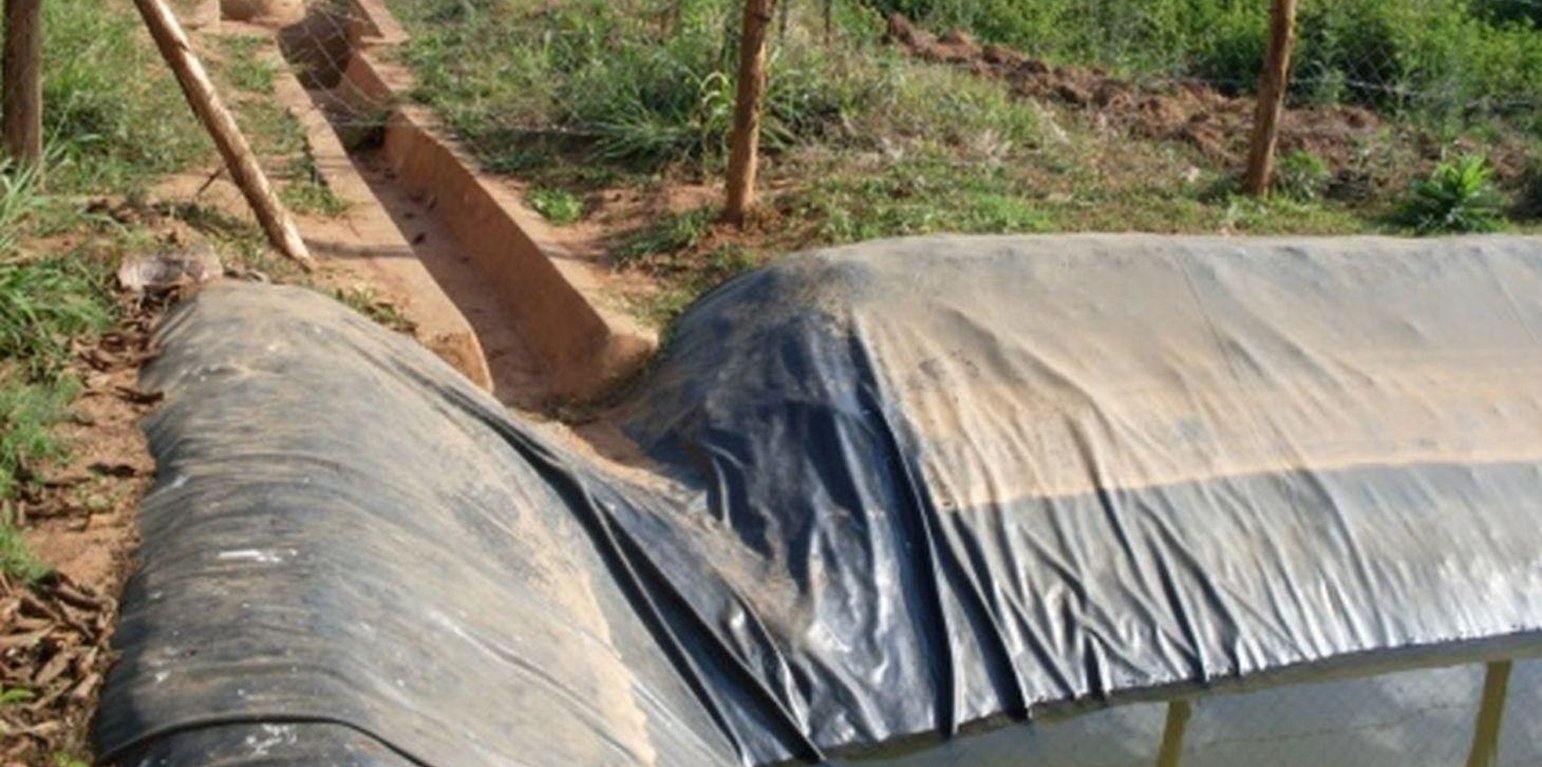




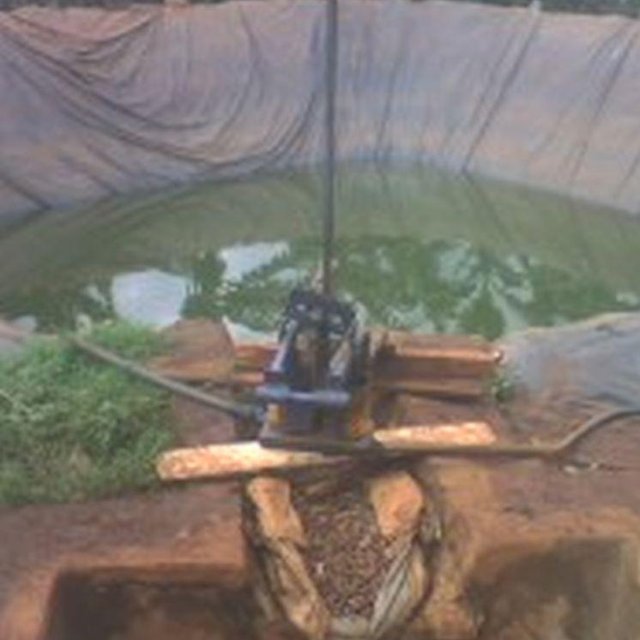
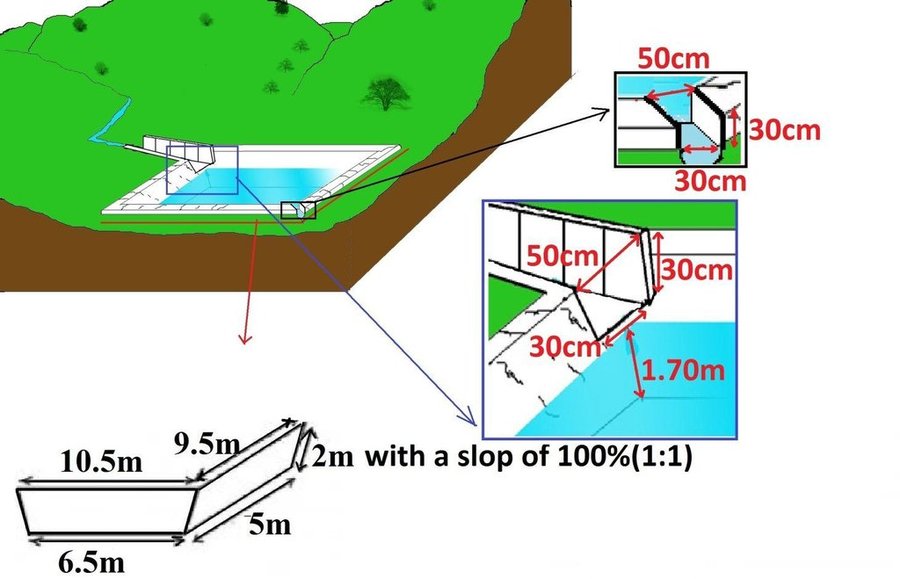
Rainwater harvesting initiatives were introduced in Rwanda in 2007, through a government-supported project on a pilot basis in three districts (Ruhango, Bugesera and Kirehe). By 2011, the technology had expanded at exponential rates such that the demand has exceeded the supply. Now the supply policy has shifted from government to private still there is a shortage of plastic lining. The typical design of each pond is trapezoidal in shape, measuring 10.5 by 9 meters top-width, 6.5 by 5 meters bottom width and 2 meters depth and a total storage volume about 120 m3. The plastic lining is factory–manufactured with standard shape and size to fit these dimensions. The ponds are made with this standard design to enable bulk purchase and supply of geo-membranes, to make use of economies of scale. The cost of the geo-membranes was subsidized by up to 100% by the government until 2010 but now only 20% are provided by the government. When this project was initiated, activities related to soil excavation was done by the government. However, with time the government pulled out and farmers are now covering the total cost of excavation and the government intervenes only for the technical compliance. The government provides technicians to train farmers on the safety and management of ponds. The volume of water harvested and stored in the ponds is on average 90 m3. However, water retention within the ponds over time differs with from farm to farm as affected by usage, evaporation and seepage losses. Treadle pumps are sometimes used to lift water by some of the farmers. Among most households, the water from the pond is used for domestic, livestock and supplemental irrigation, especially of horticultural crops. About 20% of the water is used for seedling and fruit production, 75% for livestock watering and 5% for domestic use. When the excavation of the pond is complete, the beds as well as sides of the pond have to be leveled and prepared for laying the lining plastic. Any rocks, large stones or other projections, which might damage the lining plastic, should be removed from the beds and sides of the excavated ponds.
Purpose of the Technology: Lining geomembrane plastic for water storage is designed to reduce seepage losses in ponds. This water is used by smallholder farmers to cope with the beginning of dry season and enhance crops to reach the maturity stage safely.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A periodical inspection is required for better life of the pond, thus timely maintenance hold the key of success for longer time. The maintenance includes inspection, repairing damages. Regular investigations are required on the pond sides, bottom, the inlet and the emergency outlet. In addition, the pond should be protected from intrusion of animals by constructing a fence around the pond. It is also important to remove aquatic vegetation, silt and sediment periodically that accumulate on the bottom of the pond.
Lugar: Kayonza District (East provice), Rwanda, Ruanda
No. de sitios de Tecnología analizados:
Difusión de la Tecnología: distribuida parejamente sobre un área (approx. < 0.1 km2 (10 ha))
¿En un área de protección permanente?:
Fecha de la implementación: hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
Tipo de introducción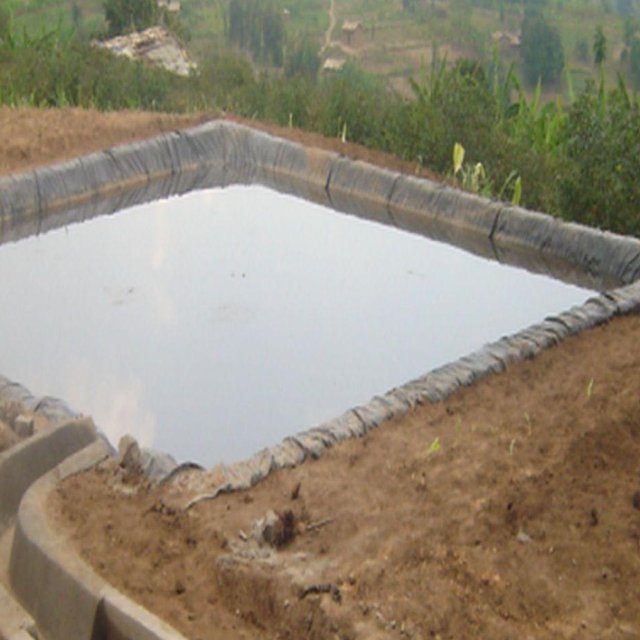





| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (Rwandan francs) | Costos totales por insumo (Rwandan francs) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Surveying | persons/day/ha | 4,0 | 45000,0 | 180000,0 | |
| Construction of pond | persons/day/ha | 180,0 | 1000,0 | 180000,0 | 80,0 |
| Equipo | |||||
| Tools | pieces/ha | 100,0 | 3000,0 | 300000,0 | 20,0 |
| Material de construcción | |||||
| Cements | kg | 300,0 | 200,0 | 60000,0 | |
| Plastic sheet | m2 | 24,0 | 2500,0 | 60000,0 | |
| Stone | m3 | 8,0 | 562,5 | 4500,0 | |
| Sand | m3 | 8,0 | 390,625 | 3125,0 | |
| Fencing wire | m2 | 24,0 | 625,0 | 15000,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 802'625.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 1'254.1 | ||||
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (Rwandan francs) | Costos totales por insumo (Rwandan francs) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Regular maintenance | persons/day/ha | 10,0 | 1000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 10'000.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 15.63 | ||||
Cantidad antes de MST: 200 kg
Cantidad luego de MST: 800 kg
Cantidad antes de MST: 50%
Cantidad luego de MST: 10%
Cantidad antes de MST: 40%
Cantidad luego de MST: 80%
40% of income increases due to increase of agriculture
The technology improved the productivity so that farmers had means to take health insurance
Increases up to 15%
It has increased income of household hence enhance life.
60% improved
Cantidad antes de MST: 20%
Cantidad luego de MST: 50%
It increases the predominance of mosquito