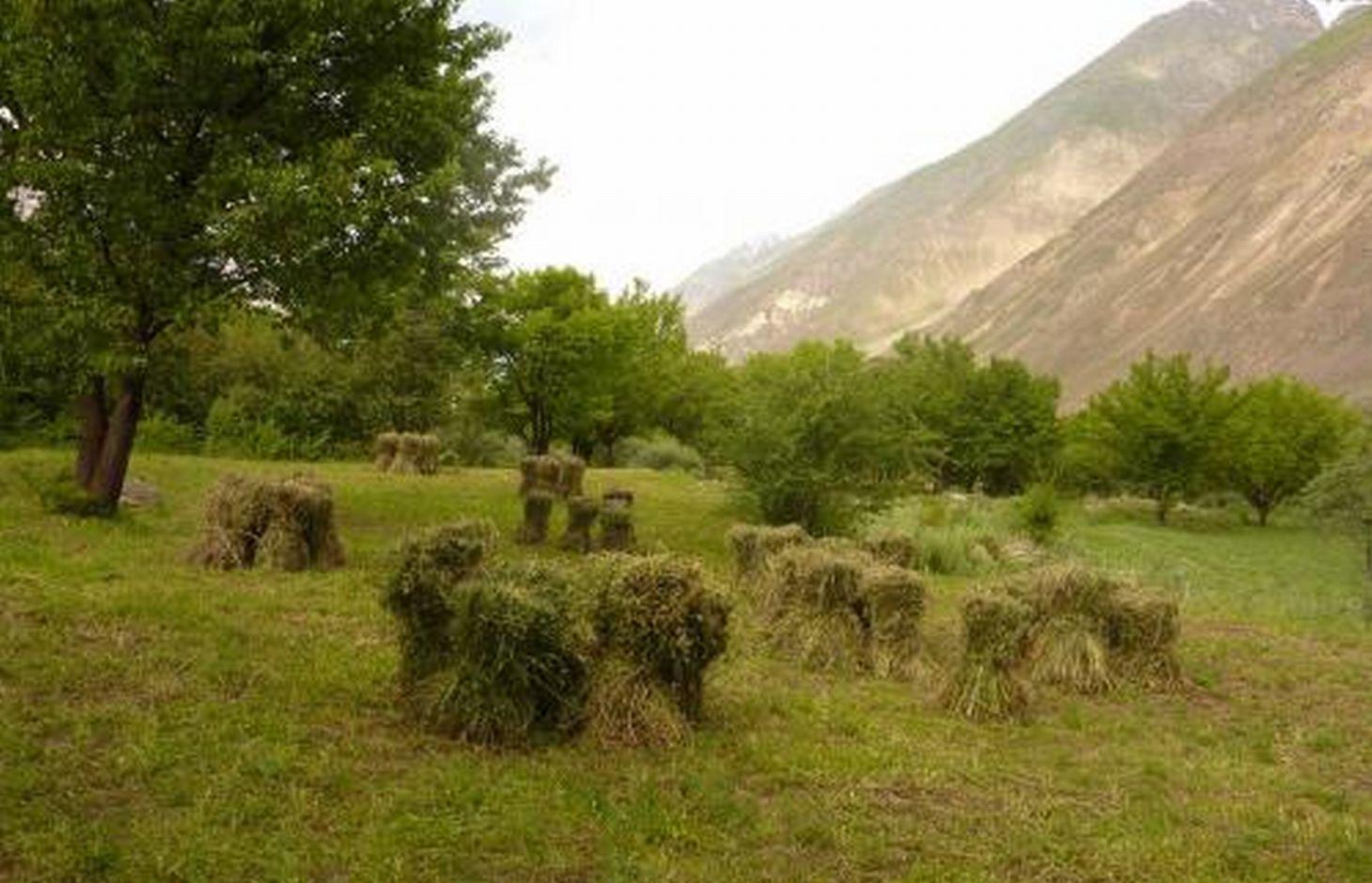
Description:
Before the technology was applied, this stony slope was used as a low-productive pasture. First of all, the area was cleaned of stones. The removed stones were used for construction of a fence around the plot. An irrigation canal was built along the upper border of the plot. An irrigation trench awas dug across the slope. No planting of this stony surface was carried out. Apricot trees were planted along the drainage ditches. Perennial herbaceous fodder plants such as alfa-alfa and esparzet were intercropped in the apricot orchard. Collected stones were used to fence the land area and so to protect the territory from animals.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the technology is to increase productivity of these stony slopes with the use of irrigation, and intercropping with perennial herbaceous fodder plants in the apricot orchard.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Removing stones from the plot, construction of a fence, construction of an irrigation canal, construction of drainage ditches across the plot, planting trees, ploughing the intercropped area, and planting perennial fodder plants.
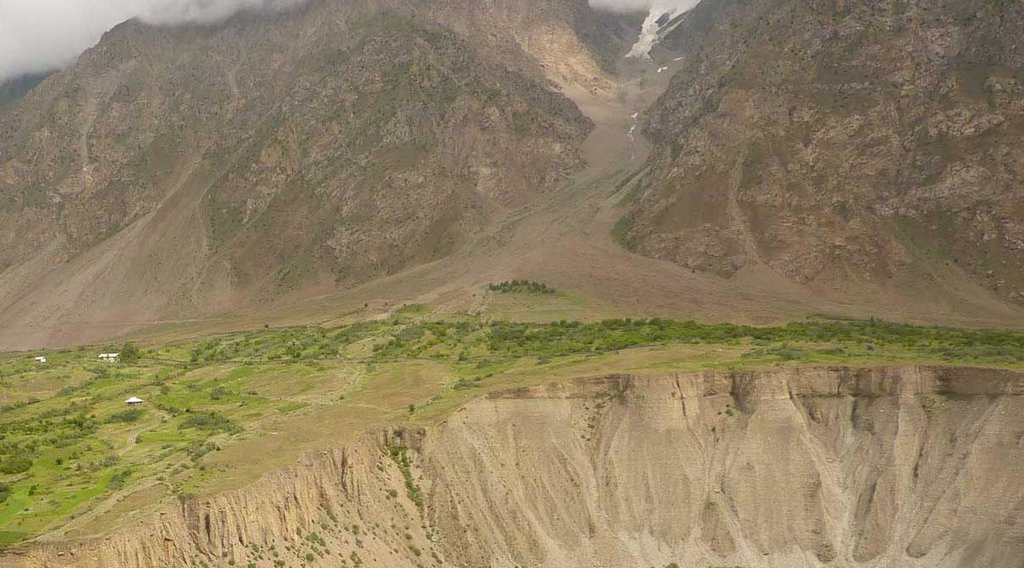
Natural / human environment: The plot is located in an arid zone, and 60% of the surface is covered with stones. Vegetation cover mostly consists of ephemers which have a short growing period. The land is used as summer, low productive pastures.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Tajikistan
Further specification of location:
GBAO, Vanj, Jovid
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- during experiments/ research
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Землепользователи принимали участие лишь в технической реализации технологии.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping

Mixed (crops/ grazing/ trees), incl. agroforestry
- Agroforestry
Comments:
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
If land use has changed due to the implementation of the Technology, indicate land use before implementation of the Technology:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- full irrigation
Comments:
Water supply: полностью орошаемое, полностью орошаемое
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Livestock density (if relevant):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- agroforestry
- improved ground/ vegetation cover
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 km2
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.2 m2.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover
- V2: Grasses and perennial herbaceous plants

structural measures
- S6: Walls, barriers, palisades, fences

management measures
- M1: Change of land use type
Comments:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: structural measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, legume inter-planting, minimum tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing, droughts, population pressure
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
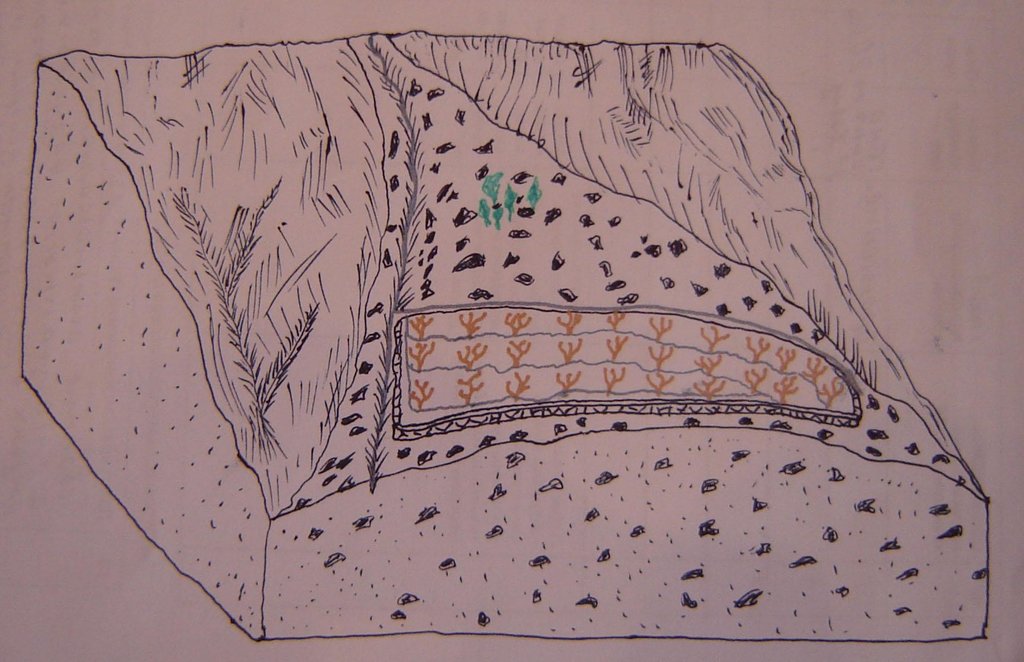
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
Location of apricot orchard on the slope
Location: Jovid Jamoat. GBAO, Vanj
Date: 2010,06,16
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs, C : perennial crops
Wall/ barrier
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 3000
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3000
Change of land use type
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
Somoni
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
4.5
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
7.00
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction of fence | Structural | 1 year |
| 2. | Construction of irrigation canal | Structural | 1 year |
| 3. | Purchase of seedlings | Structural | 15 days |
| 4. | Planting seedlings | Structural | 2 months |
| 5. | Removing stones from an area of 20 ha | Structural |
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Construction of fence | meter | 3000.0 | 15.0 | 45000.0 | 30.0 |
| Labour | Construction of irrigation canal | meter | 1300.0 | 23.07692 | 30000.0 | 10.0 |
| Labour | Planting seedlings | Pieces | 6400.0 | 1.0 | 6400.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Removing stones | ha | 20.0 | 2625.0 | 52500.0 | 30.0 |
| Plant material | Seedlings | Pieces | 6400.0 | 5.0 | 32000.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 165900.0 | |||||
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- arid
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
> 50 m
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Gender:
- women
- men
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly disadvantaged land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
Comments:
2-5 ha is cropland and 0.5-1 ha for grazing
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
Land use rights:
- leased
Comments:
The land belongs to the state and the land users rented this plot.
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
fodder production
Water availability and quality
demand for irrigation water
Income and costs
farm income
economic disparities
Socio-cultural impacts
food security/ self-sufficiency
recreational opportunities
situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups
Livelihood and human well-beeing
Comments/ specify:
Implementation of this technology allowed the farmer to earn 12500 somoni from selling hay and apricots. This Income provided him a chance to invest for education, health and increasing the number of livestock and things needed for a household.
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Soil
soil moisture
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
biomass/ above ground C
habitat diversity
Other ecological impacts
Competition
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | not well |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
negative
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
very positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 10-50%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
30 household
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
40% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
30 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: At the moment this technology is not being widely adopted due to lack of finances of other land users in the region.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
|
It does not require any special engineering facilities How can they be sustained / enhanced? During the implementation of the technology |
|
The local material was used for fencing How can they be sustained / enhanced? During the implementation of the technology |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
No engineering structures are needed How can they be sustained / enhanced? In the course of the use of technology |
|
No additional materials and equipment are used How can they be sustained / enhanced? In the course of the use of technology |
|
Local material is used for fencing How can they be sustained / enhanced? In the course of the use of technology |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Technology's effectiveness depends on availability of irrigation water | Implement water-saving technology |
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules