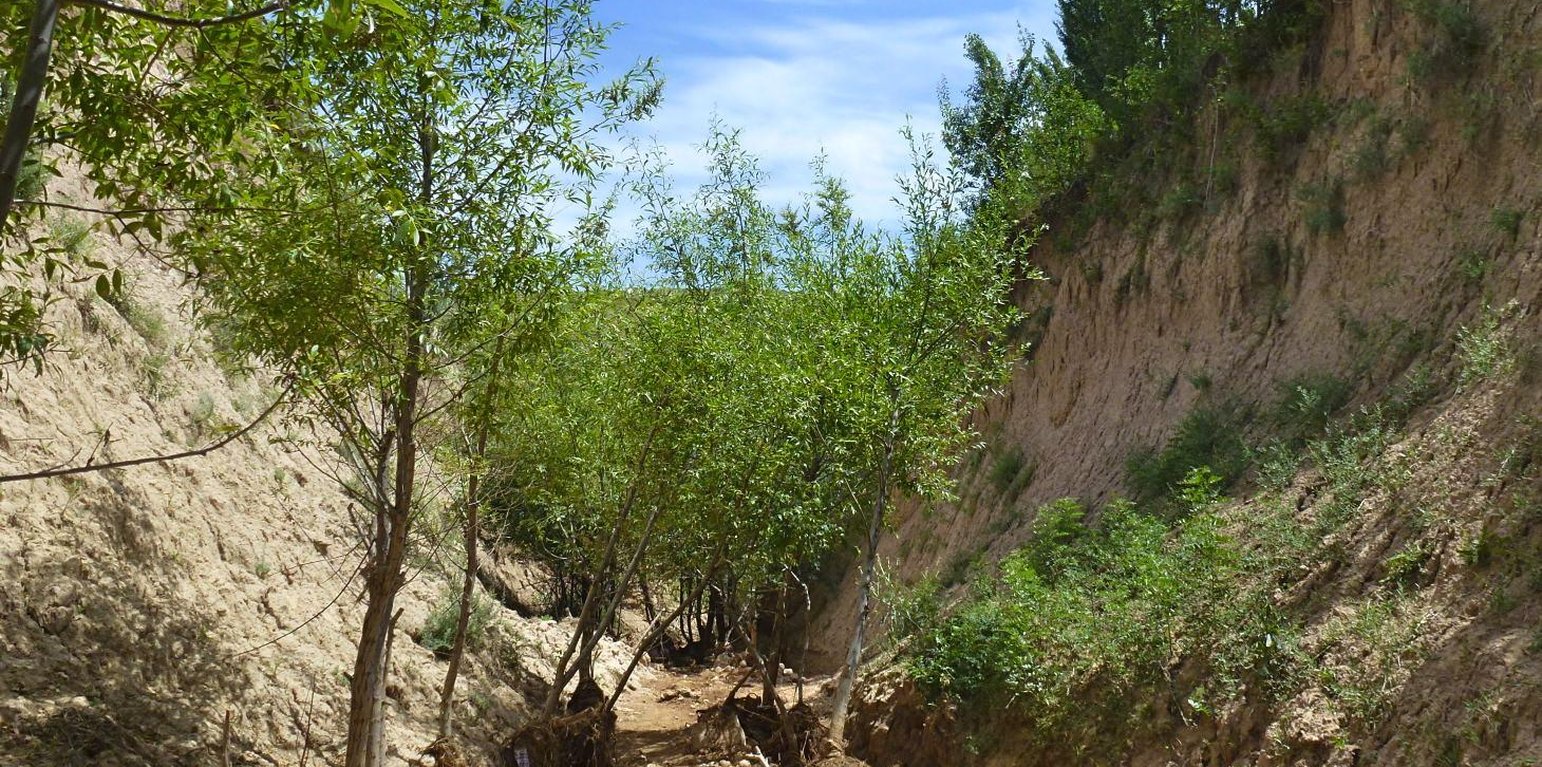




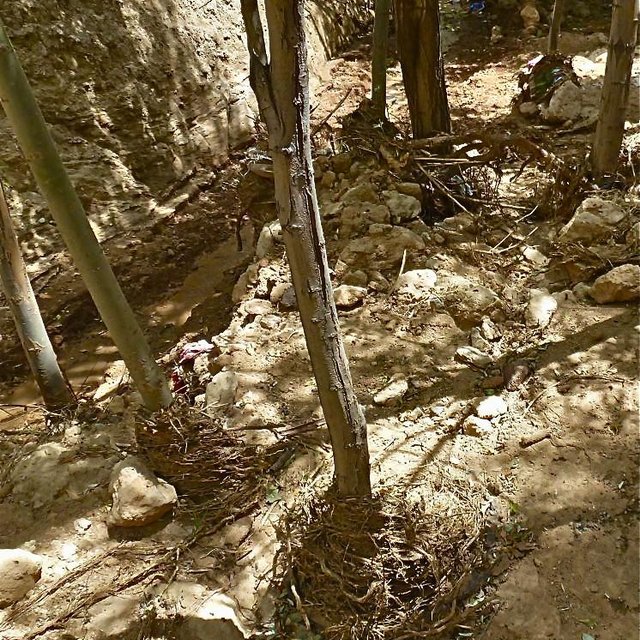
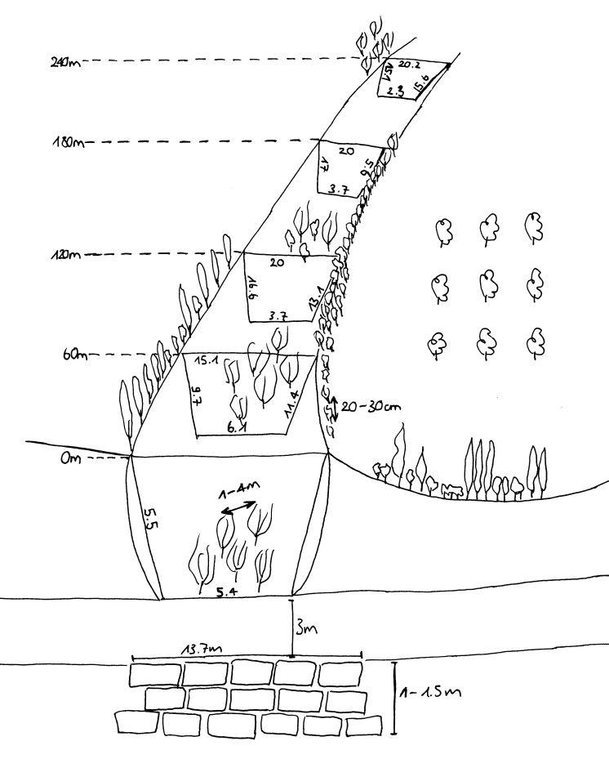
The extension of a deep incised gully, which borders a fertile orchard, is stopped and sediments are trapped by the help of vegetative and structural measures. The gully floor is vegetated with different trees inter alia willow, poplar, cherry, blackberry and walnut which are arranged in random groups. At the bottom of the gully where it intersects the road there is a stonewall, which collects the sediments that are washed down during heavy rainfalls mostly in spring. A dense bush line with Russian olives, apricots, cherries, walnuts, plums and buxus has been planted on the top of the side slopes of the gully, and roots of those bushes keep the soil stable and at the same time they prevent landslides and expansion of the gully. These tree lines are cut from time to time, otherwise they grow and become heavy and due to their weight the trees would possibly fall into the gully.
Purpose of the Technology: (1) The deep roots of willow trees on the bottom of the gully protect the soil and prevent it from being eroded during the heavy spring floods. Trees also help to collect sediment and to accumulate it in the gully. (2) The dense bush lines with its deep roots, on the top of the gully slope, stop the horizontal erosion, which endangers the fertile orchard close to the gully. (3) A stonewall at the lower end of the gully collects sediments which have been washed down. Once in a while a heightening of the stonewall has to be done. The technology with its three measures prevents from further gully expansion and supports its rehabilitation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: These three measures, the tree line, the bottom vegetation and the stonewall were developed and implemented by the farmer's own initiative. The farmer implemented the technology on his own and expands it every year. The entire technology doesn’t have to be established at once, which allows investing money and time whenever it is available. For maintenance new trees are planted both in the gully and in the tree line, which has to be cut and pruned from time to time. The technology is relatively affordable and facile to implement. At the beginning the farmer bought some seedlings. Meanwhile, the plants reproduce themselves and the farmer doesn't have to buy seedlings for further maintenance. The stones can be collected for free in the nearby riverbed. The work is done manually; no special tools are needed for the technology.
Natural / human environment: The farmer is proud of the outcome of his initiative. However he wishes that his neighbours would follow his lead, as for them it would be beneficial to implement the technology as well. He stated that usually people do not listen to a common farmer, but if the technology would be introduced by an official person it would spread out quickly.
Lugar: Faizabad, Javonon, Chinoro, Tajikistan, Tayikistán
No. de sitios de Tecnología analizados:
Difusión de la Tecnología:
¿En un área de protección permanente?:
Fecha de la implementación: 10-50 años atrás
Tipo de introducción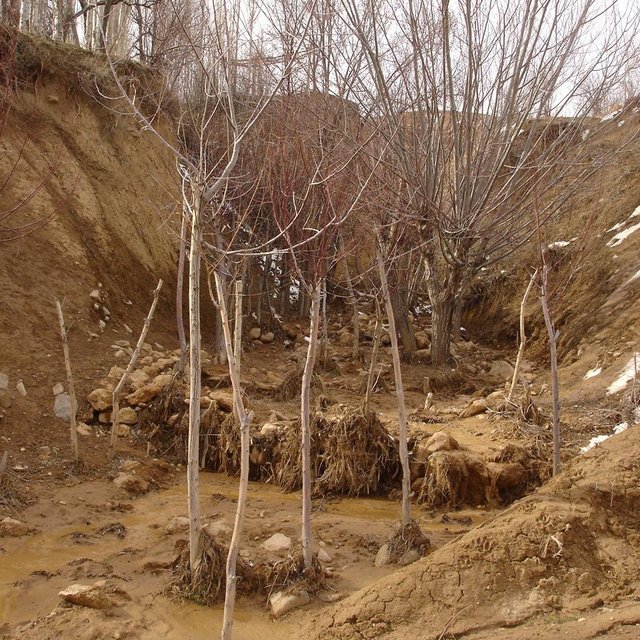





| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (Tajik Somoni) | Costos totales por insumo (Tajik Somoni) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Build wall | wall | 1,0 | 125,0 | 125,0 | 100,0 |
| Planting trees | Persons/day | 3,0 | 12,0 | 36,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | |||||
| Tree seedlings | 1,0 | 166,0 | 166,0 | ||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 327.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 69.57 | ||||
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (Tajik Somoni) | Costos totales por insumo (Tajik Somoni) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Add trees | Persons/day | 1,0 | 12,0 | 12,0 | 100,0 |
| Increase the hight of the wall | - | ||||
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 12.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 2.55 | ||||
Especially at the time of establishment.
Land users acquired new knowledge.
Treeline