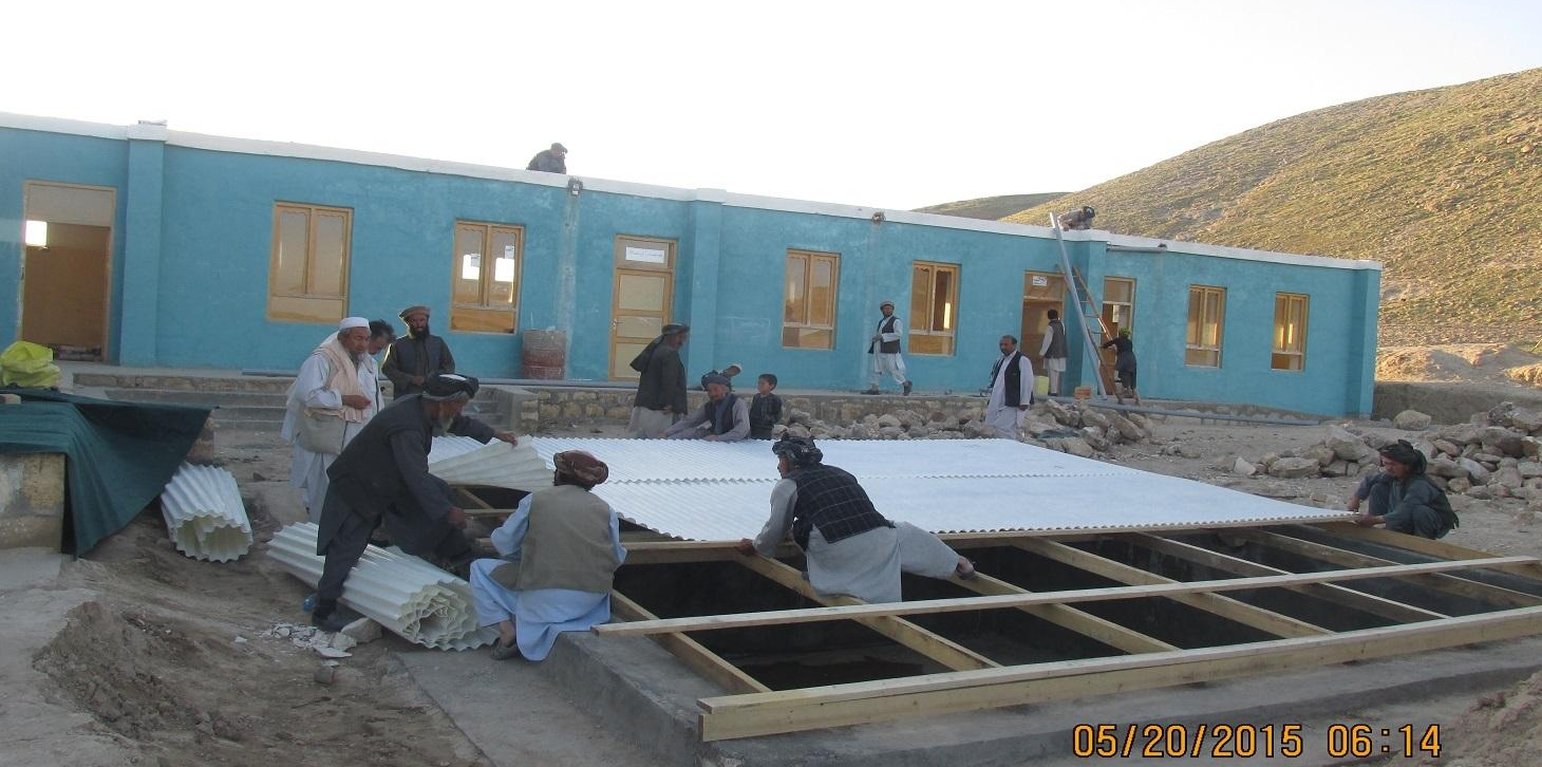




Kishendeh district is extremely mountainous with low precipitation and with a shortage of water storage facilities. Underground reservoirs, called kandas, traditionally serve as water storage, catching rain water over the two/three wet months of the year for use throughout the rest of the year. The kandas tend to run out of water before the next rains come, and tend to be positioned very far away from villages in difficult to reach spots. Alika village, where this technology is implemented, suffers from the scarcity and unavailability of irrigation, livestock and even safe drinking water. Scarcity of water during the summer season makes the lives of the community members more difficult and results in their immigration from the village in the past.
Purpose of the Technology: To ease water shortage in the target community, in addition to the introduction of drought-resistant crops and soil and water conservation techniques, People in Need (PIN) has applied roof rain water harvesting technology in Alika elementary school, Alika village, Chakana cluster. The site where this technology has been applied belongs to the state. The water use right is common and poor families that do not have access to kandas are given priority for using this reservoir. The school and households near the school use this water for drinking and washing.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The project started in October, 2014 and was completed in April, 2015. For the establishment of the roof rain water harvesting technology the following inputs were used:
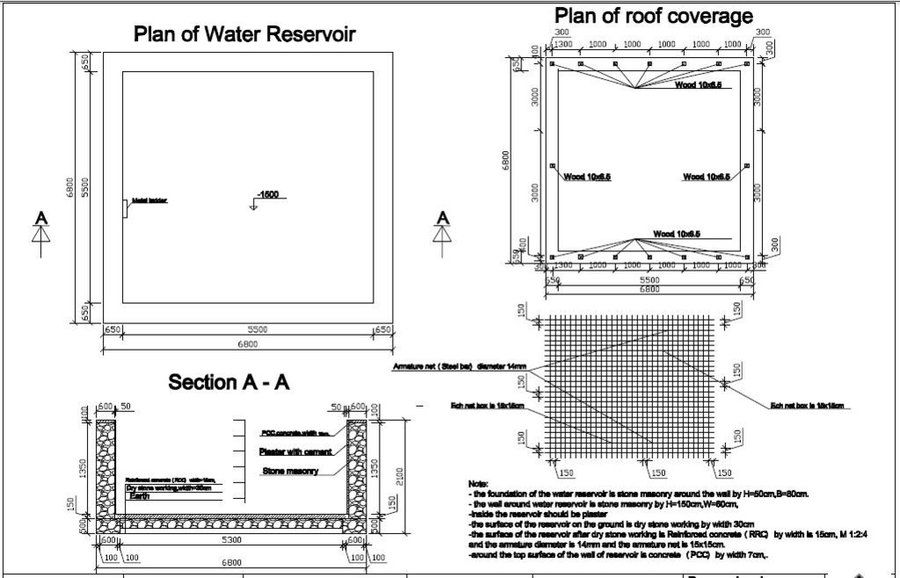
360 square meter tin was used to cover the roof. The pipe system is 45 meters in total. Three inch PVC pipes as well as elbows and T-joints were used. The water reservoir’s dimension of 0.80x0.50 m stone masonry foundation and 0.60x1.50x24.4 m wall; The dry stone masonry is 30cm wide; the surface of the reservoir, reinforced concrete (RCC) is 15cm wide. The reservoir was plastered with water proofing. The roof of the reservoir was constructed using wooden sketch covered with hard plastic material.
141 person/day were required for accomplishing this project. The establishment cost was 5,296$. The total value of community contribution is 7,500 Afghani/145 US$. Excavation by community members of a 50 m3 area is valued at 20,000 Afghani/385 US$. Thus the total community contribution is 10% of the total costs.
The head master of the school assumes the responsibility for maintenance. The reservoir needs to be cleaned five times a year, this is a low cost exercise. In the rainfall season it needs to be done once a month. Cleaning can be done by one person. The estimated cost for the maintenance is 500 Afghani or 10 US$ and is fully contributed by the community members.
Natural / human environment: Balkh province has a semi-arid climate and receives about 280 mm rainfall per year. The main economic activities are agriculture and livestock. The community members of the Kishendeh district have a low access to health services, employment, roads and transport and to drinking water and sanitation. Lack and scarcity of water in this village has caused many internal displacements as well.
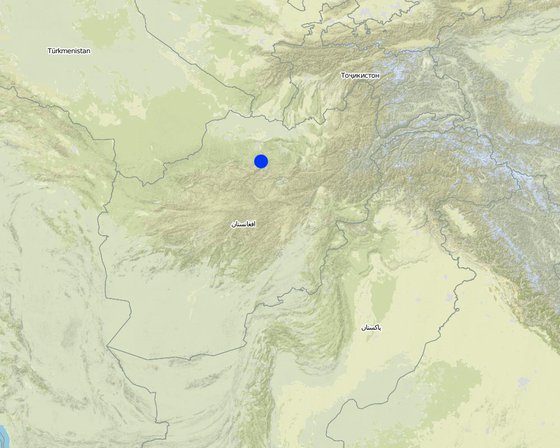
Lugar: Kishendeh, Balkh, Afganistán
No. de sitios de Tecnología analizados:
Difusión de la Tecnología: distribuida parejamente sobre un área (0.00105 km²)
¿En un área de protección permanente?:
Fecha de la implementación: hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
Tipo de introducción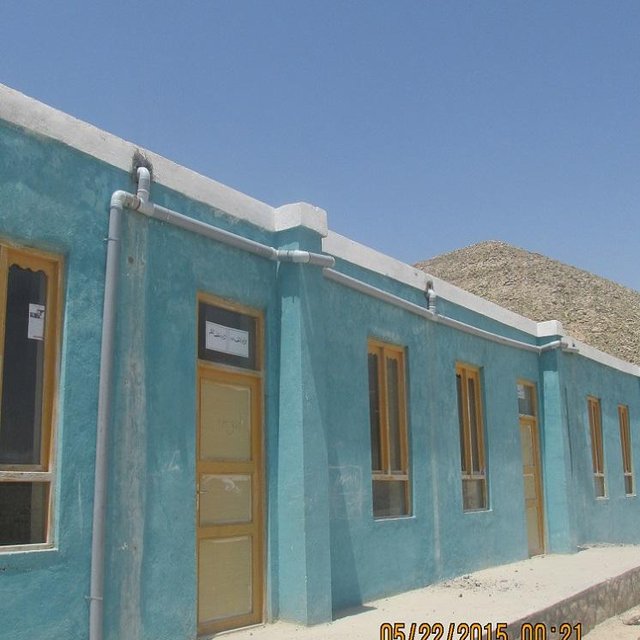




| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (USD) | Costos totales por insumo (USD) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Excavation of the foundation Construction of the reservoir | persons/day | 141,0 | 5,0 | 705,0 | 10,0 |
| Equipo | |||||
| Tools and pipes | ha | 1,0 | 344,0 | 344,0 | |
| Material de construcción | |||||
| Cement | bags | 1,0 | 376,0 | 376,0 | |
| Stone | m3 | 159,575 | 24,25818 | 3871,0 | 10,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 5'296.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 5'296.0 | ||||
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (USD) | Costos totales por insumo (USD) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Cleaning of the reservoir | persons/day | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 50.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 50.0 | ||||
It has provided the access to drinking water for human beings and livestock. As well as it provides irrigation water to kitchen gardens for the HHs who lives near by the Alika Elementary School.