Common village herding
(Tayikistán)
Navbati Poda (succession of herders)
Descripción
Village herding system with daily alternation of the herders including each household in a monthly turnus.
Aims / objectives: The herding system has to be easy and little labour-intensive, because children are the main workforce. It is a collective system and thus requires the participation of all households with families: For instance in the village Karsang with 141 households (not all having livestock) and two village herds, each family has to send monthly one child for herding or pay if it does not have workforce. In addition, always at least one adult has to accompany the herd. This means that children of big families only rarely miss school whereas those from small families miss more frequently. The final objective is to nourish animals maximally so they need a minimum of costly hay and concentrated feed (in terms of labour respectively in financial terms).
Methods: Children and adults are taught by the elders, the parents and the village land use committee how the rotation works: They should not stay at one place longer than three days, they should not chase the animals which otherwise lose energy unnecessarily and they shall not lose animals. Children not obeying are punished. In case of lost animals different approaches exist: Mostly the family of the herder who was responsible for the herd on the respective day reaches an agreement with the tenant's family.The village committee or elders can also arbitrate.
Stages of implementation: It is difficult to say when this system first emerged. A land user says that during Soviet Union there were village herds with a fix herder or an alternation like nowadays and, parallely, wealthy people had their own herd with a paid herder. During civil war only a few rich villagers kept animals and only at the beginning of the 2000s collective herding reemerged.
Role of stakeholders: The implementation of herding is a matter of each family's participation. The collaboration of the villagers with institutions is especially important in questions of taxes. In most villages the households pay per capita animal taxes. In order to improve SLM the land use committee on district level and the forest administration (as far as the village has such pastures) together with the local representants of the ecology commission advise the land use committees of each village to take the appropriate measures. And these talk with the herders to influence their comportment. A teacher from the local land use committee says that a lot is said about SLM, but little is effectively done.
Lugar
Lugar: Faizabad, Region of Republican Subordination, Tayikistán
Georreferencia de sitios seleccionados
Dato de inicio: 1920
Año de conclusión: n.d.
Tipo de Enfoque
-
tradicional/ local
-
iniciativa local reciente/ innovadora
-
proyecto/ basado en un programa
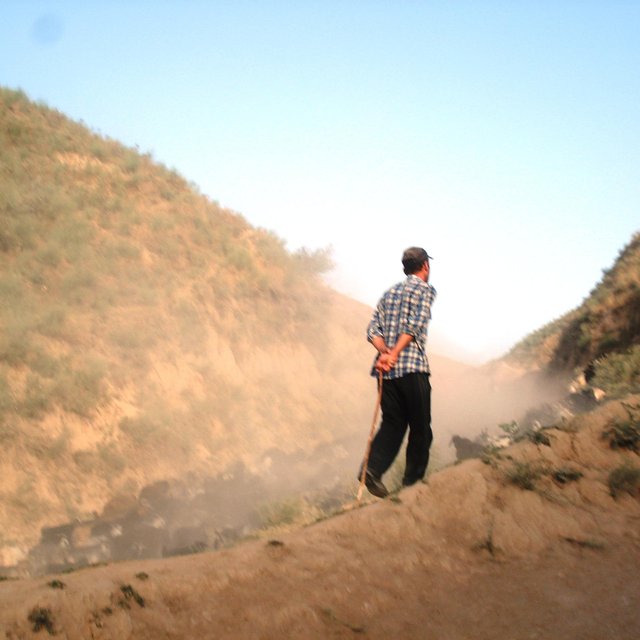

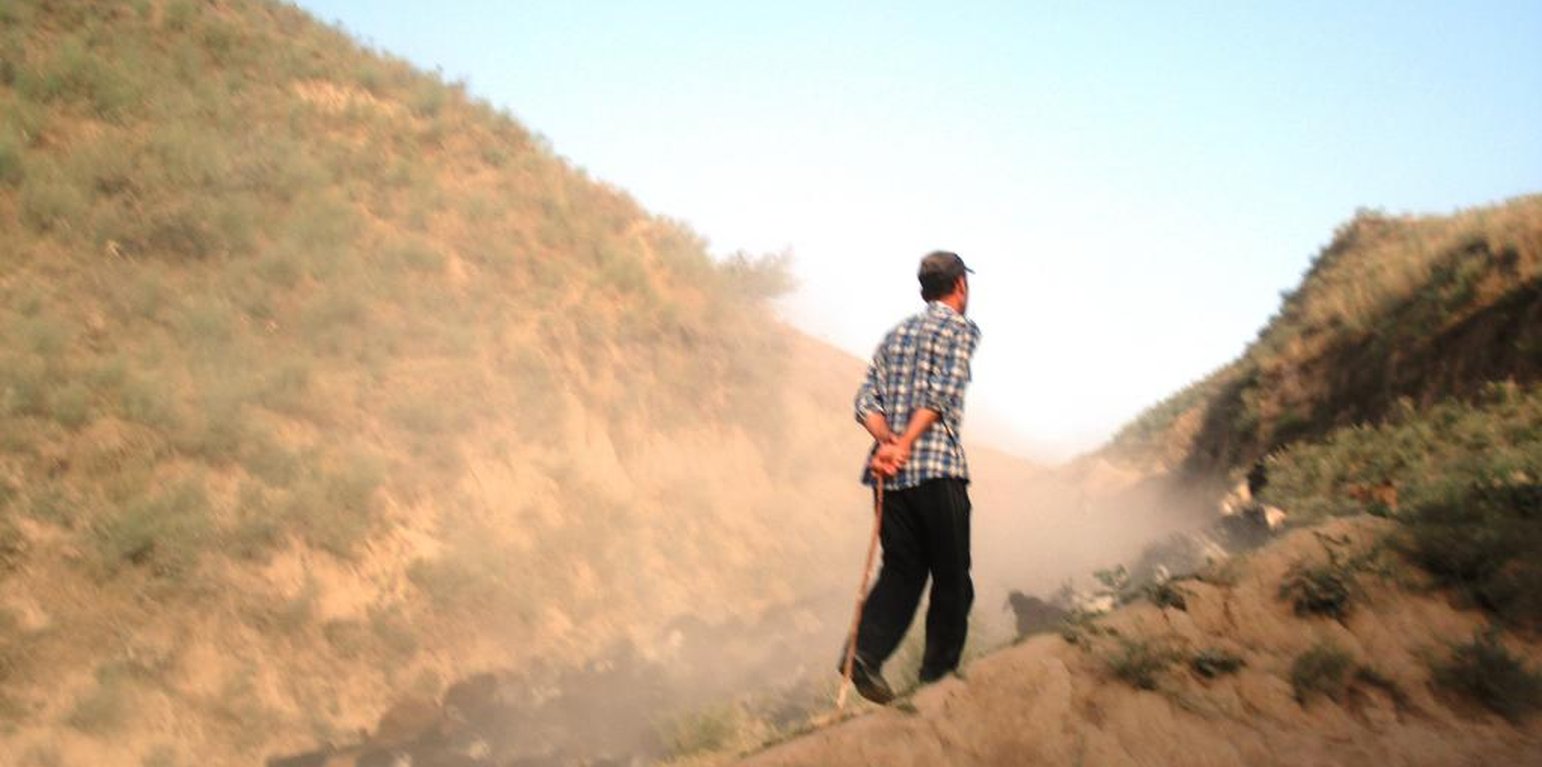
Herder of a large village-herd, with a dust cloud. (Christian Wirz, Switzerland (Switzerland))
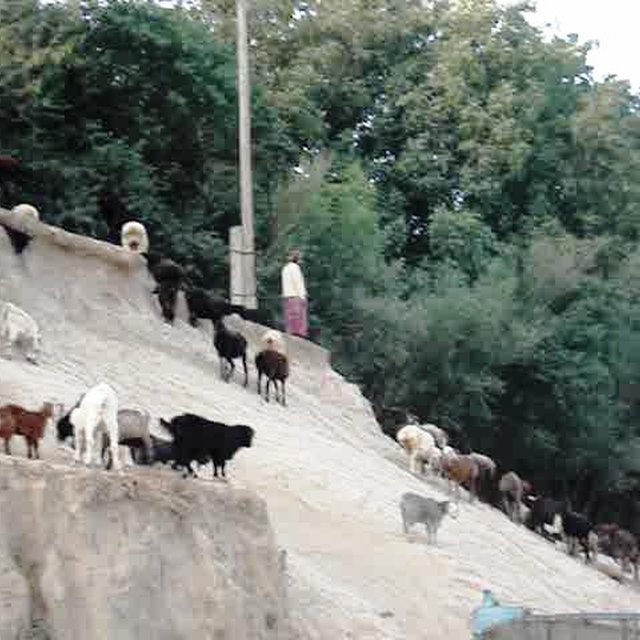

Children of the village bring their animals to the gathering place. (Christian Wirz, (Switzerland))
Metas del Enfoque y entorno facilitador
Propósitos/ objetivos principales del Enfoque
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (Maximal nutrition of livestock with child labour.)
In animal husbandry the semi-monetary value of livestock is important. Therefore, 'everyone would like to have more animals', says a land user. At the same time agricultural population has other activities such as the cultivation of kitchen-gardens and of cropland. And labour shortage is omnipresent, with many young men staying in Russia for work. In these multistrategies efforts for herding must be minimised which is best possible if children are sent as herders.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The approach needed and needs to be compatible with the traditionally sedentary culture and with the new employment and income sources in local economy: be it the work as a taxi-driver or selling vegetables on the local market. Today herding has to be especially cheap (finance, labour) because there is a multitude of preferences how to invest resources: building a (better) house, buying a mobile phone and a car or enabling (higher) education of children.
Condiciones que facilitan la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
-
Marco de trabajo legal (tenencia de tierra, derechos de uso de tierra y agua): The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately helped the approach implementation: The fact that a great part of grassland of former collective farms has not yet been attributed to farmers' associations makes it possible for everyone to use them. The only disadvantage in the eyes of land users is that they have to pay rent fees for this land.
Condiciones que impiden la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
-
Disponibilidad/ acceso a recursos y servicios financieros : Keeping animals is expensive because you have to nourish them (see costs of technology).
Treatment through the SLM Approach: The use of comparatively cheap grazing land of the former collective farms that is under village administration and contracts with forest administration for cheaper land are the solution.
-
Entorno institucional: If the defined herding system is not respected, cover is damaged, especially trees. And institutions have little authority in implementation, partly because of their own corruption.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Implementation is based on the households: They do not only send their children for herding, but they also punish them if they treat animals badly.
-
Carga de trabajo, disponibilidad de mano de obra: It is difficult to find labour force that is able to walk to the pastures with the animals, because many young men are in Russia.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Children are cheap and mobile.
Participación y roles de las partes interesadas involucradas
Partes interesadas involucradas en el Enfoque y sus roles
| ¿Qué partes interesadas/ entidades implementadoras estuvieron involucradas en el Enfoque? |
Especifique las partes interesadas |
Describa los roles de las partes interesadas |
| usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales |
ny people with animals participate in collective herding. Especially poor families cannot afford professional herding. |
There are both boys and girls working as herders. Among adults, men more often working as herders than women.
The role of women is traditionally associated with domestic work and kitchen gardens. |
| especialistas MST/consejeros agrícolas |
Different institutions: land use committees, forest administration, committee for ecology. |
|
| profesores/ niños en edad escolar/ estudiantes |
|
|
Agencia líder
Mainly land users supported by SLM specialists
Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales en las distintas fases del Enfoque
ninguno
pasivo
apoyo externo
interactivo
auto-movilización
iniciación/ motivación
Initiatation and planning was organised among villagers. They based themselves on experiences from Soviet times and from before.
implementación
Recently the institutions mentioned have become more important.
La toma de decisiones en la selección de Tecnología MST
Las decisiones fueron tomadas por
-
solamente usuarios de tierras (autoiniciativa)
-
principalmente usuarios de tierras con el apoyo de especialistas MST
-
todos los actores relevantes, como parte de un enfoque participativo
-
principalmente por especialistas MST en consulta con usuarios de tierras
-
solo por especialistas MST
-
por políticos/ líderes
La toma de decisiones se basa en
-
la evaluación de conocimiento MST bien documentado (la toma de decisiones se basa en evidencia)
-
hallazgos de investigaciones
-
la experiencia personal y opiniones (no documentadas)
Apoyo técnico, fortalecimiento institucional y gestión del conocimiento
Las siguientes actividades o servicios fueron parte del enfoque
-
Construcción de capacidades / capacitación
-
Servicio de asesoría
-
Fortalecimiento institucional (desarrollo institucional)
-
Monitoreo y evaluación
-
Investigación
Monitoreo y evaluación
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by other through observations; indicators: Local land use committees go to the pastures in spring to decide whether soils are dry enough and gr
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored by land users through observations; indicators: Land users control if their animals are fat and if they give milk. Otherwise they might not send the
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
Financiamiento y apoyo material externo
Presupuesto anual en dólares americanos para el componente MST
-
< 2,000
-
2,000-10,000
-
10,000-100,000
-
100,000-1,000,000
-
> 1,000,000
Precise annual budget: n.d.
Approach costs were met by the following donors: local government (district, county, municipality, village etc) (Meetings of administration with leaders.): 20.0%; local community / land user(s) (Organising herding: low costs.): 80.0%
Los siguientes servicios o incentivos fueron proporcionados a los usuarios de las tierras
-
Apoyo financiero/material proporcionado a los usuarios de tierras
-
Subsidios para insumos específicos
-
Crédito
-
Otros incentivos o instrumentos
Análisis de impacto y comentarios de conclusión
Impactos del Enfoque
No
Sí, un poco
Sí, moderadamente
Sí, mucho
¿El Enfoque ayudó a los usuarios de tierras a implementar y mantener Tecnologías MST?
¿El Enfoque empoderó a grupos en desventaja social y económica?
Especially poor population could profit from cheap communal pastures and thus afford keeping livestock.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
It can be assumed that this somehow logical solution of herding for settled people (not like in other Central Asian countries) emerged as a part of self-sufficient strategies during USSR. Similar herding patterns might though have existed already before USSR, according to local experts.
Motivación principal del usuario de la tierra para implementar MST
-
producción incrementada
-
incremento de la renta(bilidad), proporción mejorada de costo-beneficio
-
reducción de la degradación de la tierra
-
reducción del riesgo de desastres naturales
-
carga de trabajo reducida
-
pagos/ subsidios
-
reglas y reglamentos (multas)/ aplicación
-
prestigio, presión social/ cohesión social
-
afiliación al movimiento/ proyecto/ grupo/ redes
-
conciencia medioambiental
-
costumbres y creencias, moral
-
conocimiento y capacidades mejorados de MST
-
mejoramiento estético
-
mitigación de conflicto
-
well-being and livelihoods improvement
Sostenibilidad de las actividades del Enfoque
¿Pueden los usuarios de tierras sostener lo que se implementó mediante el Enfoque (sin apoyo externo)?
Conclusiones y lecciones aprendidas
Fortalezas: perspectiva del usuario de tierras
-
This form of herding is not conflictive: all people can afford it and everyone contributes to it by sending an own family member for herding. And, if a herder loses a villager's animal, the villager knows that he will also be a herder and might lose an animal, too. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: The institutions - be it elders or the land committee - must implement the technology.)
Fortalezas: punto de vista del compilador o de otra persona recurso clave
-
Common herding has a strong social component as it makes herders cooperate in order to maintain reputation (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Projects in Muminabad proposed by the village with a professional herder elected in a village meeting )
Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos: perspectiva del usuario de tierrascómo sobreponerse
-
The dependance upon children rather hinders the implementation of SLM, according to some land users. Children prefer to play rather than to respect rules about herding, says for example a teacher. And he adds that also adults do not always respect the established rules and that nobody controls effective implementation of the technology.
It is difficult to find adult herders. One village - Chujamar - decided to engage a professional herder, who would lead the cows to the pastures separately. Because cows cannot be lead only by children like little animals, according to the chief of that village. The villagers pay around 2$ per cow and season for herding.
Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos: punto de vista del compilador o de otra persona recurso clavecómo sobreponerse
-
Land users mention that implementation is difficult with herders (often children) that lack the necessary knowledge to implement SLM.
It is difficult to abolish child labour. But, by completing the herders' team with at least one professional, paid herder, progress in SLM would be possible perhaps. And making pastures a subject in school might help to araise awareness about SLM.
Referencias
Fecha de la implementación: 23 de febrero de 2010
Últimas actualización: 5 de julio de 2017
Personas de referencia
-
Christian Wirz (christian.wirz@students.unibe.ch) - Especialista MST
Descripción completa en la base de datos de WOCAT
La documentación fue facilitada por
Institución
- CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suiza
Proyecto






