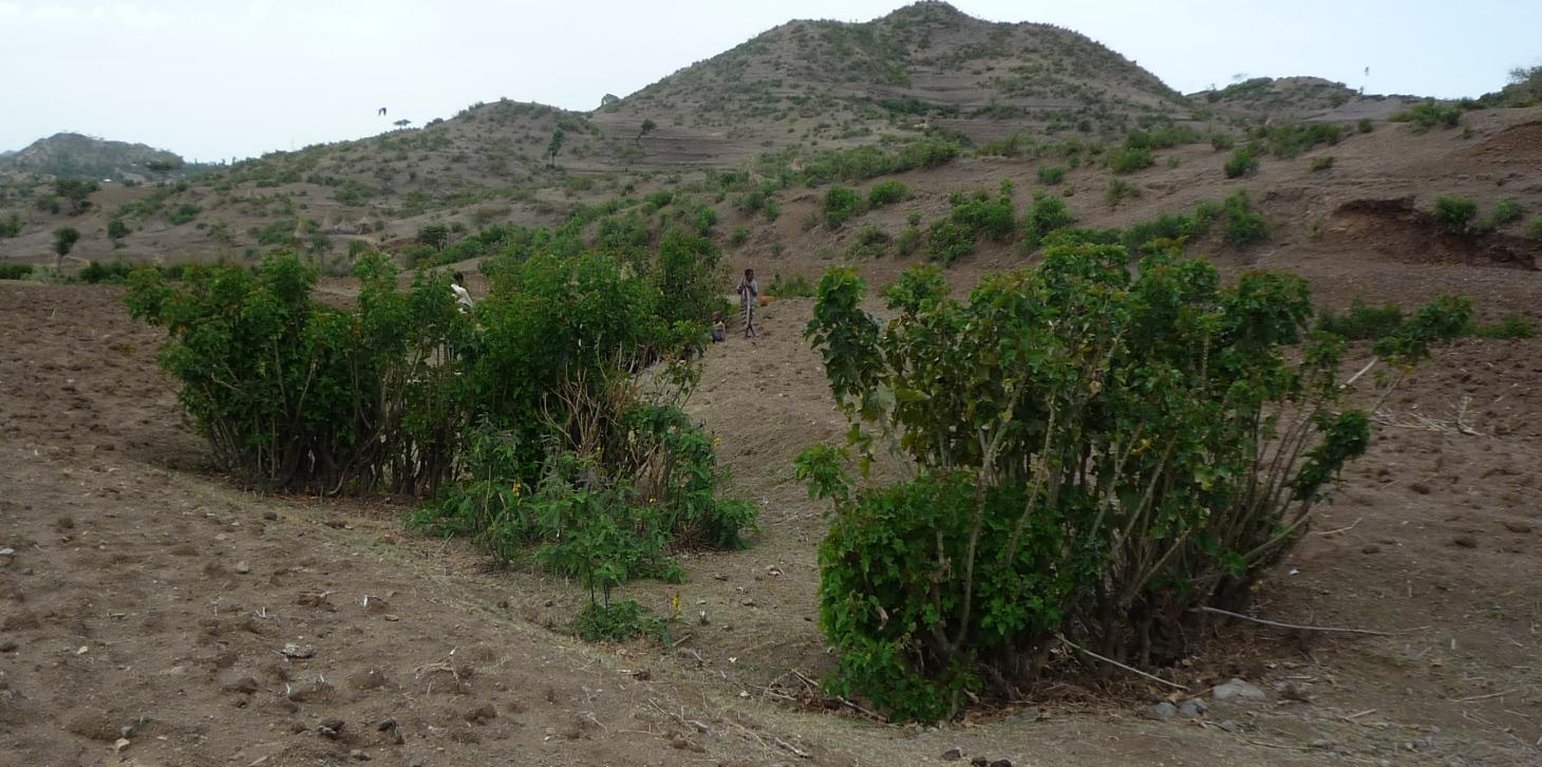




In the area around Bati in Ethiopia, Jatropha is used to stabilize hills ore to rehabilitate gullies. The technology was introduced during the last decade by local farmers on their plots. The advantage of Jatropha against other shrubs is that it is poisonous and therefore not browsed by animals. Additionally the seeds can be collected by household members and sold on the local market. The seed's oil can be used as a lamp oil or even for the production of bio-fuel.
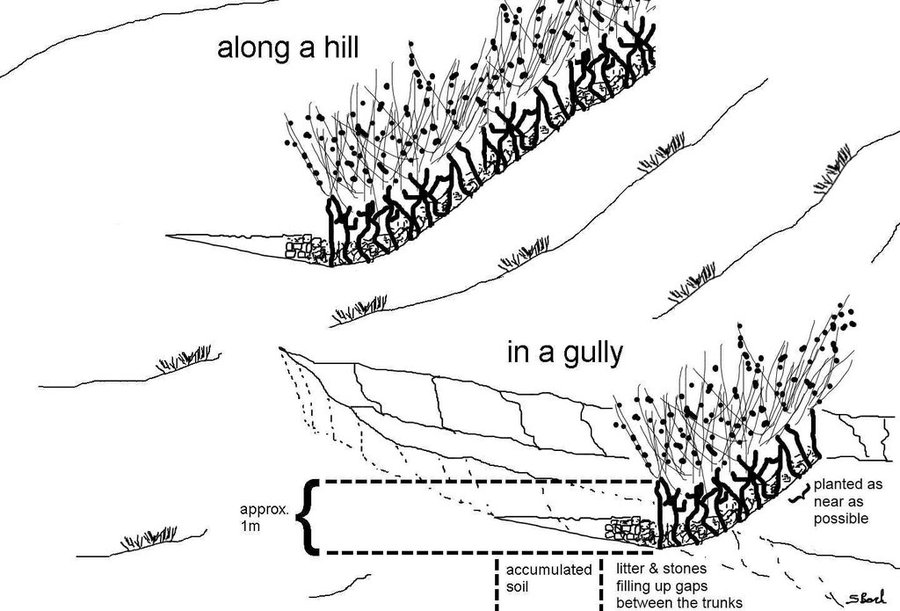
Purpose of the Technology: Besides hedges and living fences, Jatropha is used for combating sheet or gully erosion. To stop erosion processes the Jatropha cuttings are planted across a gully or along hill sides to stabilize them in the same manner as check dams or terraces do. The plant is chosen because of its very tolerant character, rather high accessibility in the area and because it is easy to propagate by cuttings. Often Jatropha is used in combination with traditional stone check dams or terraces aiming for an increased stability of the technology itself. For that purpose Jatropha is planted in front of the stone walls or also on top of them.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In earlier times Jatropha was planted by seeds but nowadays, since there are a lot of plants in the area, propagation by cuttings is the more prominent form. Since the plants are pruned every year anyway, the cuttings are accessible almost in any case for free. At markets further away, the cuttings cost around one cent per piece. In order to rehabilitate a gully Jatropha cuttings are planted as near as possible in the selected area in a row across the gully. After rooting, the spaces between the plants are filled up with litter, shrubs or stones. In order to have a thick stem and avoid competition with crops, the plants are pruned every year. The thick main stems reach a height of approximately one meter which delineates the maximum height of possible soil collection. If the area behind the filled up gaps and the cuttings has silted up, the height is increased by adding new litter in the higher up gaps. In off farming season, the Jatropha seeds are collected and sold on the market to create additional income.
Natural / human environment: The case study site, Bati, lays in an semiarid climatic zone on 1600 m a.s.l. Rainfalls are erratic and the rain sum per year is between 500-1000 mm. The landscape is very hilly with rather steep slopes. The area has a high population density and growth. The agricultural sector is very dominant and lead by a lot of small scale farming with a lot of livestock and small plots of cropland.
Lugar: Bati, Ethiopia / Amhara Region, Etiopía
No. de sitios de Tecnología analizados:
Difusión de la Tecnología:
¿En un área de protección permanente?:
Fecha de la implementación: 10-50 años atrás
Tipo de introducción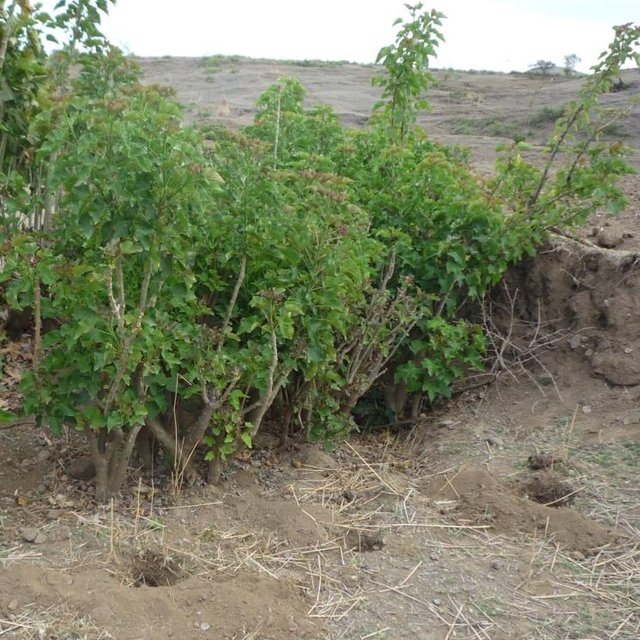





| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (Ethiopian Birr) | Costos totales por insumo (Ethiopian Birr) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Seeding | person day | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 |
| Cutting of the Jatropha cuttings | person day | 12,5 | 1,0 | 12,5 | 100,0 |
| Planting of the Jatropha cuttings | person day | 12,5 | 1,0 | 12,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | |||||
| Tools for cutting | 500m | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | |||||
| Seeds | kg | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 33.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 1.96 | ||||
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (Ethiopian Birr) | Costos totales por insumo (Ethiopian Birr) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Collection of Jatropha seeds | Person days | 5,0 | 1,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Filling up the gaps with litter | Person days | 5,0 | 1,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Pruning of the Jatropha | person days | 15,0 | 1,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | |||||
| Tools | Person days | 15,0 | 0,333333333 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | |||||
| Wood | 500m | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Stone | 500m | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 30.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 1.78 | ||||
gullies are transformed to fields
improving soil moisture
selling the Jatropha curcas seeds
gullies are transformed to fields. Structure needs space but also gains space
gully is now flat land and traversable, structure as a new obstacle
Jatropha curcas seed oil as a biofuel
alluvial soil is relatively fertile
new fields lead to higher productivity
selling the Jatropha curcas seeds
additional income by selling Jatropha seeds
slightly labor increase, establishment and maintenance work
additional space for new fields
positive examples for other land users
up -downstream problems may be solved
Accumulation of soil leads to new space for fields and additional food security or even income (if crop surplus is sold). Collection of Jatropha curcas seeds - they can be sold (additional income) or processed to oil (lamp oil etc.)
increased soil moisture
Jatropha curcas dam blocks water flow
increased infiltration, reduced flow velocity
increased infiltration
maybe due to the Jatropha curcas canopy
Jatropha curcas dam blocks water flow,. But additional groundwater may be logged
Jatropha curcas canopy
alluvial accumulation behind the structure
increased rooting
increased rooting
Jatropha curcas leaves & litter
Jatropha curcas leaves & litter
Jatropha curcas biomass
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
Jatropha curcas new habitat for worms etc
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
new habitat for rodents etc.
flood controll by Jatropha curcas dams
little effect by additional plants
Jatropha curcas wood is a bad fire wood
Jatropha curcas shrub as a wind breaker
Over water and sunlight
possibility of spring development
if a spring can develop
increased infiltration/reduced flooding
trapping of the sediments by the structure
trapping of the sediments by the structure
increased infiltration
due to gully rehabilitation
due to gully rehabilitation