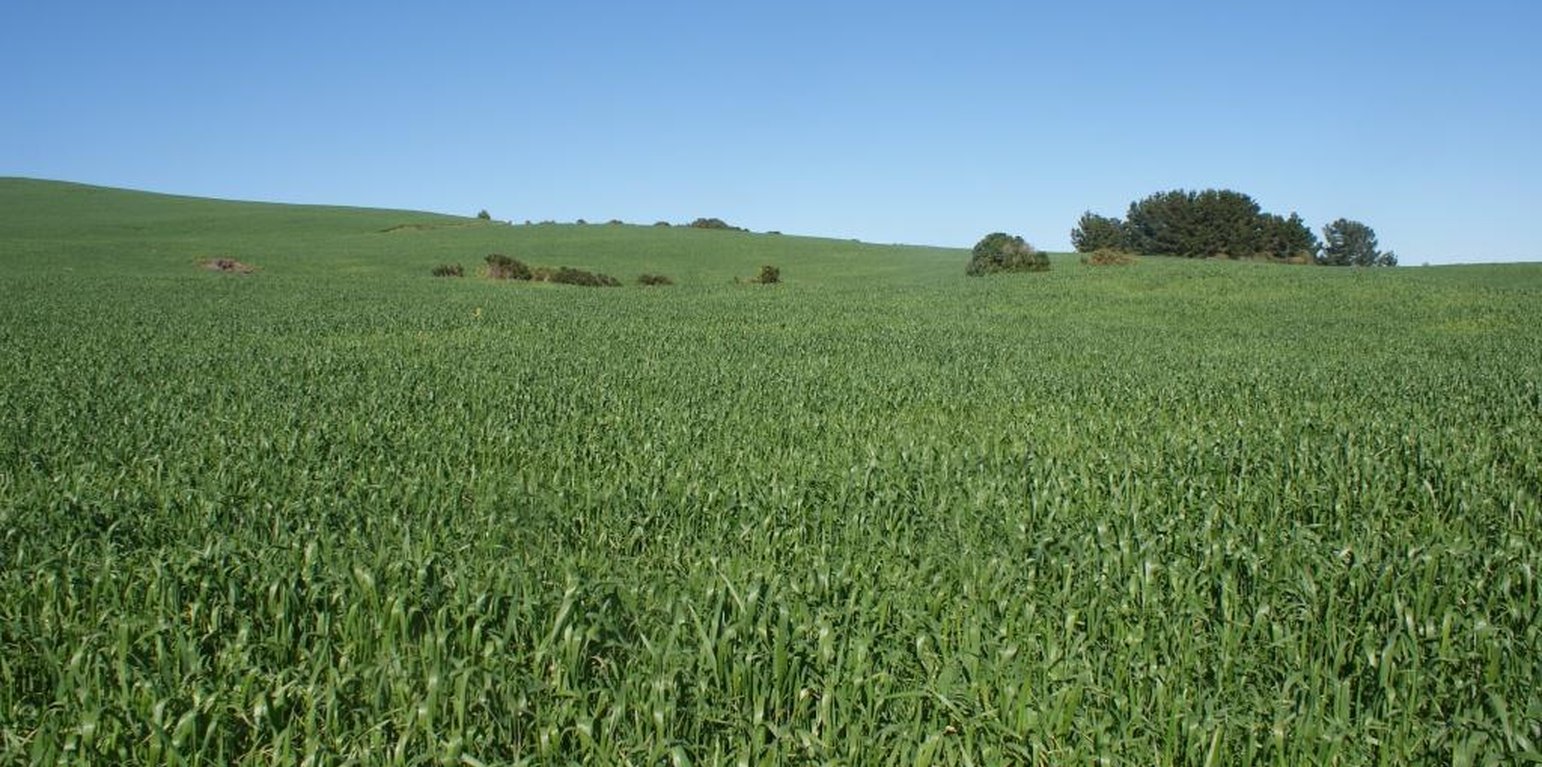




In the “secano interior” of the Mediterranean climate area of central Chile, water erosion and inappropriate agricultural systems along hillslopes are the major causes of soil degradation.
Subsoil tillage is performed with a three-pointed 50-cm chisel plough (see photo), without turning the soil. Subsoiling is needed every five years to break the hard pan after soil compaction. Then crops are directly seeded without any tillage and with stubble left on the field.
Purpose of the Technology: Subsoiling before zero tillage agriculture mitigates water erosion compared to the traditional tillage. In heavy rainfall events, zero tillage reduced soil loss by more than 72% compared to conventional tillage. In addition, the runoff coefficient during the rainy period was 70% lower with zero tillage These results show the importance of conservation tillage and crop stubble management for decreasing erosion, especially in years when extreme rainfall events lead to a high potential for soil erosion. In relation to soil compaction, comparing the resistance to penetration in the soil profile, the traditional tillage system showed a strongly compacted layer at a depth of 10 cm (>1300 kPa), which increased to over 2000 kPa at depths of 15-20 cm. In contrast, no tillage preceded by subsoiling showed less compaction, beyond 20 cm below the threshold of 2000 kPa, defined by several authors as the critical threshold for radicular growth. Moreover, cereal production showed higher biomass and grain yield. It is concluded that subsoiling before no tillage agriculture with stubble retained on the surface was the best option to mitigate soil erosion.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The main disadvantage of the system is that the farmer requires more capital to lease machinery, which in the traditional system is done with animal traction, and the horses or oxen are from their own property. However, the improved yield covers the machinery lease costs. Additionally, the system pushes small farmers into co-operatives, because it is not possible for everyone to own the equipment. To resolve this problem the project promoted the creation of small enterprises (of 10 people) to jointly purchase no-tillage machinery.
Natural / human environment: The area has a subhumid Mediterranean climate with an average annual precipitation of 695 mm (80% concentrated in winter), with five months of drought. Soils are Alfisols of the Cauquenes type, classified as Ultic Palexeralfs. The soil is made up of materials of granite origin with moderate acidic conditions and low organic carbon. Soil clay content is 15% between 0 and 18 cm depth, below this depth it is higher than 44%. Topography is a hillside with 10 to 20 % slope and the main traditional crop rotation is oat-wheat or wheat-natural pasture.
Lugar: Cauquenes, Bíobio and Maule region, Chile
No. de sitios de Tecnología analizados:
Difusión de la Tecnología: distribuida parejamente sobre un área (10.0 km²)
¿En un área de protección permanente?:
Fecha de la implementación: hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
Tipo de introducción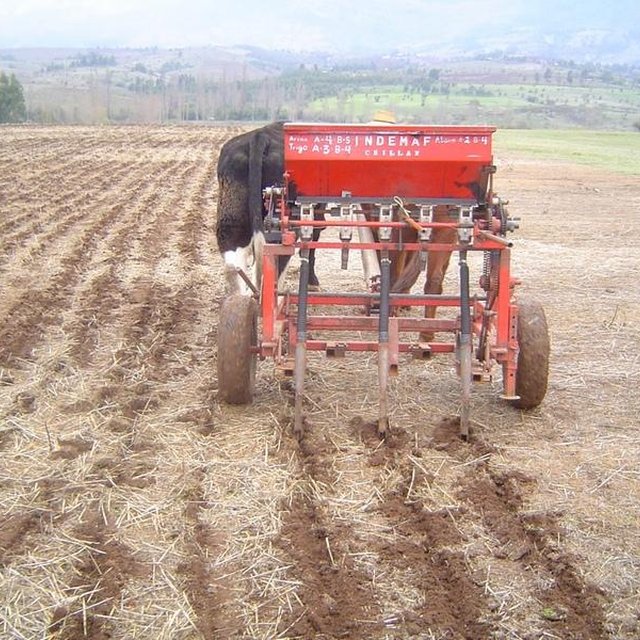





| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (USD) | Costos totales por insumo (USD) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Subsoiling | unit | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | |||||
| Renting seeder machine | unit | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | |
| Renting subsoiling machine | unit | 1,0 | 70,0 | 70,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 180.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 180.0 | ||||
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (USD) | Costos totales por insumo (USD) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Herbicide application | unit | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | |
| Equipo | |||||
| Renting seeder machine | unit | 1,0 | 60,0 | 60,0 | |
| Material para plantas | |||||
| Seeds | unit | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | |||||
| Fertilizer | unit | 1,0 | 174,0 | 174,0 | |
| Herbicide | unit | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 324.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 324.0 | ||||
mproved tillage improves crop yields and thus household income increases