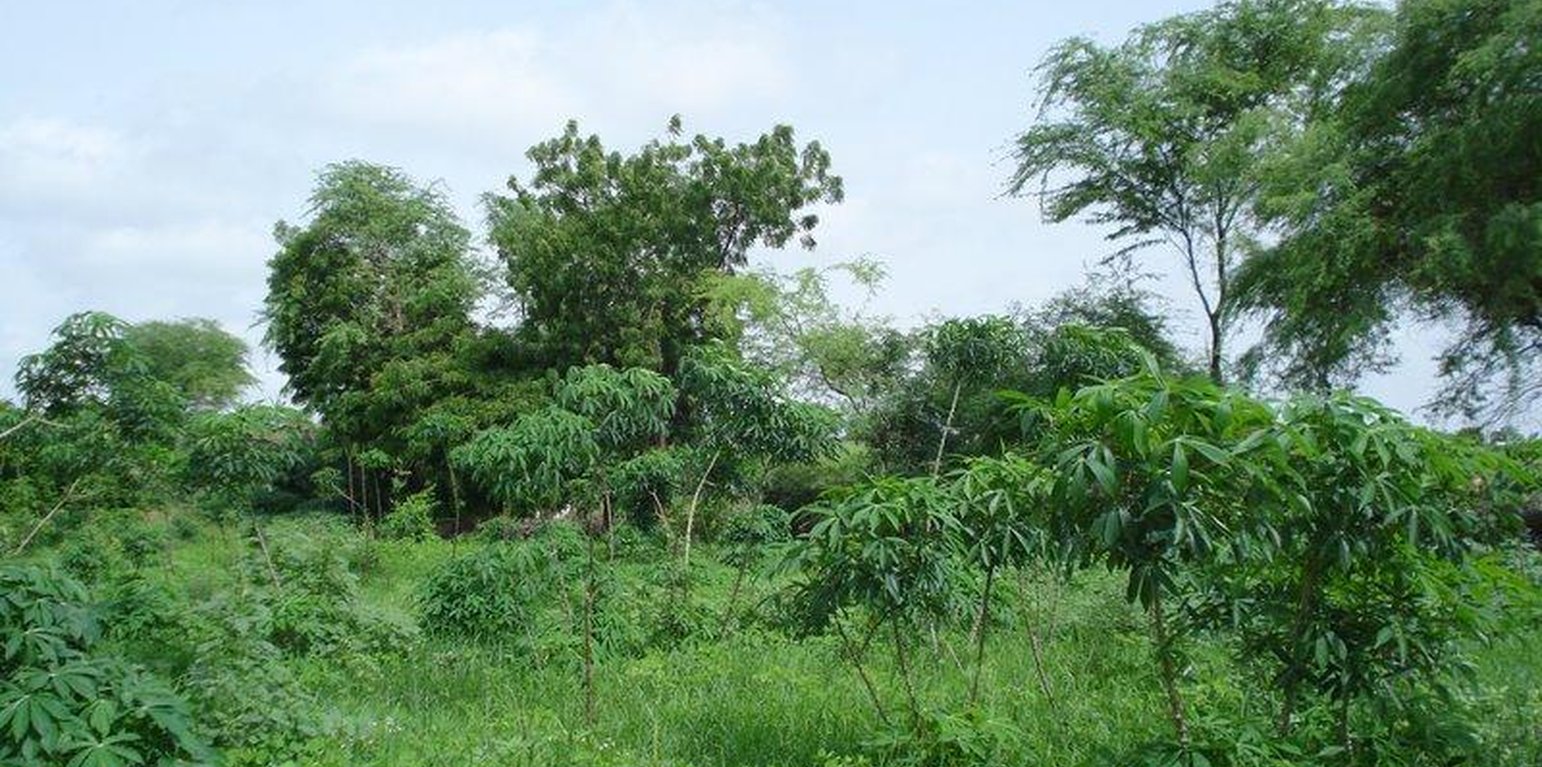




During the dry season, tomato, eggplant, chili, beans, cabbage, okra and bissap are cultivated, in the rainy season replaced with maïz. One part of the garden is cultivated with cassava, planted in the rainy season and harvested all year round. Main tree species are Prosopis juliflora, Citrus sp. and Eucalyptus camaldulensis. A hedge of mainly dead wood, alive Euphorbia balsamifera shrubs and few Eucalyptus camaldulensis trees is protecting the homegarden from roaming animals. It has the positive off-site effect of preventing the temporary pond beneath the plot from being filled up with sediments, as a consequence of wind erosion. Organic manure obtained from cattle faeces is used as a natural fertilizer.
Purpose of the Technology: The garden was established and is managed by a single land user and his family. Main objectives are to provide food security for his family, to make a wide range of fruits and vegetables available in a zone far from the next market and to improve income through diversification. As the plot is situated on a slope (7 %) and prone to water erosion during heavy rains, a further objective is to prevent the formation of gullies and ravines through better soil stabilization.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Trees planted in this plot were chosen upon seed or seedling availability in other peoples land as the land user planted whatever he could obtain. He constructed a fence of dead wood with the aim to turn it into a life fence of Eucalyptus camaldulensis trees later. A small retention basin was built to assure the storage of water tapped from the village borehole. However, because of breakdowns of the pump and the generally low outflow of the borehole, lack of water caused high mortality in the tree nursery of Eucalyptus camaldulensis seedlings. The fence therefore remains a mainly dead fence and is very weak in certain places. The main cost of the technology is the access to the borehole which costs the landuser 20'000 CFA (US-Dollar 45) per month. For the purchase of seeds for horticulture about 15'000 CFA (US-Dollar 33.50) are spent per year. The use of organic manure does not involve any costs as cattle is abundant in the area.
Natural / human environment: This SLM technology site is located in the sylvopastoral region of the Ferlo in the north of Sénégal. The agro-climatic zone is classified as semi-arid with mean annual precipitation of 300-400 mm. The main land use type in the area is extensive pastoralism followed by rainfed agriculture. Pastoralism is primarily practiced by transhumant Fula (Peulh) herders and further by Mauritanian Moor herders with herds of dromedaries. Vegetation cover in the area has largely been degraded due to cutting for domestic uses and cattle feeding, bushfires and overgrazing. The soil is exposed to wind erosion which carries away nutrients in the topsoil and therefore declines soil fertility. During intense rains in the rainy season, surface runoff is accelerated and leads to the formation of gullies and ravines.
Lugar: Barkédji / Diagali, Louga / Linguère, Senegal
No. de sitios de Tecnología analizados:
Difusión de la Tecnología: distribuida parejamente sobre un área (approx. < 0.1 km2 (10 ha))
Fecha de la implementación: hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
Tipo de introducción






| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (CFA) | Costos totales por insumo (CFA) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Material para plantas | |||||
| Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 33,0 | 33,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | |||||
| Irrigation water | ha | 1,0 | 45,0 | 45,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 78.0 | ||||
Increased food security, improved diversification of alimentation