Couloirs de passage [Niger]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Lemma Ababu
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1353 - Niger
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
GREAD (GREAD) - Niger1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Pastoralism in Niger: monitoring system for movements and … [Niger]
This approach, traditional in nature and supported by the National Mechanism for the Prevention and Management of Disasters and Food Crises (DNPGCCA), consists of a Geographical Information System, which integrates the water resources, the movement of populations, and the spatial distribution of grazing land, also in terms of the quantities …
- Compiler: Soumaila Abdoulaye

Champ Ecole Pastorale [Niger]
Le Champ Ecole (CE) Pastorale, une école «sans murs», est un cadre de rencontre et de formation pour un groupe de 20 à 30 éleveurs de la zone pastorale du Niger, qui se déroule sur une aire de pâturage communautaire, tout au long de l'année. C’est un lieu d’échange d’expériences …
- Compiler: Soumaila Abdoulaye
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
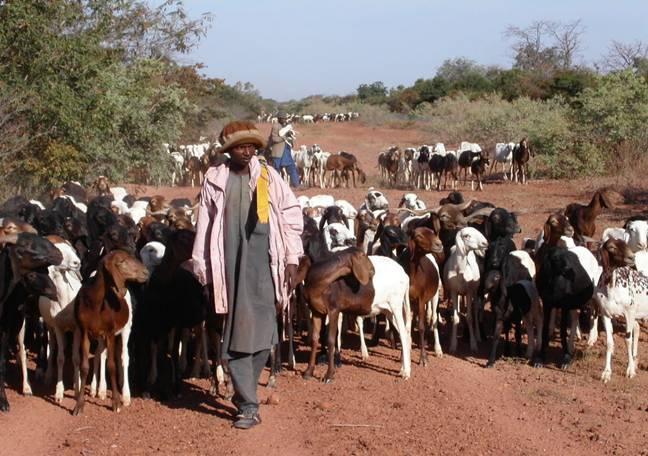
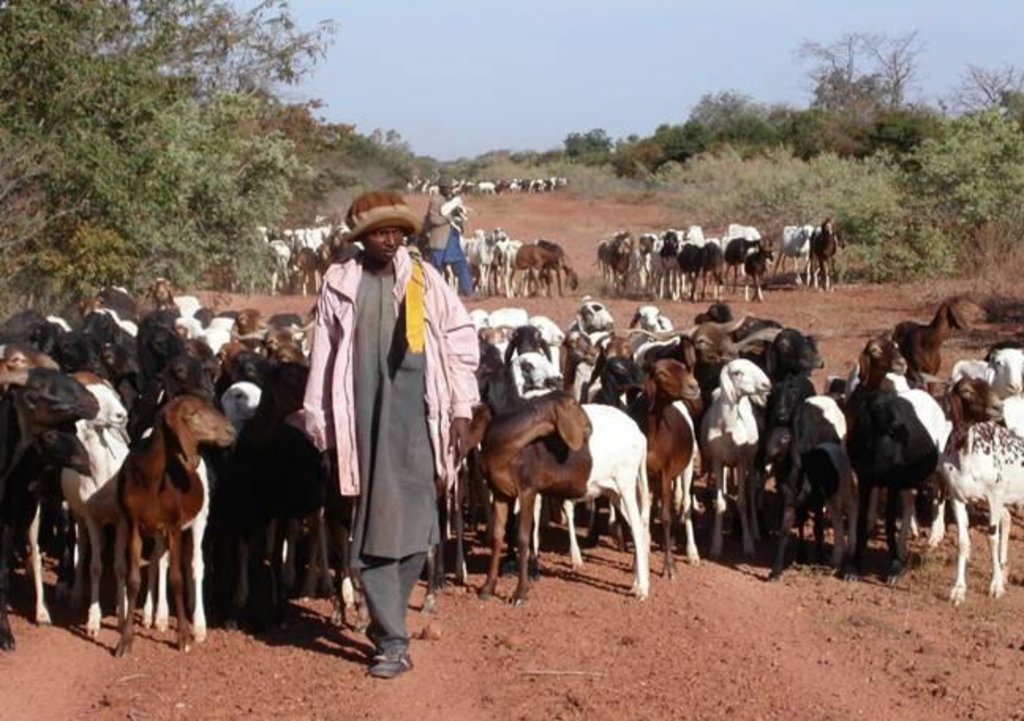
The ‘couloirs de passage’ are formally defined passageways which channel the movements of livestock herds in the agro-pastoral zones of Niger, by linking pastures, water points and coralling areas, be it within village areas (internal couloirs) or on open land (external couloirs).
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
The main goal of the couloirs is the prevention of conflict between agriculturalists and pastoralists regarding the use of limited land and water resources. These conflicts are often provoked by cattle entering cropping areas. The establishment of demarcated passageways allows the livestock to access water points and pastures without causing damage to cropland. The corridors are regulated through the ‘code rural’ – a national law defining the land use rights of the pastoralists. Demarcation of couloirs is based on a consensual decision of all concerned interest groups. Internal couloirs are negotiated in a general on-site assembly involving all stakeholders (farmers, breeders, women’s groups, local authorities). For the demarcation of external couloirs the involvement of transhumance herders and neighboring villages is indispensable. Once an agreement on the course of the couloir is achieved, demarcation with stones and/or boundary planting with selected tree species is carried out by the local land users - with financial and technical assistance of the government or NGOs. Common species involve: Euphorbia balsamifera, Acacia spp. (A. nilotica; A. senegal); and Faidherbia albida. Management committees at the community level draw up regulations for the management of the couloirs (maintenance and protection of vegetation). Protection of plants is achieved through dead branches (at the initial stage), daily control by forest guards, and information campaigns. The technology is a sustainable solution to the described conflicts. As a valuable by-product the trees along the demarcation lines provide of wood and non-woody by-products.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Niger
Region/ State/ Province:
Tillabéri North
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Map
×2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- create beneficial social impact
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Yes
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Silvo-pastoralism

Grazing land
Extensive grazing:
- Semi-nomadic pastoralism

Forest/ woodlands
Comments:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion by water, soil erosion by wind and biological degradation; Primary problem addressed is conflicts between livestock and agriculture producers around natural resources
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Ms: Silvo-pastoralism
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)

Cropland
- Annual cropping
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- pastoralism and grazing land management
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover

management measures
- M3: Layout according to natural and human environment
Comments:
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

soil erosion by wind
- Et: loss of topsoil

biological degradation
- Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Et: loss of topsoil, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (facilitator of code rural)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (pastors and workers)
Main technical functions: increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Trees/ shrubs species: Euphorbia balsamifera, Acacia spp. (A. nilotica; A. senegal) and Faidherbia albida
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- USD
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
1.5
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Identification of an existing couloir or definition of a new passageway by means of a general assembly | |
| 2. | Alignment of corridor boundaries e.g. by establishing stone lines. Internal couloirs are 10 to 50 m wide, whereas external couloirs exceed a width of 50 m | |
| 3. | Digging 40 cm deep pits; tree planting along boundaries (with a spacing of 1-3 meters, depending on the species selected and the secondary objective) |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Identification of an existing couloir or definition of a new passageway | persons/day | 25.0 | 1.5 | 37.5 | 5.0 |
| Plant material | Tree planting along boundaries (seedlings) | pieces | 670.0 | 2.05 | 1373.5 | 5.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 1411.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1411.0 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
Government or NGO's
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Protection of trees (through dead branches, guards, information campaigns) | |
| 2. | Replanting tree seedlings to fill gaps (annually, beginning of rainy season) |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Protection of trees | persons/day | 4.0 | 1.5 | 6.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | Replanting tree seedlings | pieces | 67.0 | 2.0448 | 137.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 143.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 143.0 | |||||
Comments:
Costs for seedlings were calculated for a couloir length of 1 km and a spacing of 3 m between plants (one tree line on each side). Seedling production is financed by projects, only transport costs are met by land users.
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
The costs of the planning meeting (general assembly) and the stones for delimitation were not taken into account. Daily salary for field work is US$ 1.5.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- coarse/ light (sandy)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good but low in case of soil crusting
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Individuals or groups:
- groups/ community
Level of mechanization:
- animal traction
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- communal (organized)
- individual
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
fodder production
fodder quality
animal production
Income and costs
farm income
Socio-cultural impacts
cultural opportunities
community institutions
Comments/ specify:
Through mutual aid in technology implementation
national institutions
Comments/ specify:
Code rural secretariat
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil cover
soil loss
nutrient cycling/ recharge
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
biomass/ above ground C
animal diversity
Climate and disaster risk reduction
fire risk
wind velocity
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
wind transported sediments
damage on neighbours' fields
damage on public/ private infrastructure
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Comments:
Technology is sensitive to climatic extremes (such as droughts and floods)
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
Comments:
Peace between communities is the key result on short term and on long term. Ecological and economic benefits are linked to the plantation of trees and the improved management of natural resources
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: for prevention of conflicts and land degradation
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| The technology provides a sustainable solution to conflicts between agriculturalists and pastoralists |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Implementation constraints: plant production is very expensive and reaching a consensus on the transformation of private cropland to communal passageways is very difficult | definition of the couloirs as public infrastructure and enhancement of organizational capacities of the local population through training and information sessions |
| Maintenance constraints: maintenance can only be realized by adjacent land owners, as the community organizations are weak | reinforce the institutional capacities of livestock owners and farmers to manage the couloirs |
| In the pastoral zone the couloirs lead to conflicts between pastoralists and private ranches | establish community-based land tenure commissions and introduce new laws on land property in the pastoral zone |
7. References and links
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Projet LUCOP/Tillabéry. 2004. Referential des measures techniques de recuperation, de protection et d’exploitation durable des terres, 2nd edition, 2004, 51 pp
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Hiernaux P., E. Tielkes, E. Schlecht. 2001. Elevage et gestion des parcours au Sahel, Workshop proceedings organised by Eric Tielkes et Abdoulaye Soumaila, Verlag Ulrich E. Grauer, Beuren, Stuttgart, Germany, 2001
7.3 Links to relevant online information
Title/ description:
Soumaila A.S. 2003. Base de données du code rural
URL:
www.case.ibimet.cnr.it/den/Documents/code_rural/start.html
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Pastoralism in Niger: monitoring system for movements and … [Niger]
This approach, traditional in nature and supported by the National Mechanism for the Prevention and Management of Disasters and Food Crises (DNPGCCA), consists of a Geographical Information System, which integrates the water resources, the movement of populations, and the spatial distribution of grazing land, also in terms of the quantities …
- Compiler: Soumaila Abdoulaye

Champ Ecole Pastorale [Niger]
Le Champ Ecole (CE) Pastorale, une école «sans murs», est un cadre de rencontre et de formation pour un groupe de 20 à 30 éleveurs de la zone pastorale du Niger, qui se déroule sur une aire de pâturage communautaire, tout au long de l'année. C’est un lieu d’échange d’expériences …
- Compiler: Soumaila Abdoulaye
Modules
No modules