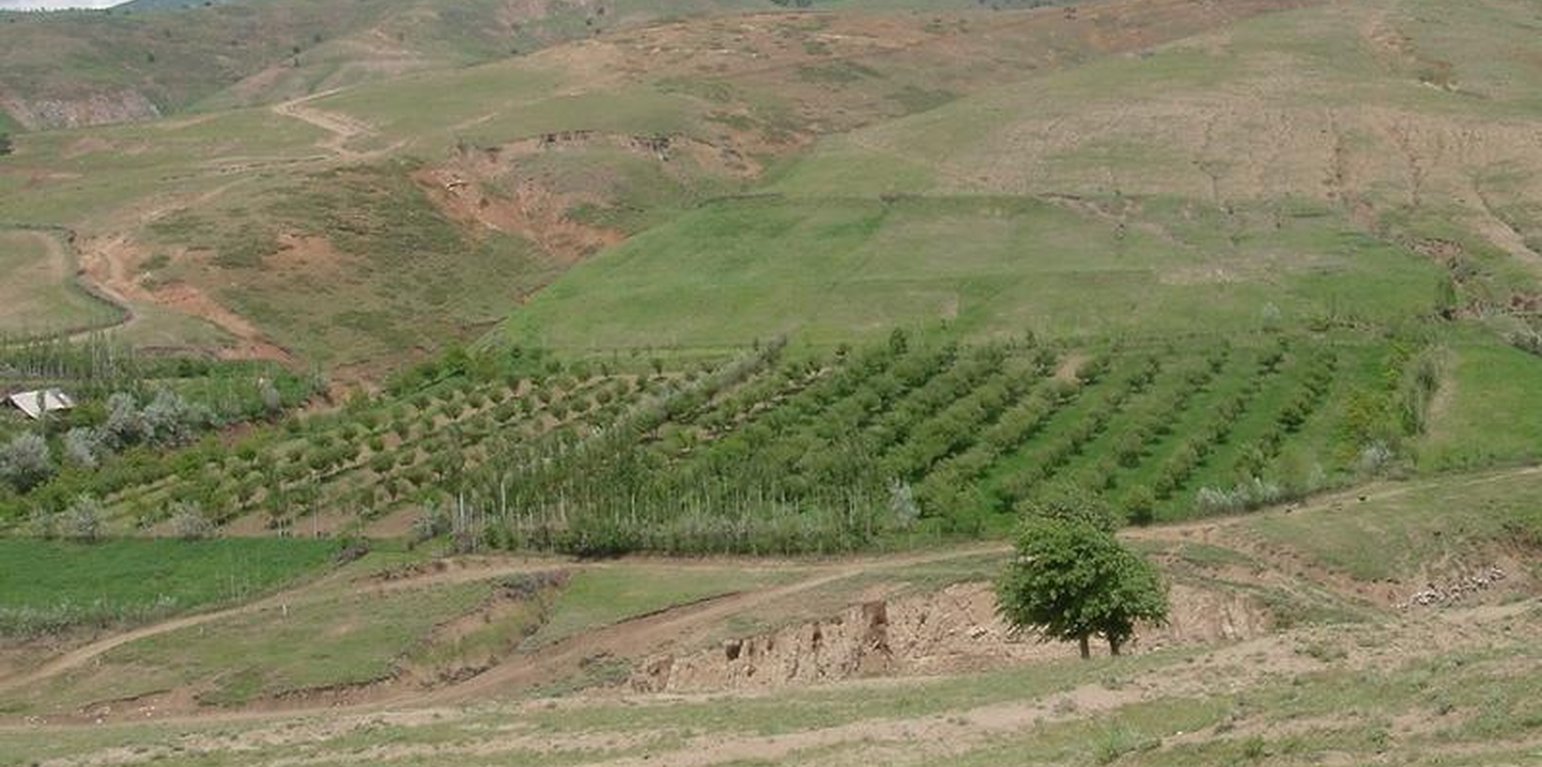
Orchard-based Agroforestry (establishment of orchard)
(Tayikistán)
Descripción
Establishment of an orchard intercropping system on severely degraded cropland.
A fruit orchard (consisting of apples, apricots, cherries, pears and nut trees) was established on degraded cropland. Intercropping of annual crops such as wheat, flax, chick peas and vegetables as well as perennial herbaceous fodder plants (alfa-alfa and esparzet) were planted after the first year of the establishment of the orchard. Only the onion plot is rotated systematically since the farmer states that fertility declines due to heavy soil losses result from over-irrigation. Spacing of tree rows varies between 8-10m, the intercropping system is cultivated using a tractor. Fruit trees are aligned in the direction of the slope to facilitate irrigation. At the top of the field an irrigation channel (40cm wide, 15cm deep) stabilised with aligned poplar trees directs water onto the orchard system. During the rainy season the channel serves as a cut-off drain, protecting the land from water running on. Along the trees, a 2.5 m wide grass strip protects the ground from splash erosion.
Purpose of the Technology: The orchard system was established to increase farm production by integrating different resources, while simultaneously conserving soil and water resources and preventing development of gullies. Prior to tree planting, the area had been levelled with a bulldozer to restore the severely degraded cropland. The bought seedlings were planted in hand-dug pits. During summer, the orchard system is watered three days per week; manure is applied around the fruit trees on an annual basis. Pruning of the trees is done in early spring. Due to irrigation, the grass strips can be harvested twice a year for haymaking. Farming two crops at a time means gross farm production could be considerably increased, which is the reaon why the farmer considered the technology successful. However, establishment and maintenance of the technology is cost intensive and, in this case study, was only affordable due to the farmers off-farm income. Since the tree rows are aligned up and down the slope, soil erosion is solely reduced by the capability of the irrigation channel (and aligned tree barrier) to prevent the system from runon. Planting tree rows on the gradient would increase the technologies potential to reduce soil loss.
Lugar
Lugar: Faizabad Rayon, RRS, Tayikistán
No. de sitios de Tecnología analizados:
Georreferencia de sitios seleccionados
Difusión de la Tecnología: distribuida parejamente sobre un área (approx. 0.1-1 km2)
¿En un área de protección permanente?:
Fecha de la implementación:
Tipo de introducción
-
mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
-
como parte de un sistema tradicional (> 50 años)
-
durante experimentos/ investigación
-
mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
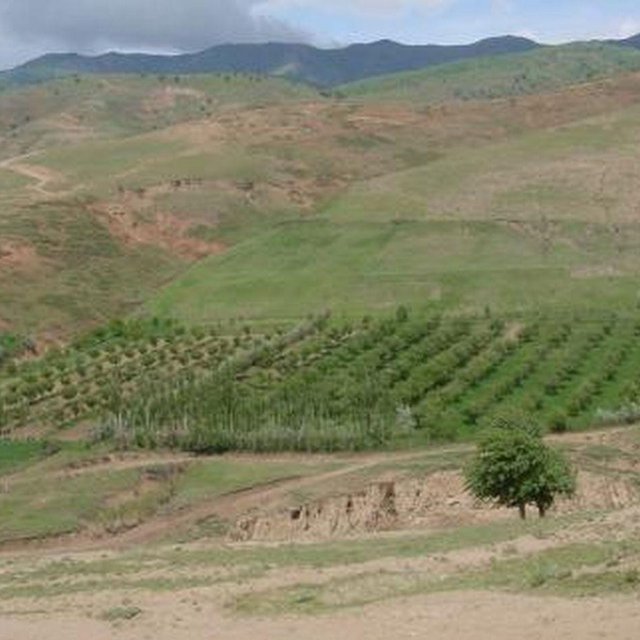

Overview of a SWC field and next to it, degraded pasture and a haymaking field. Similar gullies and rills were on the cropland as well, prior to establishment of the orchard (Erik Bühlmann (Berne, Switzerland))

Irrigated orchard system established on severely degraded cropland (Erik Bühlmann (Berne, Switzerland))
Clasificación de la Tecnología
Propósito principal
-
mejorar la producción
-
reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
-
conservar el ecosistema
-
proteger una cuenca hidrográfica/ áreas corriente abajo – en combinación con otras Tecnologías
-
preservar/ mejorar biodiversidad
-
reducir el riesgo de desastres naturales
-
adaptarse al cambio climático/ extremos climáticos y sus impactos
-
mitigar cambio climático y sus impactos
-
crear impacto económico benéfico
-
crear impacto social benéfico
Uso de tierra
Mezcla de tipos de uso de tierras dentro de la misma unidad de tierras: Sí - Agroforestería
-
Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual: leguminosas y legumbres - arvejas , cultivos para producción de fibras - lino, cáñamo, otros, cereales - trigo (verano), cultivos para forraje - alfalfa, vegetales - otros, esparzet
- Cosecha de árboles y arbustos: frutas, otros, frutas de hueso (durazno, albaricoque, cerezos, ciruelas, etc), frutos secos (castañas, pistachos, nuez, almendras, etc.), frutas de pepita (manzanas, peras, membrillo, etc.)
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año: 1
¿Se practica el intercultivo? Sí
Provisión de agua
-
de secano
-
mixta de secano – irrigada
-
totalmente irrigada
Propósito relacionado a la degradación de las tierras
-
prevenir la degradación de la tierra
-
reducir la degradación de la tierra
-
restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
-
adaptarse a la degradación de la tierra
-
no aplica
La degradación considerada
-
erosión de suelos por agua - Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie , Wg: erosión en cárcavas
-
deterioro químico del suelo - Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)
Medidas MST
-
medidas agronómicas - A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo , A2: materia orgánica/ fertilidad del suelo
-
medidas vegetativas - V5: Otros
-
medidas estructurales - S11: Otros
-
medidas de manejo - M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
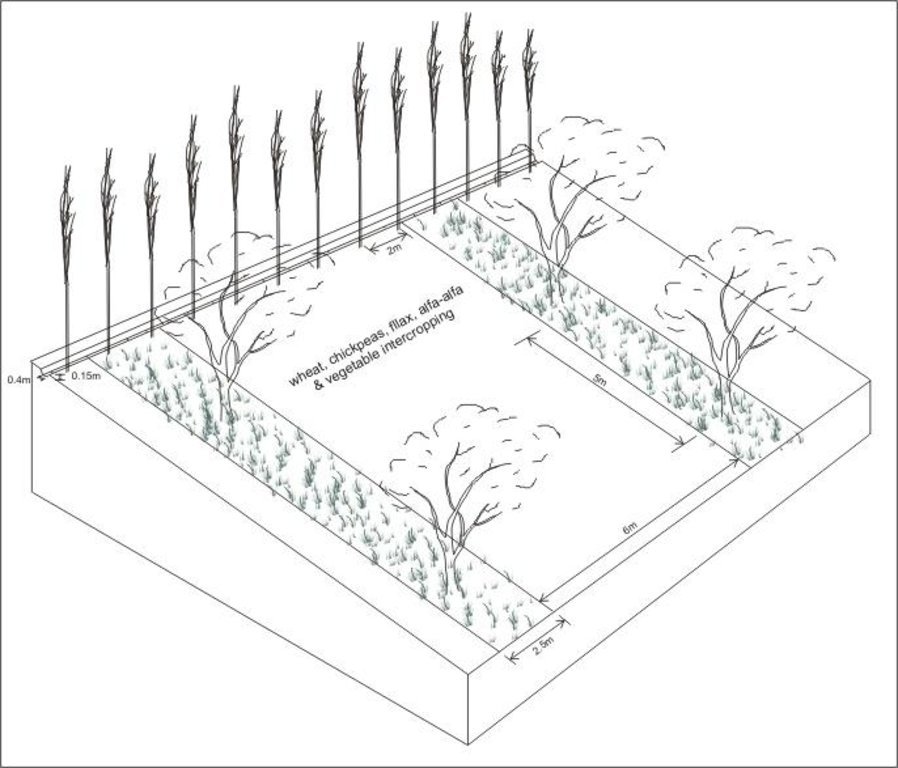
Dibujo técnico
Especificaciones técnicas
Irrigated orchard system with intercropping; irrigation channel (stabilised by aligned poplar trees) also acts as a cut-off drain to prevent runon.
Location: Chinoro. Faizabad Rayon, RRS
Date: 18.07.2005
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase in soil fertility
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: wheat, chickpeas, flax, vegetables, alfa-alfa, esparzet
Remarks: between tree rows
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: manure
Quantity/ density: 20kg/tree
Remarks: spreading around fruit trees
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: silitra and/or superphosphate
Quantity/ density: 200kg/ha
Remarks: only if wheat is intercropped
Vegetative measure: aligned: slope direction
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 8
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vegetative measure: aligned: slope direction
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 8
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vegetative measure: aligned: along irigation channel on contour
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 50
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: poplar trees
Fruit trees / shrubs species: apple, pear, cherry, apricot, peach and nut trees
Grass species: grass cover with esparzet and alfa alfa (sown to improve grass cover)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 17.00%
Structural measure: diversion ditch / cut-off drain
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.15
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.4
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Construction material (earth): earth was moved to fill gullies and large rills
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 17%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Author: Erik Bühlmann, Berne, Switzerland
Establecimiento/ mantenimiento: actividades, insumos y costos
Cálculo de insumos y costos
- Los costos se calculan:
- Moneda usada para calcular costos: USD
- Tasa de cambio (a USD): 1 USD = n.d.
- Costo promedio por día del sueldo de la mano de obra contratada: 3.00
Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos
Number of trees planted: since the establishment and maintainance require considerable financial and labour inputs; expenditures for tree seedlings bought from the market: N.B. if nursing the trees is completed by land user himself, establishment costs can be halved.
Actividades de establecimiento
-
land levelling and filling up of gullies (Momento/ frequencia: winter/early spring)
-
digging of irrigation channel (Momento/ frequencia: spring)
-
acquiring tree seedlings on market or at sovkhoze (Momento/ frequencia: None)
-
digging of pits (Momento/ frequencia: early spring)
-
planting seedlings in pits (Momento/ frequencia: early spring)
-
sowing of esparzet and alfa alfa (grass strips) to get intact grass cover (Momento/ frequencia: spring)
Insumos y costos para establecimiento
| Especifique insumo |
Unidad |
Cantidad |
Costos por unidad (USD) |
Costos totales por insumo (USD) |
% de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
|
Mano de obra
|
| land levelling |
ha |
1,0 |
45,0 |
45,0 |
100,0 |
|
Equipo
|
| tools |
ha |
1,0 |
25,0 |
25,0 |
100,0 |
| machine for land levelling |
ha |
1,0 |
150,0 |
150,0 |
|
|
Material para plantas
|
| seedlings |
ha |
1,0 |
250,0 |
250,0 |
100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología |
470.0 |
|
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD |
470.0 |
|
Actividades de mantenimiento
-
clearing of irigation channel/cut-off drain from washed in soil (Momento/ frequencia: rainy season/weekly)
-
periodical irrigation (3x a week) (Momento/ frequencia: summer /three days/week)
-
periodical irrigation (3x a week) (Momento/ frequencia: summer /three days/week)
-
application of manure (Momento/ frequencia: early spring /annual)
-
application of manure (Momento/ frequencia: early spring /annual)
-
application of pesticides (Momento/ frequencia: spring /annual)
-
application of pesticides (Momento/ frequencia: spring /annual)
-
pruning of fruit trees (Momento/ frequencia: winter/early spring /annual)
-
pruning of fruit trees (Momento/ frequencia: winter/early spring /annual)
-
cutting of grass (haymaking) (Momento/ frequencia: summer /twice a cropping season)
-
cutting of grass (haymaking) (Momento/ frequencia: summer /twice a cropping season)
-
ploughing of area between tree rows (disc plough) (Momento/ frequencia: depending on crop / annual)
-
applying of mineral fertilisers (Momento/ frequencia: spring / annual (only for intercropped wheat))
-
weeding (Momento/ frequencia: spring / regularly)
-
applying manure around fruit trees (Momento/ frequencia: winter/spring /annual)
Insumos y costos de mantenimiento
| Especifique insumo |
Unidad |
Cantidad |
Costos por unidad (USD) |
Costos totales por insumo (USD) |
% de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
|
Mano de obra
|
| ploughing of area |
ha |
1,0 |
20,0 |
20,0 |
100,0 |
| sowing and weeding |
ha |
1,0 |
18,0 |
18,0 |
|
| pruning of fruit trees |
ha |
1,0 |
30,0 |
30,0 |
|
| spraying trees with biocides |
ha |
1,0 |
12,0 |
12,0 |
|
|
Material para plantas
|
| seeds |
ha |
1,0 |
30,0 |
30,0 |
100,0 |
|
|
|
1,0 |
|
|
|
Fertilizantes y biocidas
|
| fertilizer |
ha |
1,0 |
50,0 |
50,0 |
100,0 |
| biocides |
ha |
1,0 |
10,0 |
10,0 |
100,0 |
| compost/manure |
ha |
1,0 |
40,0 |
40,0 |
100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología |
210.0 |
|
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD |
210.0 |
|
Entorno natural
Promedio anual de lluvia
-
< 250 mm
-
251-500 mm
-
501-750 mm
-
751-1,000 mm
-
1,001-1,500 mm
-
1,501-2,000 mm
-
2,001-3,000 mm
-
3,001-4,000 mm
-
> 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
-
húmeda
-
Sub-húmeda
-
semi-árida
-
árida
Especificaciones sobre el clima
growing period between 180-210 days
Pendiente
-
plana (0-2 %)
-
ligera (3-5%)
-
moderada (6-10%)
-
ondulada (11-15%)
-
accidentada (16-30%)
-
empinada (31-60%)
-
muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas
-
meseta/ planicies
-
cordilleras
-
laderas montañosas
-
laderas de cerro
-
pies de monte
-
fondo del valle
Altura
-
0-100 m s.n.m.
-
101-500 m s.n.m.
-
501-1,000 m s.n.m
-
1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
-
1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
-
2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
-
2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
-
3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
-
> 4,000 m s.n.m
La Tecnología se aplica en
-
situaciones convexas
-
situaciones cóncavas
-
no relevante
Profundidad promedio del suelo
-
muy superficial (0-20 cm)
-
superficial (21-50 cm)
-
moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
-
profunda (81-120 cm)
-
muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable)
-
áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
-
mediana (limosa)
-
fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Textura del suelo (> 20 cm debajo de la superficie)
-
áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
-
mediana (limosa)
-
fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable
-
elevada (>3%)
-
media (1-3%)
-
baja (<1%)
Agua subterránea
-
en superficie
-
< 5 m
-
5-50 m
-
> 50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales
-
excesiva
-
bueno
-
mediana
-
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar)
-
agua potable de buena calidad
-
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
-
solo para uso agrícola (irrigación)
-
inutilizable
¿La salinidad del agua es un problema?
Incidencia de inundaciones
Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado
-
subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
-
mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
-
comercial/ mercado
Ingresos no agrarios
-
menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
-
10-50% de todo el ingreso
-
> 50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza
-
muy pobre
-
pobre
-
promedio
-
rico
-
muy rico
Nivel de mecanización
-
trabajo manual
-
tracción animal
-
mecanizado/motorizado
Sedentario o nómada
-
Sedentario
-
Semi-nómada
-
Nómada
Individuos o grupos
-
individual/ doméstico
-
grupos/ comunal
-
cooperativa
-
empleado (compañía, gobierno)
Edad
-
niños
-
jóvenes
-
personas de mediana edad
-
ancianos
Área usada por hogar
-
< 0.5 ha
-
0.5-1 ha
-
1-2 ha
-
2-5 ha
-
5-15 ha
-
15-50 ha
-
50-100 ha
-
100-500 ha
-
500-1,000 ha
-
1,000-10,000 ha
-
> 10,000 ha
Escala
-
pequeña escala
-
escala mediana
-
gran escala
Tenencia de tierra
-
estado
-
compañía
-
comunitaria/ aldea
-
grupal
-
individual, sin título
-
individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra
-
acceso abierto (no organizado)
-
comunitarios (organizado)
-
arrendamiento
-
individual
Derechos de uso de agua
-
acceso abierto (no organizado)
-
comunitarios (organizado)
-
arrendamiento
-
individual
Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
Impacto
Impactos socioeconómicos
área de producción (nuevas tierras bajo cultivo/ en uso)
loss of land for wheat production
manejo de tierras
obstaculizado
simplificado
machines used for land cultivation cannot operate so easily
fruit yields
due to lack of fertilisers and biocides
Impactos socioculturales
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
mitigación de conflicto
disputes on land use rights with other villagers, since orchards are in great demand
Impactos ecológicos
drenaje de agua en exceso
prevention of land from gullies and large rills
Impactos fuera del sitio
inundaciones río abajo (no deseadas)
Análisis costo-beneficio
Beneficios comparados con los costos de establecimiento
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy negativo
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo
muy negativo
muy positivo
Beneficios comparados con costos de mantenimiento
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy negativo
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo
muy negativo
muy positivo
Adopción y adaptación
Porcentaje de usuarios de la tierra que adoptaron la Tecnología
-
casos individuales / experimentales
-
1-10%
-
11-50%
-
> 50%
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
Número de hogares y/ o área cubierta
20 households in an area of 0.1 - 1 km2
¿La tecnología fue modificada recientemente para adaptarse a las condiciones cambiantes?
¿A qué condiciones cambiantes?
-
cambios climáticos / extremos
-
mercados cambiantes
-
disponibilidad de mano de obra (ej. debido a migración)
Conclusiones y lecciones aprendidas
Fortalezas: perspectiva del usuario de tierras
-
increase in overall farm income
-
prevention of gully and large rill erosion
Fortalezas: punto de vista del compilador o de otra persona recurso clave
-
orchard system is protected from runon
-
effectively prevents formation of gullies and large rills
-
significant increases in gross farm production
-
effective way of rehabilitating bad lands
-
increases soil fertility
How can they be sustained / enhanced? consequent mulching would increase the organic matter content of the soil, and hence soil fertility
Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos: perspectiva del usuario de tierrascómo sobreponerse
-
fruit trees vulnerable to pests, frost and strong winds
Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos: punto de vista del compilador o de otra persona recurso clavecómo sobreponerse
-
high establishment and maintainance costs
if nursing of tree seedlings is carried out by the land user himself, establishment costs can be reduced
-
does not prevent soil erosion, soil losses especially where irrigated
By planting tree rows on gradient (not up and down the slope)
-
management of orchard systems requires considerable inputs which often cannot be afforded by poor people
Referencias
Revisado por
-
David Streiff
-
Alexandra Gavilano
-
Joana Eichenberger
Fecha de la implementación: 8 de marzo de 2011
Últimas actualización: 2 de noviembre de 2021
Personas de referencia
-
Erik Bühlmann - Especialista MST
-
Bettina Wolfgramm - Especialista MST
Descripción completa en la base de datos de WOCAT
La documentación fue facilitada por
Institución
- CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suiza
- NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - Kirguistán
Proyecto
- Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)
















