



The technology is applied in already existing degraded farmlands, which are individually owned. An average farm size is less than half an acre.
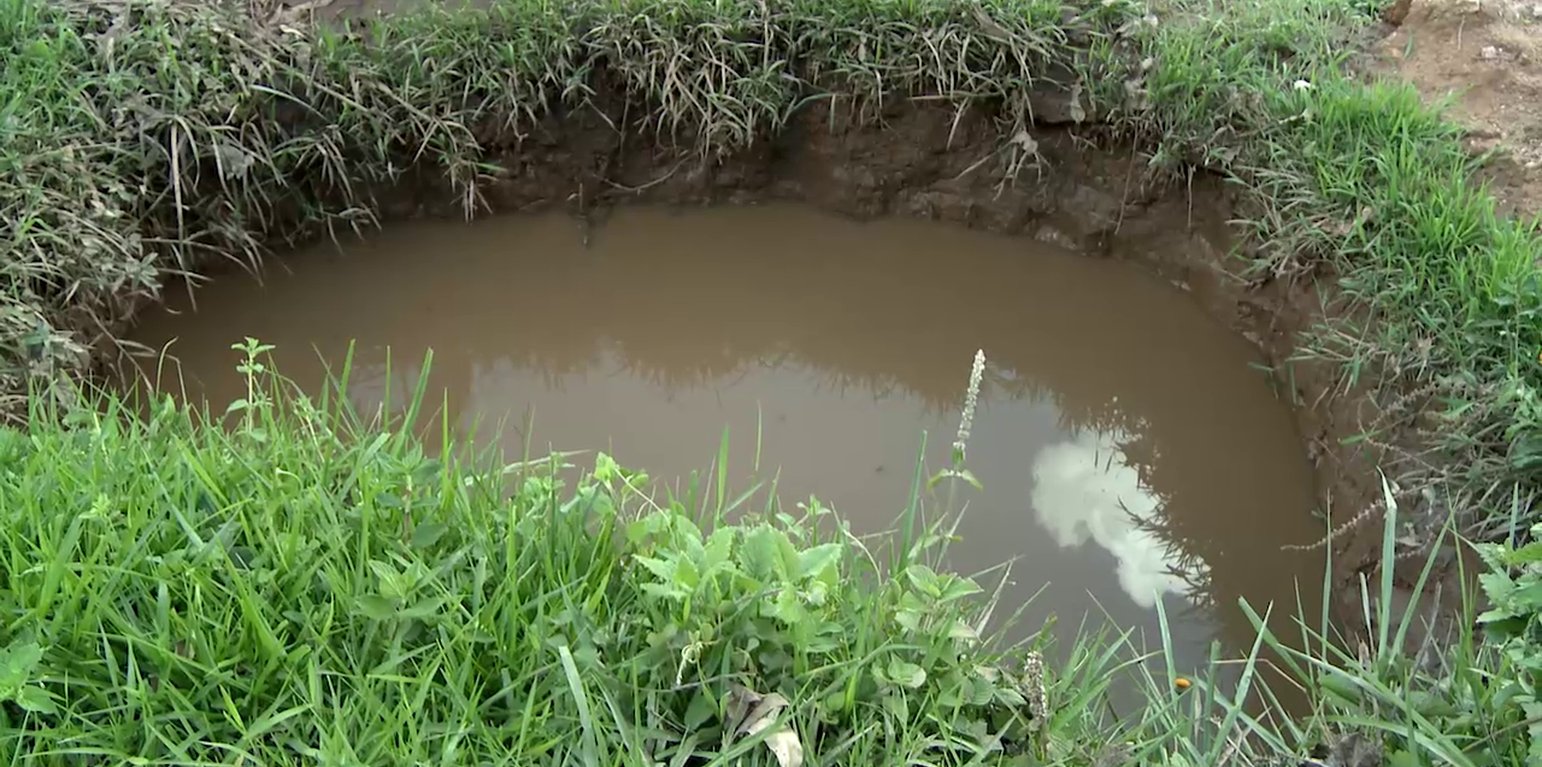
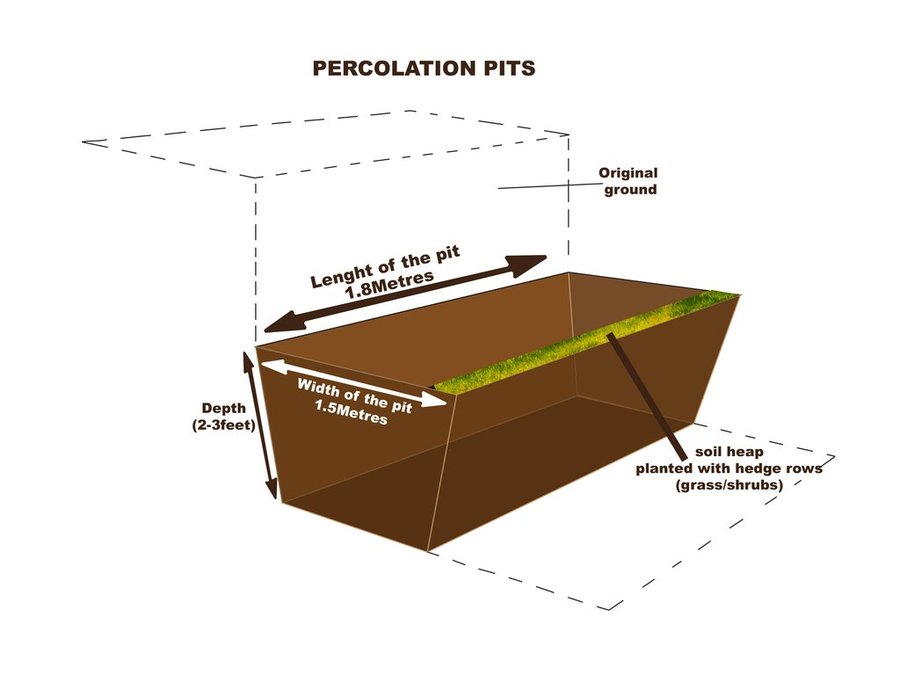
A typical percolation pit is 2m wide, 2m long and 1m deep planted with a hedge row on its lower side
This technology reduces the speed of water running down the slope during a downpour and traps the water and soil that is being washed thereby reducing soil erosion and increasing water retention
Areas which are prone to degradation by erosion are identified and later, the farmers are trained on benefits of this technology, how to construct the pit and how to maintain them by periodic de-silting and planting grasses and shrubs on the lower side
This technology helps maintain the good top soil, which would have otherwise been washed down the water course into the valley and increases water retention.
The land users like this technology because their soil is not lost by erosion. In addition it is localized, not like a conservation channel which runs along the whole contour. Percolation pits consume less land because they are located in an already existing waterway. What land users don’t like about this technology is that it has a huge sediment load and requires frequent de-silting
Lugar: Rubaya Sub County, Kabale District, South Western Region, Uganda
No. de sitios de Tecnología analizados: 100-1000 sitios
Difusión de la Tecnología: aplicada en puntos específicos/ concentrada en un área pequeña
¿En un área de protección permanente?:
Fecha de la implementación: 2015
Tipo de introducción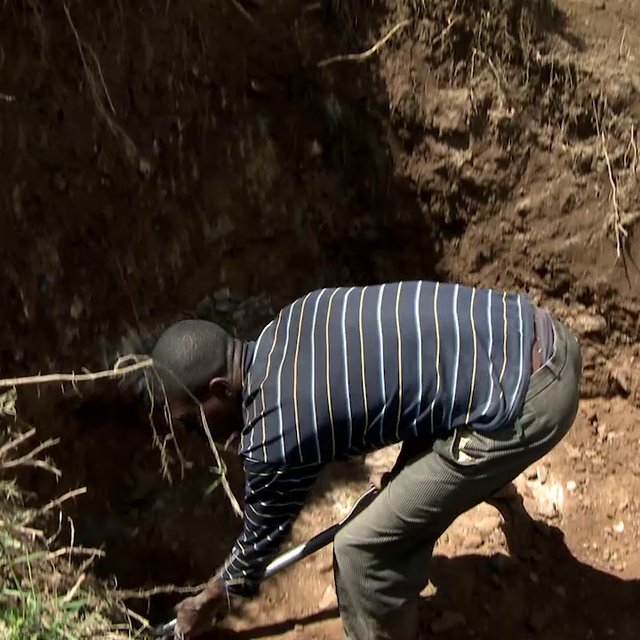
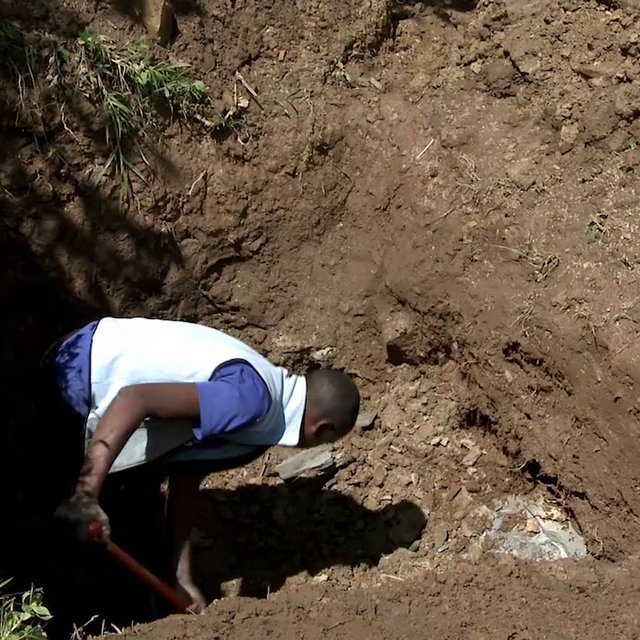






| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (USD) | Costos totales por insumo (USD) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Excavation of pit | person days | 4,0 | 2,12 | 8,48 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | |||||
| Forked hoes (1 piece can excavate 50 pits) | pieces | 0,02 | 4,55 | 0,09 | |
| Pick axes (1 piece can excavate 50 pits) | pieces | 0,02 | 4,55 | 0,09 | |
| Spades (1 piece can be used on 50 pits) | pieces | 0,02 | 4,55 | 0,09 | |
| Material para plantas | |||||
| Starria grass (1 sack for 5 pits) | per pit | 1,0 | 1,21 | 1,21 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 9.96 | ||||
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (USD) | Costos totales por insumo (USD) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Desilting the pits when half full | person days | 1,0 | 2,12 | 2,12 | 100,0 |
| Trimming of hedge rows (on 25 pits per day) | person days | 0,04 | 2,12 | 0,08 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 2.2 | ||||
The impacts are visible even after the first crop
It is expected to improve in the long term
Recharge is hoped to increase in the long term as more farmers adapt the technology
By use of manure
Flooding in the valley bottoms due to runoff reduces significantly
As more people adopt the technology this is expected to increase
The runoff which causes damage is trapped in the percolation pits
Especially on roads and water systems