



Reconstitution of soils to generate an Anthroposol is a technology based on the treatment of organic and non-organic pedomaterials or “matrices” (from “matrix” in Latin: everything that is the foundation of something) to achieve ecosystem benefits, especially in areas with degraded, desertified, barren and/or sealed soils. The technology applies a conceptual model based on the production of new soil aggregates with targeted environmental and soil characters generated via a chemico-mechanical process that entails reusing residues of specific origin. The activity is consistent with the principles of a “Circular Economy”, applying restoration ecology, use of compatible waste and saving the non-renewable resource of soil. Reconstitution is covered by two patents of the mcm Ecosistemi s.r.l. company.
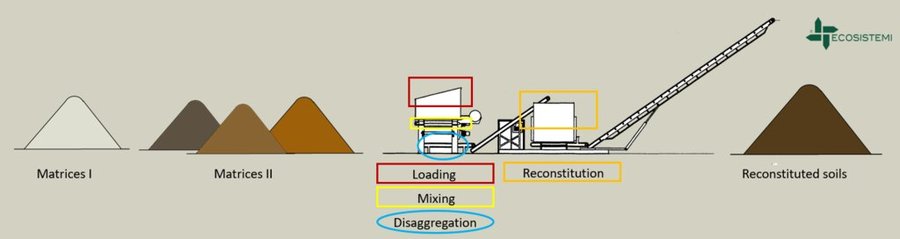
Reconstitution applies the process to two groups of pedomaterials. Firstly, primary matrices (matrices I), represent the main material to be converted into fertile soil. These could be degraded soil itself or inorganic mineral pedomaterials. Secondly, secondary matrices (matrices II) refer to byproducts and waste from production activities. Secondary matrices are divided into two. First, organic - from wood and cellulose processing production activities and from textile and agro-food industries. These are characterized by a high organic component with a high carbon/nitrogen ratio, and a high presence of plant fibres. Second, mineral matrices - especially from mining, the preparation of drinking and industrial water and the management of hydroelectric reservoirs and internal canals. There are four stages.
1) Loading: After the chemico-physico-environmental and rheological characterization of matrices I and II, the materials are selected according to the type of soil desired and then loaded in the plant. Dosage is calculated through an application program (PEDOGÉNIA), which estimates the chemical properties of the finished product.
2) Mixing: The matrices undergo mechanical mixing under controlled humidity.
3) Disaggregation: Breakup and defibering through rotating movements at variable power.
4) Reconstitution: Specifically calibrated cyclic compression and formation of reconstituted soil aggregates.
The treatment generates an Anthroposol whose characters and properties are different from the materials of origin.
The properties of the reconstituted soils and the technical-economic sustainability of the pedotechnology have been demonstrated over the years with agronomical tests and experiments, as well as comparative analysis between degraded soils and reconstituted soils. This demonstrates the reconstituted soil’s ability to create a stable pedosystem to carry out its basic functions - storage, filtration, transformation of nutrients and biodiversity pools - for various forms of land use, and ecosystem benefits. Agroforestry restoration with reconstitution has social impact, as it is demonstrated by a EU project (“New Life”), where the Park of Trebbia river has increased utility to people after restoration. Agronomic restoration allows farmers to increase yields using less fertilizer and water. Another environmental and economic advantage is that manufacturing companies which produce waste can reduce costs through the recycling process of reconstitution. For reconstitution, a plant has to be installed near the land to be restored; an overview is presented in 4.1. In addition, earth moving vehicles are needed for the transport and placement of reconstituted soil.
Lugar: Emilia Romagna, Piacenza; Piemonte, Vicolungo, Italia
No. de sitios de Tecnología analizados: 2-10 sitios
Difusión de la Tecnología: distribuida parejamente sobre un área (approx. 1-10 km2)
¿En un área de protección permanente?: No
Fecha de la implementación: hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
Tipo de introducción














| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (EUR) | Costos totales por insumo (EUR) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| 3 Workers | person/day | 232,0 | 123,0 | 28536,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | |||||
| Construction area - mobile plant | number | 1,0 | 30000,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| Earth moving vehicles | number | 2,0 | 20000,0 | 40000,0 | 100,0 |
| Otros | |||||
| Matrices to be used | m3 | 75000,0 | 15,0 | 1125000,0 | |
| Reconstitution | m3 | 100000,0 | 2,5 | 250000,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 1'473'536.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología en USD | 1'655'658.43 | ||||
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad (EUR) | Costos totales por insumo (EUR) | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras |
| Mano de obra | |||||
| 1 Worker | person/day | 20,0 | 123,0 | 2460,0 | 100,0 |
| 3 Laboratory staff | person/day | 100,0 | 115,0 | 11500,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 13'960.0 | ||||
| Costos totales para mantener la Tecnología en USD | 15'685.39 | ||||
Cantidad antes de MST: 60%
Cantidad luego de MST: 100%
increasing from 60% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils also using less fertilizers and water
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OKrAG6jrqXA
Cantidad antes de MST: 70%
Cantidad luego de MST: 95%
increasing from 70% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that wheat quality. in terms of proteins, increased in reconstituted soils
Cantidad antes de MST: 65%
Cantidad luego de MST: 100%
these increment are estimation
Cantidad antes de MST: 40%
Cantidad luego de MST: 0
decreasing from 40% to 0: this decreasing is an estimation, it's quite impossible a production failure using reconstituted soils because of their high fertility
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D0II3SGNhKo
Cantidad antes de MST: 40
Cantidad luego de MST: 100
simplified from 40% to 100%; because of the physical properties of reconstituted soils; because of the high organic carbon content and the mechanical treatment there is for example a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils, reduction of soil compaction and soil skeleton
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ld8YzGcx6Qw
Cantidad antes de MST: 60%
Cantidad luego de MST: 10%
decreasing from 60% to 10%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils also using less fertilizers and water
Cantidad antes de MST: 60%
Cantidad luego de MST: 100%
increasing from 60% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils and so also farm income increases
Cantidad antes de MST: 60%
Cantidad luego de MST: 100%
increasing from 60% to 100%; because of it's quite impossible a production failure using reconstituted soils because of their high fertility
Cantidad antes de MST: 10%
Cantidad luego de MST: 100%
increasing from 10% to 100%; in a EU project (New Life) we tested that as a consequence the agroforestry restoration with reconstitution, the area of Park of Trebbia river has increased its social usability
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BJ8gFmV1Onc
Cantidad antes de MST: 10%
Cantidad luego de MST: 100%
increasing from 10% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) we tested that as a consequence the agroforestry restoration with reconstitution, the area of Park of Trebbia river has increased its social usability
Cantidad antes de MST: 40%
Cantidad luego de MST: 15%
decreasing from 40% to 15%, this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils for example a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils, reduction of soil compaction and soil skeleton
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rMazUuMaa6o
Cantidad antes de MST: 40%
Cantidad luego de MST: 10%
decreasing from 40% to 10%; some laboratory tests demonstrated that reconstitution improves soils permeability
https://www.youtube.com/shorts/oDhW-YlBjHA
Cantidad antes de MST: 40%
Cantidad luego de MST: 100%
increasing from 40% to 100%; analyzing the water retention curves in many experimentation sites and comparing them with degraded soils, reconstituted soils has demonstrated to have better water holding capacity
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yqtl4-xYMeo
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qy_B3oCyIAM
Cantidad antes de MST: 20%
Cantidad luego de MST: 100%
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species were sprouted naturally
Cantidad antes de MST: 50%
Cantidad luego de MST: 10%
decreasing from 50% to 10%; this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils as soil stability index
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g1GhoyIy4sk
Cantidad antes de MST: 50%
Cantidad luego de MST: 0%
decreasing from 50% to 0%; we tested a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aPQRoaYmrIQ
Cantidad antes de MST: 50%
Cantidad luego de MST: 100%
decreasing from 50% to 100%; because of the high organic carbon content and the mechanical treatment there is for example a reduction of soil compaction in reconstituted soils
Cantidad antes de MST: 60%
Cantidad luego de MST: 100%
increasing from 60% to 100%; the high chemical fertility of reconstituted soils has been demonstrated in a lot of field tests
Cantidad antes de MST: 10%
Cantidad luego de MST: 80%
increasing from 10% to 80%; reconstituted soils has high organic carbon with a high C/N ratio; the SOC/clay is optimal
Cantidad antes de MST: 20%
Cantidad luego de MST: 100%
increasing from 20% to 100% in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QFnUsjYLwfw
Cantidad antes de MST: 20%
Cantidad luego de MST: 100%
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
Cantidad antes de MST: 20%
Cantidad luego de MST: 100%
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
Cantidad antes de MST: 20%
Cantidad luego de MST: 80%
increasing from 20% to 80%; in the EU project (New Life) after we planted over than 3,000 trees and shrubs of 16 indigenous species we recreated an ecological niche
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4Q8tqJNai3o
Cantidad antes de MST: 10%
Cantidad luego de MST: 80%
increasing from 20% to 80%; in the EU project (New Life) after we planted over than 3,000 trees and shrubs of 16 indigenous species we recreated an ecological niche
Cantidad antes de MST: 40%
Cantidad luego de MST: 10%
decreasing from 40% to 10%; because of high water holding capacity, high permeability, physical reconstituted soil properties
Cantidad antes de MST: 40%
Cantidad luego de MST: 0%
decreasing from 40% to 0%; because of high water holding capacity, high permeability, phisical reconstituted soil properties
Cantidad antes de MST: 40
Cantidad luego de MST: 10%
decreasing from 40% to 10%; this is an estimation considering reconstituted soils microbial activity (tests about biological fertility), soil water content (humidity), soil temperature, nutrient availability and pH-value
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ag5wzRVFg9s
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Anetp8gKaQg
Cantidad antes de MST: 20%
Cantidad luego de MST: 50%
increasing from 20% to 50%; because of the CaCO3 content of some matrices II
Cantidad antes de MST: 50%
Cantidad luego de MST: 10%
decreasing from 50% to 10%; this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils