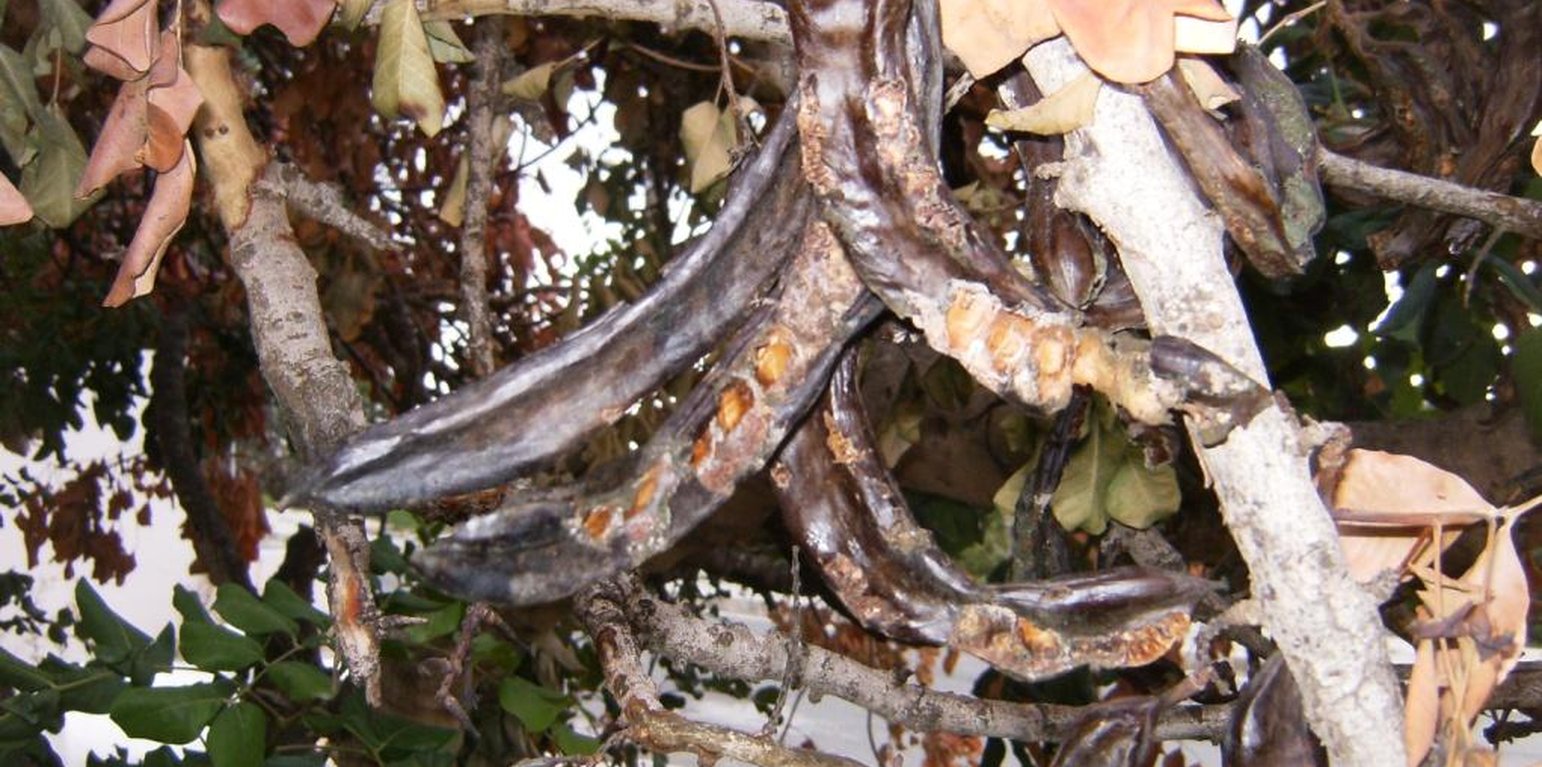




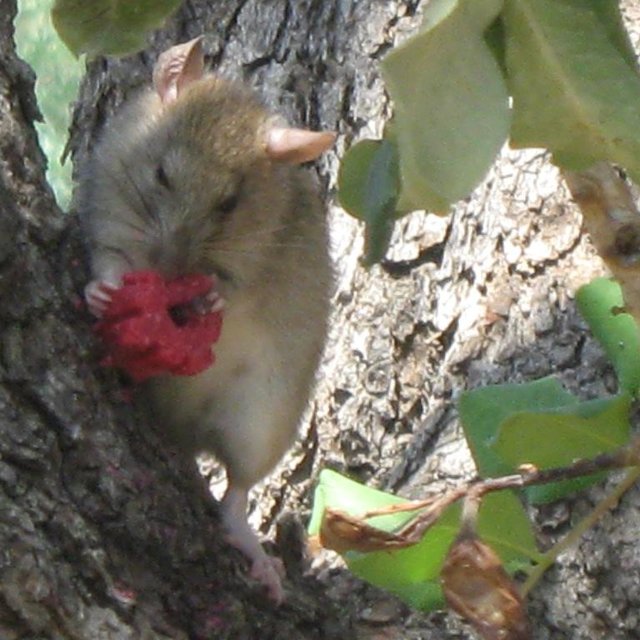
Carob trees are attacked every year by rats who nibble the trunk stem of the tree, remove the bark of the trunk and the branches sucking the juice and eat the mature fruits. Rats nibble the bark of the tree in order to reduce their teeth size which tends to enlarge year by year. This results in the death of the tree branch or even of the entire tree. The tree may also show symptoms of hemiplegia. Rats run on the tree through the trunk. Apart from the direct effect of rat attacks on carob trees, rats also cause other problems to humans and animals. Rats are vectors for serious pest and diseases
Purpose of the Technology: The rat population increases rapidly when there is enough food (such as carobs) available, and the population grows even faster in the absence of natural enemies. . Through interrupting the access from the ground to the tree trunk, or by pruning the branches which are connected to the ground, the rats are hindered from climbing the trees. Rats can also be controlled through the use of chemical baits. However, these baits should only be used by experts who know where and how to place them in order to avoid that other animals come in contact with the baits. Natural enemies such as cats, snakes and birds (e.g. Bam owl (Tyto alba)) should be breeded and established on the carob trees, and farmers, hunters and locals should be informed not to kill the natural enemies of rats.
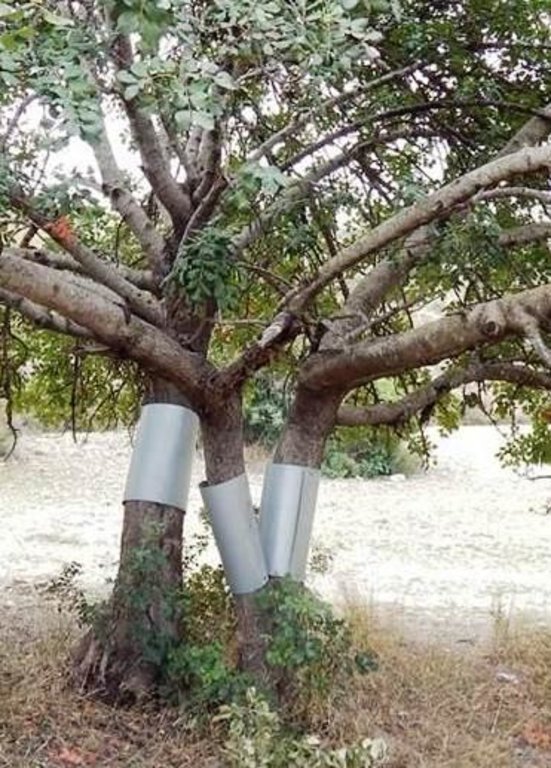
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The carob trees can be protected from rats by covering the tree neck and trunk from the ground up to 1 meter with a hard material such as aluminium with a slippery surface. This way the rats are not able to climb the trees since they will slither on the ring layer.
Natural / human environment: The carob tree protection will increase the production of carobs and therefore the income of the growers. Already established carob trees could provide a good income to growers with low production cost. The population of rats will decrease since the major source of food will not be provided anymore. Educating farmers, hunters and the local population about the benefits of natural enemies will allow that the environment regulates the rat population by itself.
Lugar: Pissouri, Limassol, Chipre
No. de sitios de Tecnología analizados:
Difusión de la Tecnología: distribuida parejamente sobre un área (50.0 km²)
¿En un área de protección permanente?:
Fecha de la implementación: 10-50 años atrás
Tipo de introducción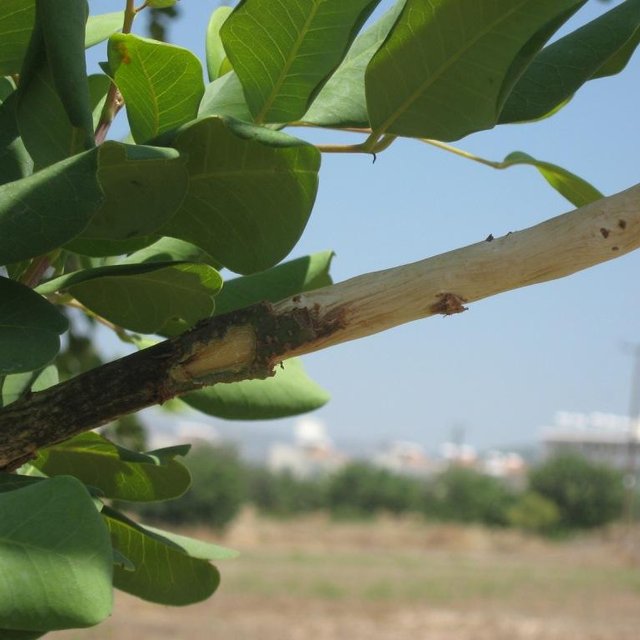







| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (euro) | Costos totales por insumo (euro) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1,0 | 265,0 | 265,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | |||||
| Tools | ha | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | |||||
| Aluminium layer | ha | 1,0 | 1116,0 | 1116,0 | 100,0 |
| Iron nails | ha | 1,0 | 11,0 | 11,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 1'393.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 1'530.77 | ||||
Cantidad antes de MST: 35 Kg/tree
Cantidad luego de MST: 45-50Kg/tree
Trunk and branch protection lead to yield increase
Although other factor like fire, frost, pests and diseases can cause production failure, rat attack is considered as the most damageable
Cantidad antes de MST: 1,5 euro/tree
Cantidad luego de MST: 1 euro/tree
During pruning, large dead branches should be removed
Cantidad antes de MST: 50 trees/day
Cantidad luego de MST: 65 trees/day
During pruning,
Carob fruits are free from infectious diseases transferred by rats
Reduction of rat populations within the production area minimizes the risk of man diseases infection like typhos,
The technology improved both livelihoods and human health. The growers income has increased more than 10-20% due to the reduction of the damage caused by rats every year. The reduction of the number of rats minimized the risk of human pathogens such as typhus which was very common in these areas.
Increase of predators in the areas around the carob trees since rats can not climb on carob trees
Fields with carob trees being attacked by rats are more sensitive to fires since they are abandoned by their owners
On small trees the aluminium layer is pressing the trunk in a way the tree can not grow normally. In this case the aluminium layer must be replaced with a layer once every few years
rat population around the SLM technology is decreased therefore the damage caused by rats to the neighbours is also decreased
Decrease in rat population rear farms also decrease the damage caused on the farm infrastructure (wires, wood, plastic equipment), by rats