Terrace approach
(China)
Descripción
Highly organised campaign to assist land users in creating terraces: support and planning from national down to local level.
Before 1964, the slopes on China's Loess Plateau were cultivated up and down by machinery. Consequently soil and water were lost at high rates, and fertility and yields declined. Accessibility to cultivated land became more and more difficult due to dissection by gullies. The first terraces were established by self-mobilisation of the local land users. However there was no standard design. Furthermore, as the individual plots were very small and scattered all over the village land, terracing needed better coordination. Between 1964 and 1978, the local government at the county level took the initiative of organising farmers and planning terrace implementation according to specific technical design on a larger scale. At that time the land was still communally managed by production brigades. Through mass mobilisation campaigns people from several villages were organised to collectively terrace the land - village by village - covering around 2,000 hectares each year. Labour was unpaid.The Yellow River Conservancy Commission (YRCC) came into being in 1948 - and the Upper and Middle Yellow River Bureau in 1977. This gave greater impetus to the implementation of SWC in the Loess Plateau. After 1978, land use rights were allocated to individuals (though official ownership was still vested in the state). SWC specialists and county level SWC bureaus started to work with groups of farmers who had land use rights within a given area. Survey and design were carried out. The farmers organised themselves, consolidated the parcels of land, and then after the conservation work was done they redistributed the terraced fields.
In the 1980s the government started to financially support land users involved in SWC projects. Subsidies ranged from (approx.) US$* 20/ha in projects at county level, to US$* 55/ha for national projects (eg through the Yellow River Commission), and up to US$* 935/ha when World Bank projects were involved - as in the recent past. Implements were provided by the farmers themselves. Then, in 1988 a nationwide project in SWC - which originally was proposed at county level - was approved by the national government. Furthermore, in 1991 a national law on SWC came into force. Protection of the Yellow River and associated dams became a priority at regional and national levels. In total, within Zhuanglang County, 60 SWC specialists/extensionists cover an area of 1,550 km2, and most of the terraces were built with low levels of subsidies. Annual plans about implementation of new SWC measures were made during summer. Small areas were planned at village or township level, whereas bigger areas (> 7 hectares) were designed at county level. Implementation then took place during winter. Terracing was implemented first where access was easiest and closest to settlements, and only later, further away. * exchange rate: 1 US$ = 8 Chinese Yuan (May 2006).
Lugar
Lugar: Gansu Province, Loess Plateau Region, China
Georreferencia de sitios seleccionados
Dato de inicio: 1964
Año de conclusión: n.d.
Tipo de Enfoque
-
tradicional/ local
-
iniciativa local reciente/ innovadora
-
proyecto/ basado en un programa
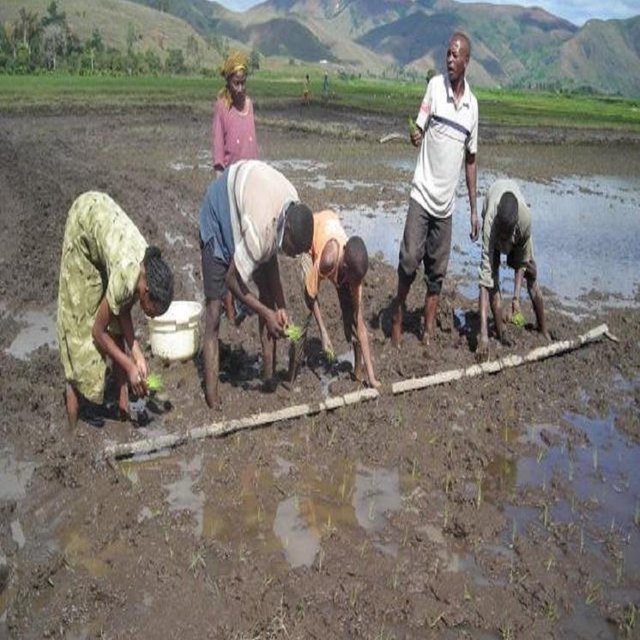

Construction of terrace risers - following instructions given by a specialist.
Metas del Enfoque y entorno facilitador
Propósitos/ objetivos principales del Enfoque
Aims of the approach are: - water conservation (this is a semi-arid area), - soil conservation: reduce soil loss on the sloping and erosion-prone land of loess plateau, - enhancing soil fertility, and consequently production, - improve people's living conditions, These primary objectives were to be achieved by building level bench terraces on a large scale through a structured and organised campaign. Finally at the national level, a fourth aim was added: the protection of the Yellow river (avoiding floods and reducing the sediment load)
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - lack of organisation, capital and technical knowledge in farmer communities to counter the underlying problems of water loss, soil loss, fertility decline and downstream effects on the Yellow River (floods and sediment) at catchment level, - absence or poor maintenance of erosion control measures
Condiciones que facilitan la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
Condiciones que impiden la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
-
Disponibilidad/ acceso a recursos y servicios financieros : Initially farmers were not paid and as they had no immediate benefit from, or security over, the use of the land. The investment in construction was a heavy burden on poor farmers.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: After 1988, labour inputs by farmers started to be partly covered by subsidies provided by local and national government
-
Marco de trabajo legal (tenencia de tierra, derechos de uso de tierra y agua): Land users leased the land from the state and land users??? rights were insecure in the long term. Investments in SWC were not encouraged.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: National government persuaded land users to implement terraces by 'selling' the benefits (increased yield and easier workability of the land). After 1978, individual user rights motivated farmers to invest in SWC.
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights hindered a little the approach implementation Ownership of land and its resources belongs to state and communities: land users only lease the land for a period of time. Due to uncertainty over future user rights and possible reallocation in response to changes in population and household needs, additional investments into measures may be hindered. 1978 a first major change took place by allocating some individual land use rights.
-
Conocimiento de MST, acceso a apoyo técnico: Poor knowledge of how to reduce water loss, soil loss and fertility loss. Technical solutions were needed at the catchment level, involving the whole population.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Enhanced guidance by SWC specialists.
Participación y roles de las partes interesadas involucradas
Partes interesadas involucradas en el Enfoque y sus roles
| ¿Qué partes interesadas/ entidades implementadoras estuvieron involucradas en el Enfoque? |
Especifique las partes interesadas |
Describa los roles de las partes interesadas |
| usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales |
|
|
| gobierno nacional (planificadores, autoridades) |
|
|
Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales en las distintas fases del Enfoque
ninguno
pasivo
apoyo externo
interactivo
auto-movilización
iniciación/ motivación
Land users started implementing terraces but SWC specialists at the country level assisted in designing standards for terrace construction and township governments and production brigades organised whole villages and watersheds
planificación
Being consulted in the planning phase. Experienced peasants may be involved in introducing the local situation.
implementación
Major organisation done through the SWC bureau specialists with the village organisation including land users. Land users were actively involved in implementation.
monitoreo y evaluación
reporting; No participation of land users
Research
on-station; No participation of land users
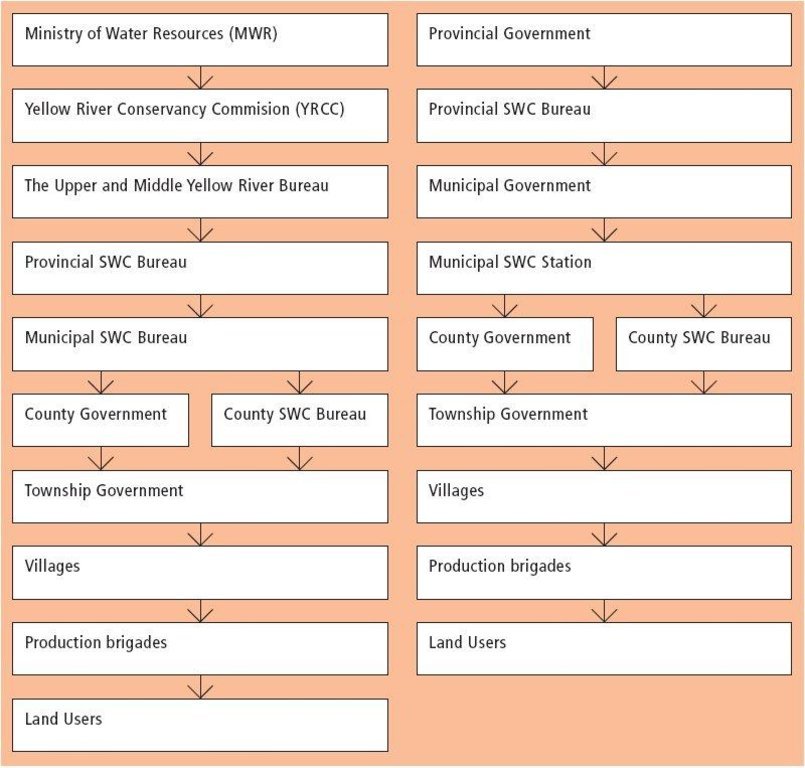
Flujograma
Terrace construction supported by projects from MWR, YRCC and international organisations (left) and terrace construction supported by provincial funds (right).
La toma de decisiones en la selección de Tecnología MST
Las decisiones fueron tomadas por
-
solamente usuarios de tierras (autoiniciativa)
-
principalmente usuarios de tierras con el apoyo de especialistas MST
-
todos los actores relevantes, como parte de un enfoque participativo
-
principalmente por especialistas MST en consulta con usuarios de tierras
-
solo por especialistas MST
-
por políticos/ líderes
La toma de decisiones se basa en
-
la evaluación de conocimiento MST bien documentado (la toma de decisiones se basa en evidencia)
-
hallazgos de investigaciones
-
la experiencia personal y opiniones (no documentadas)
Apoyo técnico, fortalecimiento institucional y gestión del conocimiento
Las siguientes actividades o servicios fueron parte del enfoque
-
Construcción de capacidades / capacitación
-
Servicio de asesoría
-
Fortalecimiento institucional (desarrollo institucional)
-
Monitoreo y evaluación
-
Investigación
Construcción de capacidades/ capacitación
Se proporcionó capacitación a las siguientes partes interesadas
-
usuarios de tierras
-
personal de campo/ consejeros
Forma de capacitación
-
en el contexto de trabajo
-
de agricultor a agricultor
-
áreas de demostración
-
reuniones públicas
-
cursos
Temas avanzados
Until 1978 the 'pyramid system' was used: the county level trained the township level, which trained the village level, which in turn trained the production brigades/farmers, who then trained other production brigades and farmers.
Servicio de asesoría
Se proporcionó servicio de asesoría
-
en los campos de los usuarios de tierras
-
en centros permanentes
Key elements: Pyramid system is also used for extension. At each government level (county, district and provincial levels) there is a SWC division in charge of SWC activities includ. extension (farm visits)
Fortalecimiento institucional
Se fortalecieron/ establecieron instituciones
-
no
-
sí, un poco
-
sí, moderadamente
-
sí, mucho
Describa la institución, los roles y las responsabilidades, miembros, etc.
Tipo de apoyo
-
financiero
-
construcción de capacidades/ entrenamiento
-
equipo
Detalles adicionales
Monitoreo y evaluación
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: runoff loss, sediment load, soil moisture
technical aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: structure of terraced areas, slope of risers, levelness of terrace surface
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: land users' perceptions of terraces
economic / production aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: yield, income of land users
area treated aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: terraced area
land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements; indicators: number of farmers directly involved in terracing and farmers benefited directly
management of Approach aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: number of small watersheds terraced
There were changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The approach changed fundamentally from self-mobilisation to organised mass movements guided by the government.
Investigación
La investigación trató los siguientes temas
-
sociología
-
economía/ marketing
-
ecología
-
tecnología
carried out at the provincial and national levels, mostly by technical staff. Land users have not been involved. Terrace building is based on scientific design, according to local conditions.
Research was carried out on station
Financiamiento y apoyo material externo
Presupuesto anual en dólares americanos para el componente MST
-
< 2,000
-
2,000-10,000
-
10,000-100,000
-
100,000-1,000,000
-
> 1,000,000
Precise annual budget: n.d.
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (national): 10.0%; local community / land user(s) (-): 90.0%
Los siguientes servicios o incentivos fueron proporcionados a los usuarios de las tierras
-
Apoyo financiero/material proporcionado a los usuarios de tierras
-
Subsidios para insumos específicos
-
Crédito
-
Otros incentivos o instrumentos
Crédito
-
Condiciones: Interest rate charged: 0.5%; repayment conditions: Credit was available at interest rates (0.5-1% per year) lower than the market rates.
-
Proveedores de crédito: n.d.
-
Destinatarios del crédito: n.d.
Análisis de impacto y comentarios de conclusión
Impactos del Enfoque
No
Sí, un poco
Sí, moderadamente
Sí, mucho
¿El Enfoque ayudó a los usuarios de tierras a implementar y mantener Tecnologías MST?
Soil and water management have improved a lot: easier workability, intensified land use, in-situ water retention, top soil and fertilizer/manure are not washed away, etc.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
As the Zhuanglang area was one of the pioneering areas for the Loess Plateau other regions were able to profit from the approach. But likewise, experiences gained in other counties helped improve the approach, and a basically similar approach has been applied over the whole Loess Plateau - though the level of subsidies for construction is much higher under World Bank projects.
Motivación principal del usuario de la tierra para implementar MST
Sostenibilidad de las actividades del Enfoque
¿Pueden los usuarios de tierras sostener lo que se implementó mediante el Enfoque (sin apoyo externo)?
Conclusiones y lecciones aprendidas
Fortalezas: perspectiva del usuario de tierras
Fortalezas: punto de vista del compilador o de otra persona recurso clave
-
Farmers are getting direct benefits: marked increase in productivity, improved workability of the land, etc.
-
The collective activities/organisation strengthens the community and enhances social stability and coherence within villages; collective activities are expanded to other sectors, such as road construction, supply of agrochemical inputs, etc.
-
Heavy investment made by the land users and local as well as national government to reduce land degradation.
-
Many people involved and trained at different levels (pyramid system; see training/extension); commitment by all stakeholders.
-
Efficient organisation, planning to cover a large area, which is very susceptible to land degradation.
Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos: perspectiva del usuario de tierrascómo sobreponerse
Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos: punto de vista del compilador o de otra persona recurso clavecómo sobreponerse
-
High costs: farmers depend on external support from the government, they are not willing to invest their labour without payments (as it used to be in communist times)
New approach: give farmers loans for construction as now they use machines to do the work. In addition, search for cheaper SWC technologies and for improving the benefits.
-
The steeper slopes which are also further away from the village, are now often not cultivated and maintained as they are too far and marginal in production
Solutions need to be found for these areas, eg afforestation.
Referencias
Revisado por
-
Laura Ebneter
-
Deborah Niggli
-
Joana Eichenberger
Fecha de la implementación: 28 de enero de 2009
Últimas actualización: 3 de enero de 2019
Personas de referencia
-
Meili WEN (baoyuan@bnu.edu.cn) - Especialista MST
-
Zhanguo Bai (zhanguo.bai@wur.nl) - Especialista MST
-
Yaolin Wang (yaolingw@gsdcri.com) - Usuario de la tierra
-
Zhanguo Bai (zhanguo.bai@wur.nl) - Especialista MST
-
Baoyuan Liu (baoyuan@bnu.edu.cn0) - Especialista MST
Descripción completa en la base de datos de WOCAT
La documentación fue facilitada por
Institución
- Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University (Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University) - China
- GEF/OP12 Gansu Project (GEF/OP12 Gansu Project) - China
- ISRIC World Soil Information (ISRIC World Soil Information) - Países Bajos
Proyecto
- Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)
Referencias claves
-
Jiangdingsheng, ACTA CONSERVATIONIS SOLI ET AQUAE SINICA, 1987. Discussion on section design of the terrace on the Loess Plateau; Vol. 1, No. 2,:
-
Corpus of economic benefits of water and soil measures, p77-102, 510-514: Water and Soil Conservation Department of Yellow River Water Resources Committee of Ministry of Wate
-
Corpus of Test Research of Water and Soil Conservation, p130-185 (the second volume): Suide Water and Soil Conservation examination station