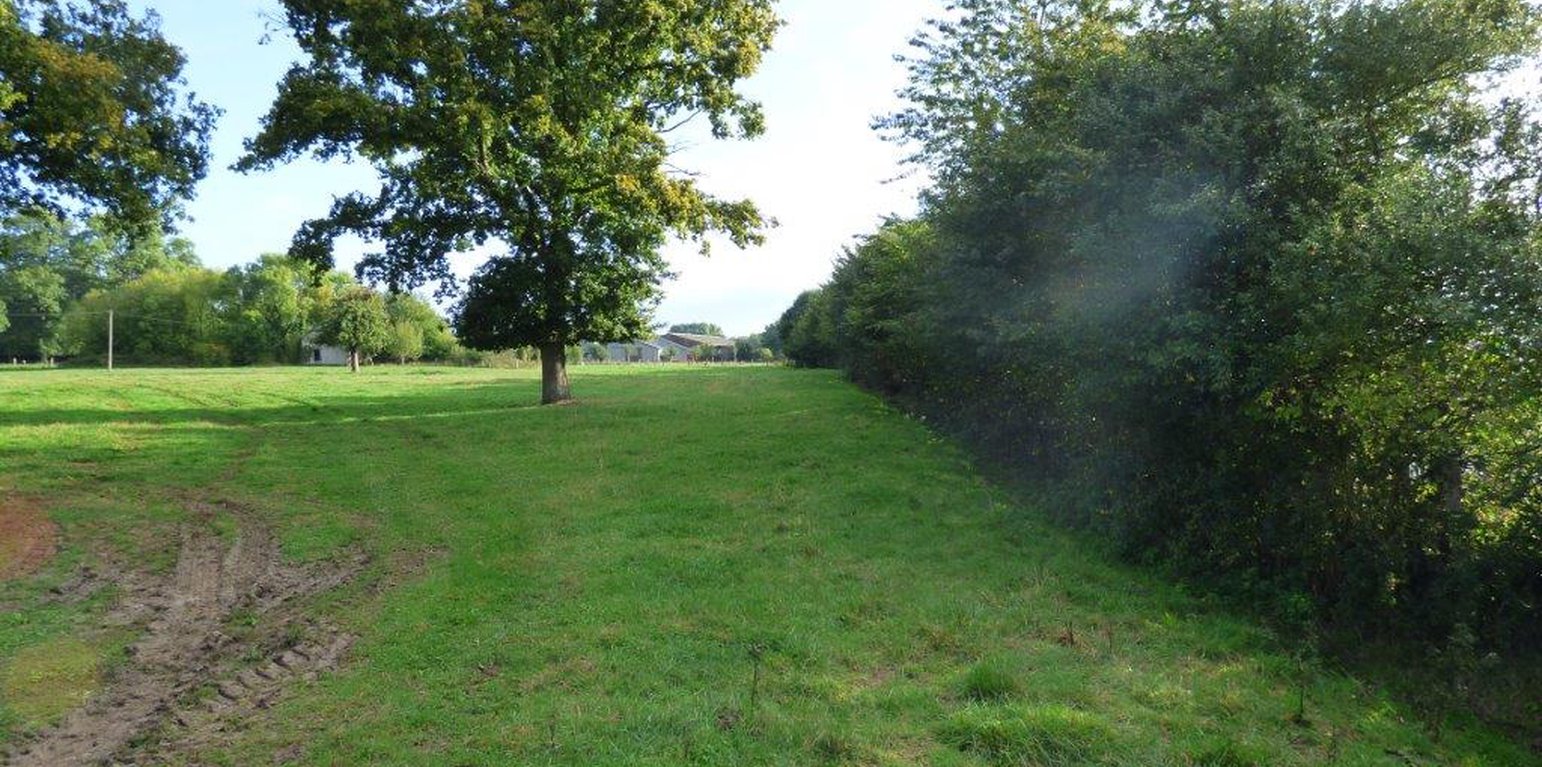




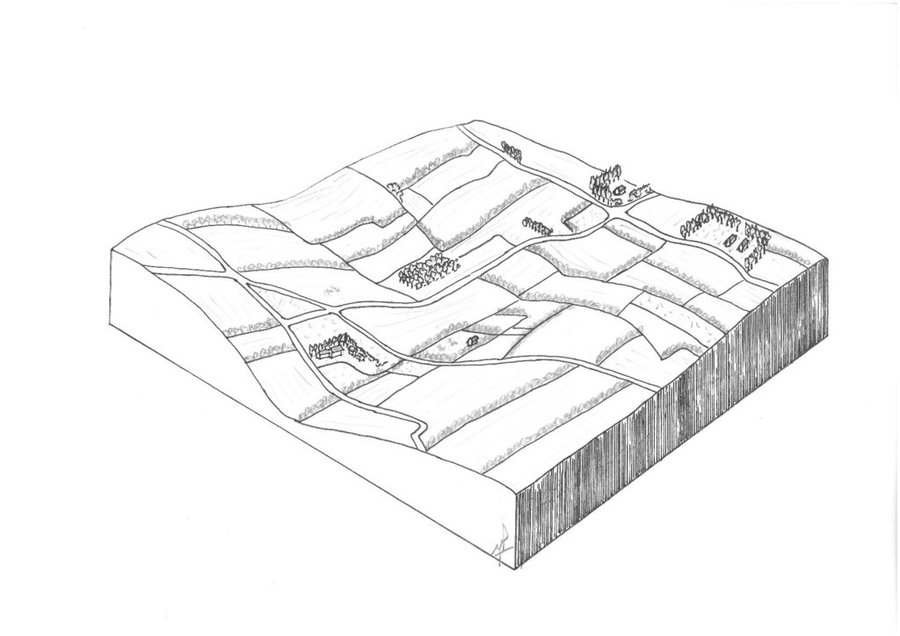
Hedgerows are typical landscape features of rural Normandy. They surround agricultural fields, whether cultivated or under grassland. Hedges were already prominent in Normandy during the 19th century, and they reached a peak between the first and second world wars. However, since the 1960s, the restructuring of agricultural land and technical and technological developments in agriculture have led to the disappearance of hedgerows. The challenge since the beginning of the 21st century has been to maintain the existing hedgerows and to establish others. This is important in the light of today’s agri-environmental and climate issues.
The technology of replacing, restoring or planting new hedgerows has been applied in an area of mixed farming for the benefit of crop and animal protection, watercourse and soil erosion buffering and protection, and landscape and habitat connectivity improvements. The technology has been applied in a locality by a small number of farmers over a number of recent years.
Hedgerows are planted on the periphery of the fields with species spaced at 0.5 to 1 m apart. There are between 1 and 3, sometimes even 4 different vegetative types used in establishing the hedgerows - herbaceous, bushy, and shrubby plants and trees. The current average length is 36 metres of hedge per hectare. The position of ancient hedgerows in the landscape is the result of the history of parcels of land. In contrast, over the last ten years, agri-environmental criteria have been taken into account in selecting planting sites. The main local species used for new hedges are: Fraxinus, Quercus, Tilia, Carpinus, Acer campestre, Crataegus, Corylus and Ilex. Each hedge is considered to have an influence ranging from 50 to 200 m away from it in terms of windspeed, runoff, and biodiversity.
Hedgerows play a very important role in preventing:
- Biological degradation through maintaining and increasing wildlife biodiversity and stimulating biological regulation of crop pests
- Climate-induced impacts both at the local level (decrease of wind speeds, decrease of evapotranspiration, shade for animals) and at global level (carbon storage, substitution of fossil energies by renewable energy)
- Water degradation through maintaining and improving qualitative and quantitative regulation of water at the watershed scale
- Soil erosion by water and chemical deterioration through the conservation of soils
- Soil erosion by wind
Despite these benefits, this SLM technology has not yet been taken up widely. It is more than necessary to restart hedgerow management with Normandy farmers, especially as the use of external inputs (e.g. fertilizers and pesticides) is increasingly expensive for both farmers and society.
The compilation of this SLM is a part of the European Interreg project FABulous Farmers which aims to reduce the reliance on external inputs by encouraging the use of methods and interventions that increase the farm’s Functional AgroBiodiversity (FAB). Visit www.fabulousfarmers.eu and www.nweurope.eu/Fabulous-Farmers for more information.
Lugar: Normandy, Francia
No. de sitios de Tecnología analizados: 2-10 sitios
Difusión de la Tecnología: distribuida parejamente sobre un área (approx. 10-100 km2)
¿En un área de protección permanente?: No
Fecha de la implementación: hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
Tipo de introducción



| Especies | Conteo |
| ganado - carne de res no lechera | 20 |








| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (€) | Costos totales por insumo (€) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Design and planning | person-days | 0,3 | 120,0 | 36,0 | 50,0 |
| Surface preparation for planting | person-days | 0,1 | 120,0 | 12,0 | 100,0 |
| Application of mulch | person-days | 0,3 | 120,0 | 36,0 | 100,0 |
| Planting trees | person-days | 11,0 | 120,0 | 1320,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | |||||
| Tractor with harrow | machine-days | 0,1 | 50,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | |||||
| Trees | Piece | 1000,0 | 2,0 | 2000,0 | 50,0 |
| Tree protection (i.e. wild animal guards) | Piece | 1000,0 | 0,5 | 500,0 | 80,0 |
| Mulching | Piece | 1000,0 | 1,3 | 1300,0 | 80,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 5'209.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 5'787.78 | ||||
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (€) | Costos totales por insumo (€) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| Hedgerow maintenance (cutting/pruning) | day | 0,2 | 120,0 | 24,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | |||||
| Maintenance cutter | day | 0,2 | 50,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 34.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 37.78 | ||||
Possible loss of some cropland replaced with hedgerows, although most hedging in this instance was reinstating old field boundaries - i.e. where historic boundary lines existed but were removed for machenery or to enlarge field size.
Greater crop protection and more beneficial species improve crop quality
Shelter belts improve animal welfare leading to better weight gain.
Hedgerows can be coppiced for wood crop.
Shelter belt reduces risk of crop failure from weather extremes (i.e. wind)
Wood crop added to diversity of products
Although loss of crop land, this is replaced with wood crop diversity
Smaller parcels of land make land management more restrictive for large machinery.
Balance of increased time and management of a diversity of crops, yet less crop management with improved pest control and phyicsl stress reduction from more shelter.
No change in balance of less crop production but addition of woody crop.
Diversity added with option of woody crop
Smaller field parcels make crop management harder having to use smaller machinery and there is an addition of hedgerow maintenence workload.
Hedgerows act as buffer strips capturing wash off from fields before it reaches the water course
Hedgerows act as buffer strips capturing wash from fields
Improved soil infiltration in hedgerows helps drain excess water
Improved soil infiltration in hedgerows helps maintain soil moisture capacity
Hedgerows act as buffer strips capturing soil wash from fields
Reduced machinery size (in places) reduces compaction, plus less soil compaction by hedgerows.
Increased organic matter in hedgerows
More year round cover
Increased wih hedgerows
More diverse species with planting for hedgerows
Increased habitat diversity and area for more animal presence and diversity
Encouragement of beneficial species with habitat creation in hedgerows that can aid natural pest and disease control through the presence of predator species that control pest species.
Within hedgerow habitat addition
Encouragement of beneficial species with habitat creation in hedgerows that can aid natural pest and disease control through the presence of predator species that control pest species.
Improved soil infiltration reduces flooding risk
Shelter belts reduce wind velocity over crops
Hedgerows act as buffer strips capturing wash off from fields before it reaches the water course
Hedgerows act as buffer strips capturing wash off from fields before it reaches the water course
Shelter belts reduce wind velocity over crops and bare soil for less erosion & transportation
Shelter belts reduce wind velocity over crops and bare soil for less erosion & transportation
Increased tree cover supports a reduction in GHG