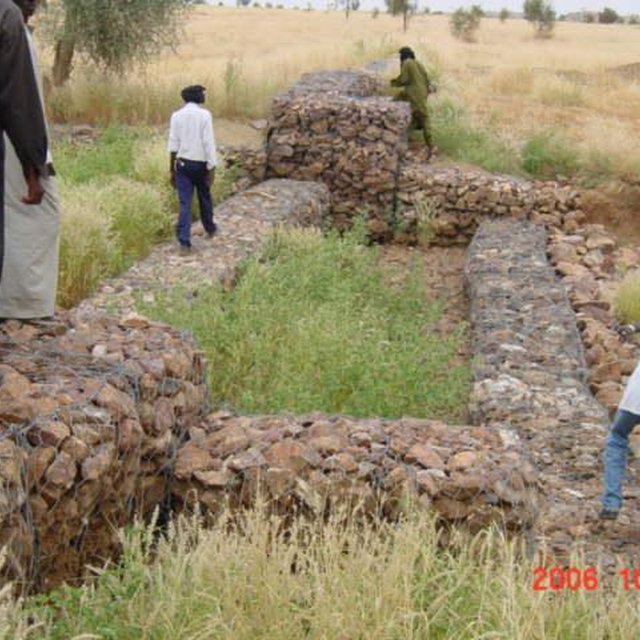
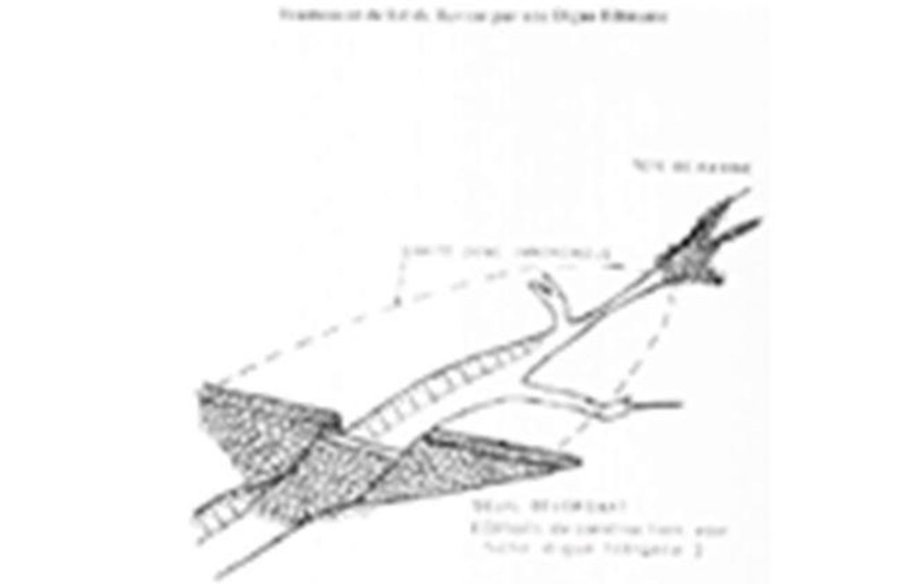
The permeable rock dam is a structure built in gullies using loose rocks and stones and sometimes reinforced with gabions. A filtering layer (blanket of gravel or small stones) is laid in a foundation trench. Further layers of medium-sized and large stones and rocks are laid on top. They are between 0.50 and 3 metres high, and the width of the foundation and the crest depends on the estimated volume of water flow. The structure built across the gully is extended to the sides with the construction of wingwalls that spread the water over a larger area to the sides of the dam. The total width of the structure is generally at least three times its height. The dams can be constructed with or without a spillway. A spillway is required when flood water flow is stronger.
Purpose of the Technology: Permeable rock dams are used to fill in gullies and control water flow. They slow the flow of floodwaters and spread the water over adjacent land. This improves infiltration, and sediment builds up behind the dams. In time, the sediment fills in the gully. This stops lateral drainage from the land on either side, increasing its productivity. High infiltration upstream of the dam contributes to recharging the groundwater system. These structures are therefore also effective in raising the water table in wells and in protecting the bottom-lands from sand filling and gully erosion. They are used in combination with other measures, such as reforestation and stone bunds, to protect and improve the surrounding area, and to increase the area of land that can be used for growing crops.
By dissipating the flow of floodwaters, they ensure better use of rainwater and are therefore important in dry periods. The conservation of water for longer periods and the fine particles of earth trapped by the structure favour the establishment of natural vegetation along it, which helps to stabilise the dam. Seeds are also trapped, favouring the spontaneous growth of grass and trees upstream and downstream, which contributes to restoring and conserving biodiversity.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The sustainability of permeable rock dams depends on the quality of construction and whether they are maintained regularly. A certain amount of expertise and good community organisation is required to repair any cracks in
the dam. Biological measures (sowing grass and planting trees) increase the stability of the structure.
The size of a permeable rock dam can vary considerably from one site to another. The cost is also affected by the distance of the site from the quarry, the topography of the terrain and the actual amount of rock carried in each lorryload. It costs less to construct this type of structure with loose stones and rocks than with gabions.
Lugar: Burkina Faso, Chad, Burkina Faso
No. de sitios de Tecnología analizados:
Difusión de la Tecnología:
¿En un área de protección permanente?:
Fecha de la implementación: 10-50 años atrás
Tipo de introducción