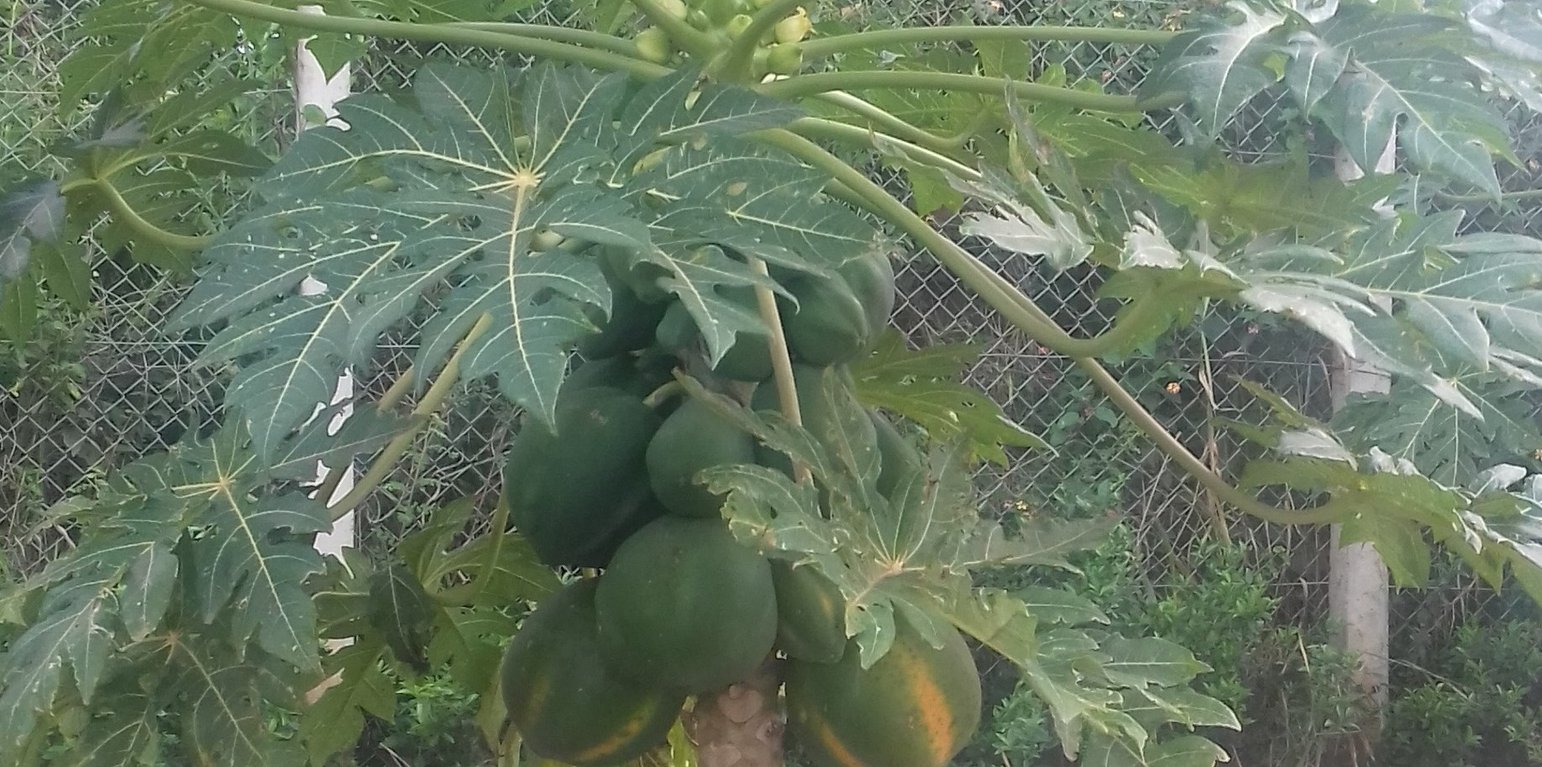




Intensification of pawpaw with mulching. It is the growing of improved pawpaw fruit tree growing for sustainable land management practices and income generation among small scale and medium farmers in Kampala. This is established on 1.5 acres of land. The technology is mostly prefered because it doesn’t require much attention or specialized planting (labour). The cultivation is pest-resistant, and thrives in well-drained soil with an equal balance of sunshine and shade as well as reduction of soil degradation. Under this technology, pawpaws are integrated with trenches with the aim of reducing soil and water erosion for increased production and soil fertility improvement. In Uganda, specifically Kampala District, the technology started in 2012 where the host farmer visited a friend in the neighbouring village, who was growing pawpaw on a commercial scale, and acquired knowledge and skills, inputs and resources needed for establishment.
To get the pawpaw seeds, I got a ripe pawpaw from which I extracted healthy seeds, which I used to make a nursery bed. The pawpaw seeds I got were of the big pawpaw with yellow flesh. I chose this variety because it has a longer shelf life compared to the red flesh variety. In addition, its fruits are big and tasty. and then I dried them in the sun. Got two Units of loam / sandy soil mixed with one basin of cow dung to improve on its drainage and fertility, filled the bags with a mixture of sandy loam manured soil, sown 1 or 2 seeds in each bag and covered with soil, then watered the beds once every day, morning or evening. (description of farmer)
The farmer also covered the bags with thatch grass to keep them warm and moist still they emerge. After one month when the seedlings had germinated he sprayed them with Vegimax, which is an Organic Supplement for all types of plants that helps improve the quality, yield, appearance as well as soil condition and later applied 'Dudu cyper' (insecticide) to kill insects that attack the leaves. When the seedlings were about 10-15 cm tall, they were transplanted onto a well prepared field. A slit was cut into the plastic bag down one side to remove the bag and place the plant into the planting pit. Spacing of plants was approximately 3 metres between rows and 3 metres between plants. Soil was raked in to cover the roots. The plants were then watered to provide moisture needed for proper rooting and growth.
Activities carried out in this technology include: Nursery bed preparation, watering once a day, garden preparation, digging of planting pits, mixing animal manure with soil, transplanting from the nursery bed to the main garden, mulching the garden using banana leaves and grass, spraying the plantations,pruning and harvesting. Proper spacing of trees is important because if they are not well spaced, they will just grow tall and fruiting will be poor. I started with one acre of pawpaw where I had initially 250 pawpaw trees but a density of up to 440 trees is possible.
The technology is good at income generating. Having one acre of the improved pawpaw the farmer can pick five to seven pawpaws every week from each tree and harvest throughout the year so every time the farmer has something to sell to the market. However Paw paws are easily perishable and this affects the market in addition to being affected by weather changes especially when it rains a lot the demand for the fruit becomes very low and when it’s the long dry spells also affect the plantations since the farmer cannot afford to irrigate through the dry season. During long dry periods, pawpaw doesn’t perform well so the harvest is low. Strong wind can cause problems to pawpaw plantations because pawpaw plants have a shallow root system, they get very top heavy as they grow older, and they blow over easily. Then there are birds and fruit bats which affect the plantation. In case of such scenarios its advisable that the farmer keeps in touch with extension worker for advisory services and all the necessary management advice (pest management, watering and marketing).
Lugar: Ttakajjunge village, Namubiru parish, Nama Village Mukono District., Mukono District, Central Region, Uganda
No. de sitios de Tecnología analizados: un solo sitio
Difusión de la Tecnología: distribuida parejamente sobre un área (approx. < 0.1 km2 (10 ha))
Fecha de la implementación: 2016; hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
Tipo de introducción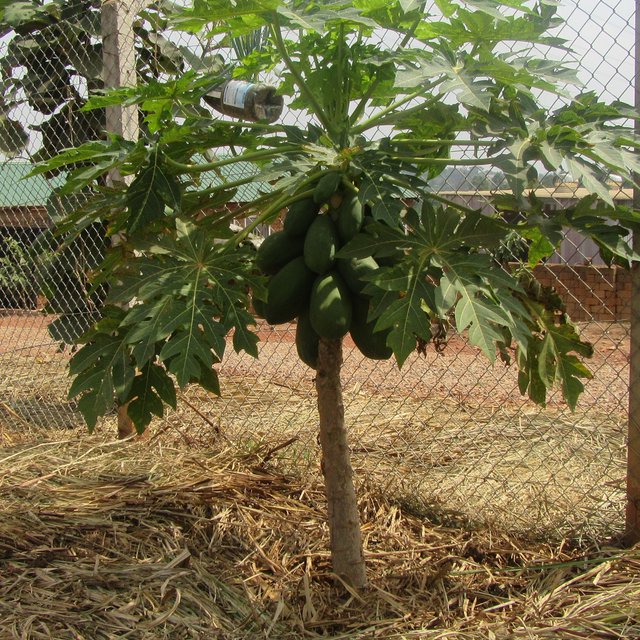








Especificaciones técnicas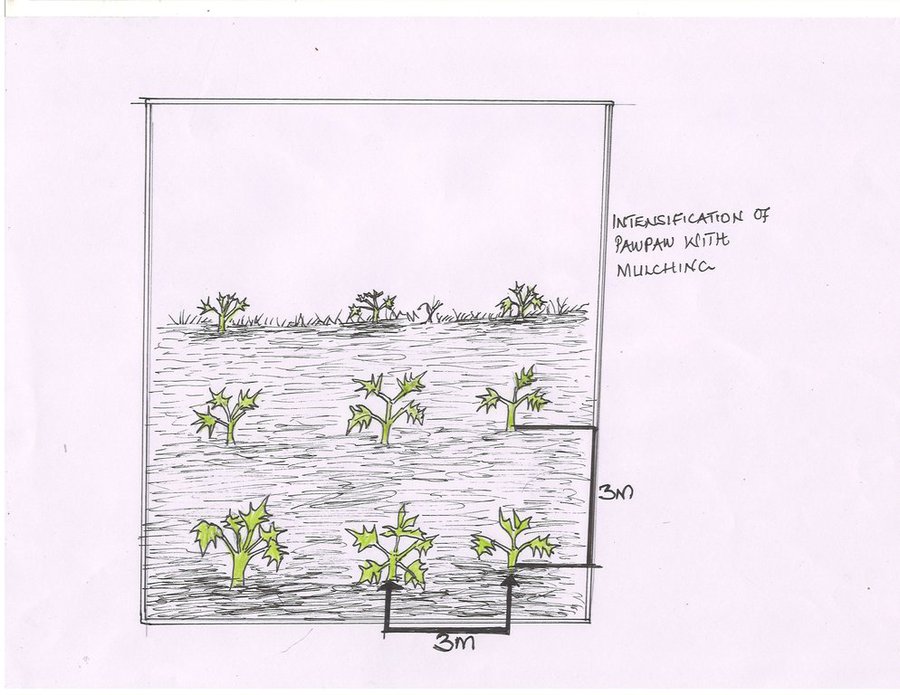
Autor: Prossy Kaheru
The technical drawing shows pawpaw trees planted at a spacing of 3 m x 3 m from one pawpaw to another pawpaw tree. The planting hole is 30 cm deep.
Slope: Gentle sloping |
|||||||||||
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (dólares americanos) | Costos totales por insumo (dólares americanos) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Nursery Preparation | Man days | 2,0 | 2,8 | 5,6 | 100,0 |
| Watering | Man days | 1,0 | 1,39 | 1,39 | 100,0 |
| Garden preparation | Man days | 4,0 | 2,8 | 11,2 | 100,0 |
| Digging pits | Man days | 4,0 | 2,8 | 11,2 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | |||||
| Animal manure and soil mixing | Man days | 2,0 | 1,39 | 2,78 | 100,0 |
| Transplanting | Man days | 5,0 | 2,8 | 14,0 | 100,0 |
| Mulching the garden | Man days | 5,0 | 2,8 | 14,0 | 100,0 |
| Spraying | Man days | 1,0 | 2,8 | 2,8 | 100,0 |
| Hoes | Pieces | 5,0 | 2,8 | 14,0 | 100,0 |
| Wheelbarrows | Pieces | 3,0 | 33,4 | 100,2 | 100,0 |
| Gumboots | Pairs | 5,0 | 3,4 | 17,0 | 100,0 |
| Sprayer pump | Piece | 1,0 | 13,9 | 13,9 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | |||||
| Watering cans | Pieces | 3,0 | 2,8 | 8,4 | 100,0 |
| Seeds | Kilograms | 5,0 | 1,39 | 6,95 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | |||||
| Vegimax, | Litres | 5,0 | 3,4 | 17,0 | 100,0 |
| Dudu cyper | Litres | 3,0 | 2,8 | 8,4 | 100,0 |
| Dythene | Kilograms | 3,0 | 6,94 | 20,82 | 100,0 |
| Animal manure | Trip | 1,0 | 11,2 | 11,2 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 280.84 | ||||
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (dólares americanos) | Costos totales por insumo (dólares americanos) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Spraying | Man day | 1,0 | 2,8 | 2,8 | 100,0 |
| Prunning | Man day | 2,0 | 2,8 | 5,6 | 100,0 |
| Mulching | Man day | 3,0 | 2,8 | 8,4 | 100,0 |
| Animal manure application to the garden | Man day | 2,0 | 2,8 | 5,6 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | |||||
| Harvesting | Man day | 2,0 | 2,8 | 5,6 | 100,0 |
| Hoes | Pieces | 5,0 | 2,8 | 14,0 | 100,0 |
| Sprayer pump | Piece | 1,0 | 2,8 | 2,8 | 100,0 |
| 1,0 | 13,9 | 13,9 | 100,0 | ||
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | |||||
| Vegimax | Litres | 5,0 | 3,4 | 17,0 | 100,0 |
| Dudu cyper | Litres | 3,0 | 2,8 | 8,4 | 100,0 |
| Dythene | Litres | 5,0 | 6,94 | 34,7 | 100,0 |
| Animal manure | Trip | 1,0 | 11,2 | 11,2 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 130.0 | ||||
The income of the farmer increased after the establishment of the technology.
Many institutions like NARO have done research which helped in developing the technology.
We use trenches in the pawpaw garden.
Mulching prevents direct sun on the soil.
The technology is mulched which prevents soil erosion to the neighbor's fields.