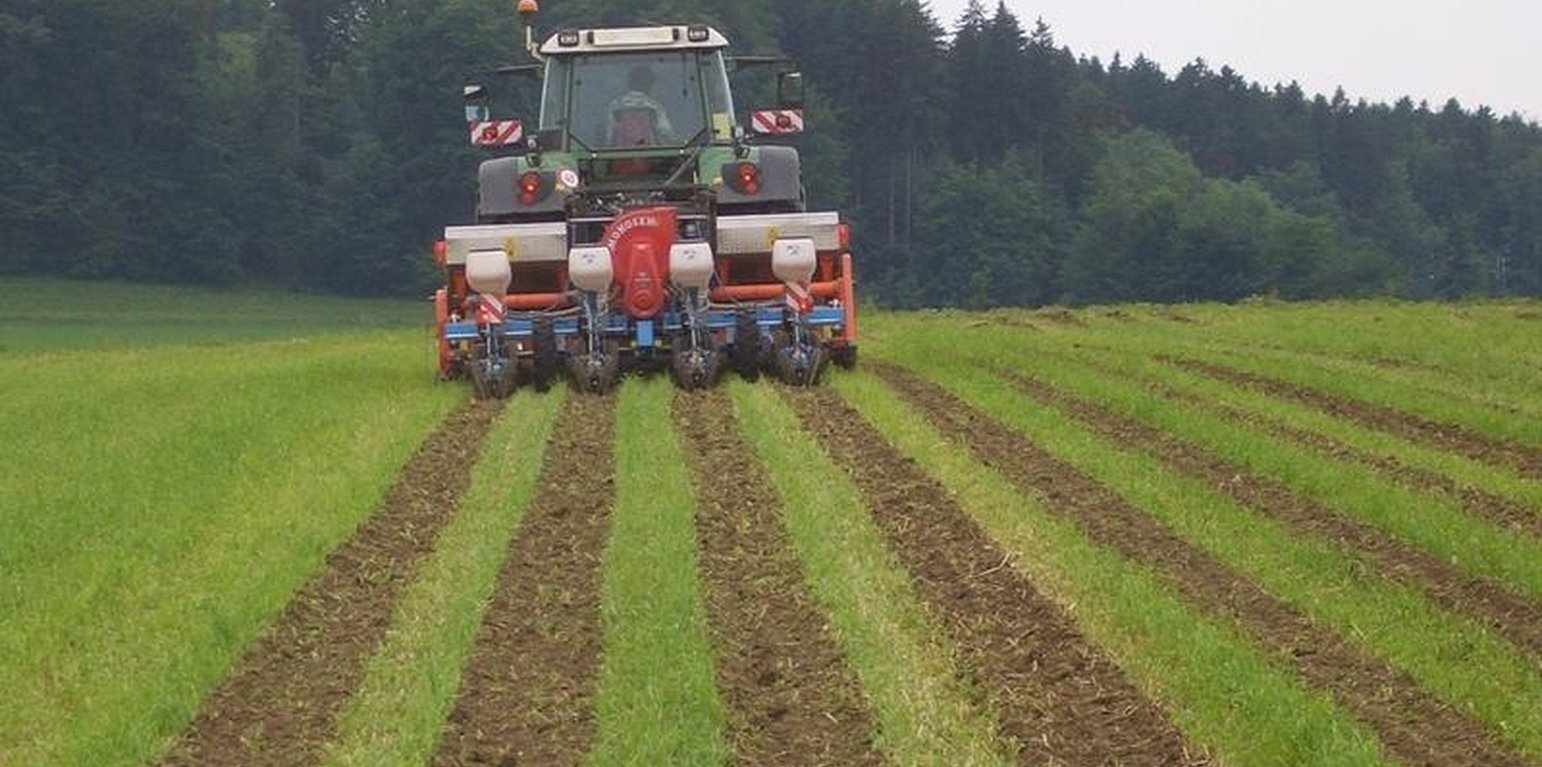




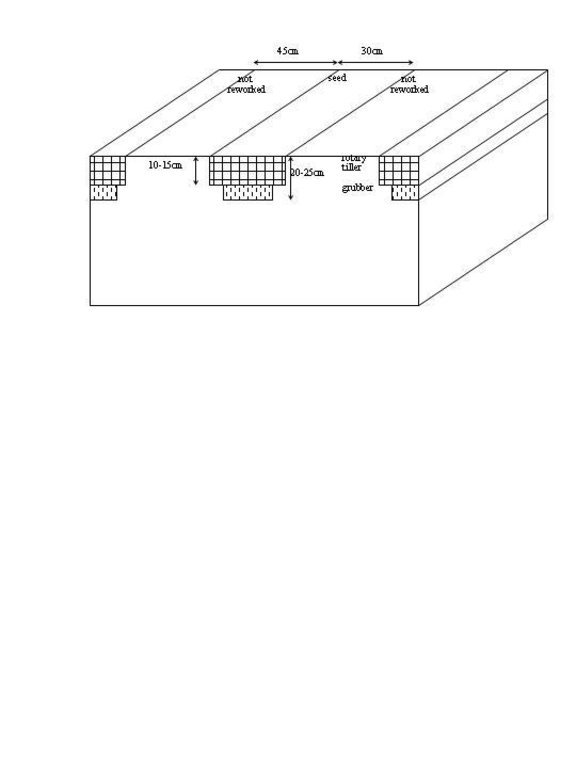
Maize strip tillage is a mixture between no tillage and conventional agriculture. The reworking of the soil greatly reduced. Instead of ploughing and harrowing a special rotary tiller including a grubber is being used. The working depht of the rotary tiller is 10-15cm, the grubber reaches to 20-25cm depht. The machine reworks the soil on stripes of 30cm width. This is where the seeds are planted. In between there are stripes of 45cm width, which are left untouched.
In Switzerland farms usually are small. A major part of the arable land is used to produce fodder. (For example maize, grain, fodder beet)
Usually maize strip tillage is being used to avoid soil erosion or for economical reasons. Compared to conventional agriculture several working steps can be saved. The reworking of the soil, manuring, seeding and applying of herbicides can be done at once.
Since the machine is expensive and a strong tractor is needed, farmers usually don’t buy it on their own. In most cases a contractor will be tasked to do this work. Of course this is not for free. But since several working step are saved, there is more time left to do other work (6.5h/ha).
The reduced reworking of the soil holds remarkable ecological advantages. Occurrence of erosion is very seldom, because the stripes covered by plant residual significantly reduce the speed of surface water. To increase this effect, the stripes are laid along the height countours, if possible. Since the soil structure is not disturbed in the stripes between the seeds, the risk of compaction is reduced there. For that reason maize strip tillage is often used before potatoes in a crop rotation. This is a crop that is very sensitive to soil compaction.
The technique brings along an ecological disadvantage, too. Before sowings the precedent crop needs to be treated with a total herbicide (glyphosat) to avoid unwanted competition. Only in wet areas, where there is enough water available it is possible to not use glyphosat. Also in long time studies, residues of glyphosat could not be detected in the soil. But if ever weeds will develop a resitance against it, that would certainly be a major problem.
The enhanced risk of crop loss is another disadvantage of the technology. In conventional agriculture the soil is left to dry for a few days after ploughing. maize strip tillage does not hold that possibility. If the conditions are wet, risk of crop failure can be a problem. However, if conditions are good (dry enough), both quality and crop yield are similar to conventional agriculture.
Lugar: Oberramsern, Kanton Solothurn, Suiza
No. de sitios de Tecnología analizados:
Difusión de la Tecnología:
¿En un área de protección permanente?:
Fecha de la implementación: 10-50 años atrás
Tipo de introducción





| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (Swiss Franc) | Costos totales por insumo (Swiss Franc) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Equipo | |||||
| Streifenfräse | Machine | 1,0 | 42000,0 | 42000,0 | 100,0 |
| Tractor | Machine | 1,0 | 115000,0 | 115000,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 157'000.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 138'938.05 | ||||
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (Swiss Franc) | Costos totales por insumo (Swiss Franc) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| tillage of stripes, seeding, | ha | 1,0 | 393,0 | 393,0 | 100,0 |
| appliance of total herbicide | ha | 1,0 | 88,0 | 88,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | |||||
| Biocides | ha | 1,0 | 53,0 | 53,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 534.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 472.57 | ||||
steeper hills can be cultivated since the risk for erosion is reduced
droughts: less water scarcity, intense rain: less erosion but the weather needs to be dryer in spring, since the soil cannot be left to dry between ploughing and seeding
Less worksteps need to be done, income remains the same. But a total herbicide and sometimes a little more manure is needed
Since the work is usually outsourced to a contractor, the farmer can use his time for other activities
less worksteps need to be done
Reduced independence if contractors are tasked
more earthworms