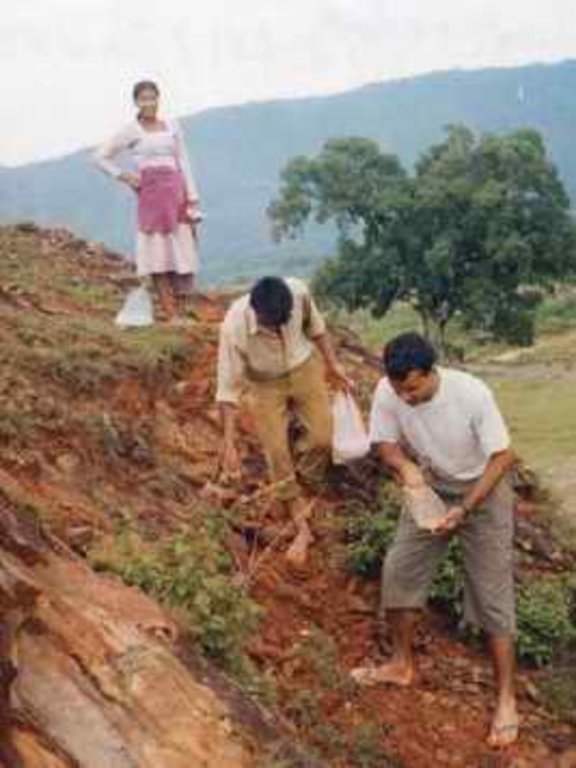
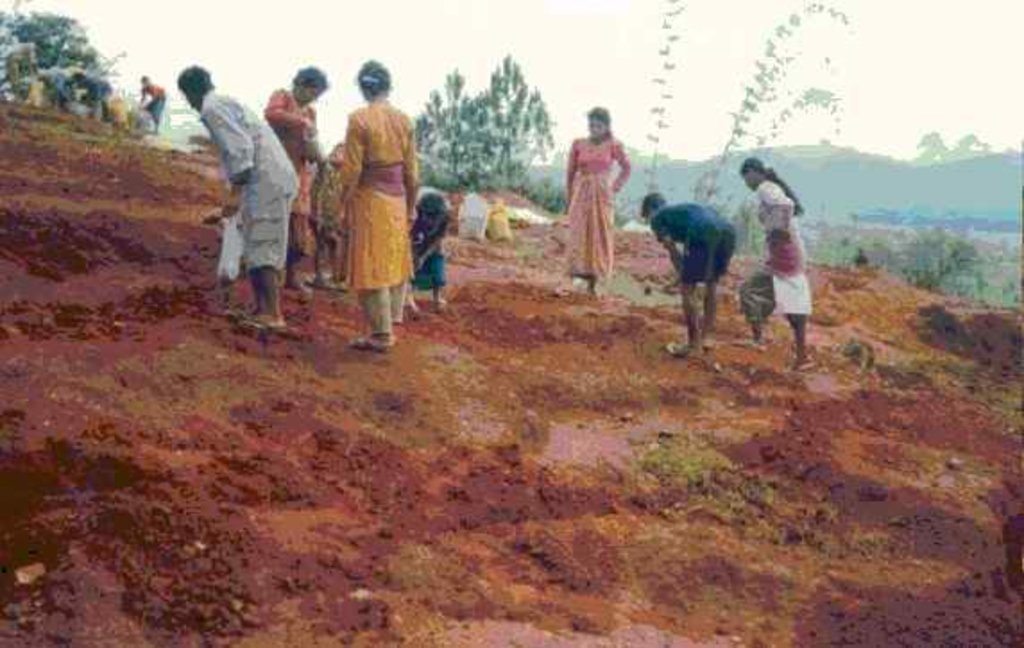
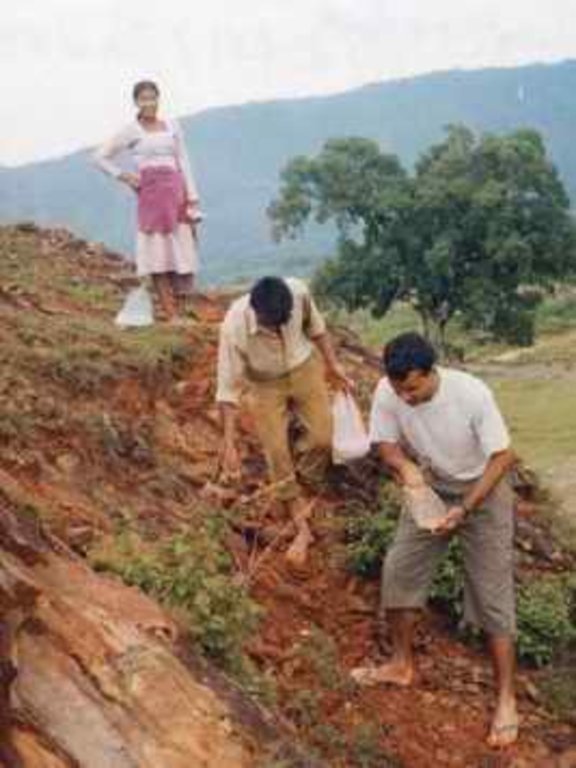
Local initiatives for rehabilitating degraded communal grazing land [Nepal]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Madhav Dhakal
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
Kshetigrasta samudayik charan bhumi punarutthan ma sthaniya agrasarata (Nepali)
approaches_2353 - Nepal
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación del Enfoque
Especialista MST:
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuizaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Nepal1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT :
Sí
1.4 Referencia/s al/los Cuestionario(s) de Tecnologías MST
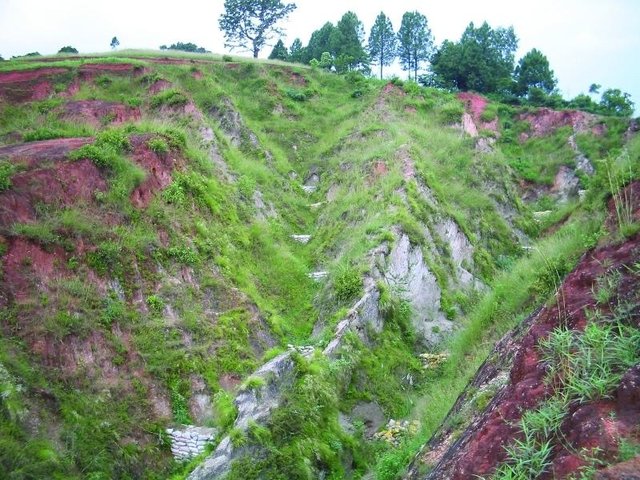

Gully plugging using check dams [Nepal]
Small dam structures constructed across erosion gullies
- Compilador: Nicole Guedel
2. Descripción del Enfoque MST
2.1 Breve descripción del Enfoque
Supporting local initiatives and building local capacity for the rehabilitation of degraded communal land in the middle mountains of Nepal.
2.2 Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST
Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST:
Aims / objectives: The main aim of the People and Resource Dynamics Project's (PARDYP) land rehabilitation activities were to help watershed residents, local groups, and line agencies understand the key issues and to test options for the improved management of water, land, and forests in a participatory way. In Dhotra VDC (Kavrepalanchok district) a local youth club (Ekantabasti Youth Club) had been trying to rehabilitate a 2.5 ha area of degraded communal land since May 2004. The club approached PARDYP for technical assistance. The area had been degraded by overgrazing with two big gullies formed and small landslips along the gullies affecting a trail and the adjoining agricultural land. An unsuccessful attempt had been made to plant the area eight years previously. It had failed due to the difficulty of retaining soil moisture in the area's compacted red soils. A series of meetings were organised to plan future activities, to ensure community participation, and to share responsibilities among local users and PARDYP. The community was committed to rehabilitating the area and took the responsibility for planting, protection, and overall management of the planted species. PARDYP provided planting materials and technical help. A needs assessment with the local people identified the most useful tree species. They entrusted the selection of appropriate grass and hedgerow species to the project's expertise. Project staff arrange for planting materials and logistical support, and showed villagers how to make eyebrow pits, plant hedgerows, and plug gullies. About 450 villagers participated in the rehabilitation activities with women contributing more than half of the labour. They worked four hours a day for 16 mornings.
Methods: A five-women strong user committee was formed to manage and protect the planted species and a five-man strong task force was set up to maintain regular links and coordination between the user committee, the youth club, and the villagers. The coordination committee, with guidance from the youth club, was responsible for facilitating and coordinating all the second season rehabilitation work in 2005.
2.3 Fotos del Enfoque
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde el Enfoque fue aplicado
País:
Nepal
Especifique más el lugar :
Kavrepalanchowk/ Jhikhu khola watershed
Map
×2.6 Fechas de inicio y conclusión del Enfoque
Año de conclusión (si el Enfoque ya no se aplica):
2005
2.7 Tipo de Enfoque
- proyecto/ basado en un programa
2.8 Propósitos/ objetivos principales del Enfoque
The Approach focused on SLM only
- To demonstrate appropriate technologies for rehabilitating degraded land and evaluating their effectiveness. - To provide training on soil and water conservation (SWC) technologies for effectively implementing the rehabilitation activities and to build the capacity of the local community to carry out the work. - To organise and mobilise a local community for implementing, protecting and managing the planted areas and the physical structures
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - Lack of awareness about low cost soil and water conservation technologies that address farmers' needs. - Weak institutional collaboration for developing and implementing technologies
2.9 Condiciones que facilitan o impiden la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
disponibilidad/ acceso a recursos y servicios financieros
- impiden
Government incentives lacking
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Cost-effective technology demonstrated; planting materials and other logistic support provided
entorno institucional
- impiden
Weak institutional collaboration for technology development and demonstration
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Collaboration with local youth club; formation of user committee and task force
marco de trabajo legal (tenencia de tierra, derechos de uso de tierra y agua)
- impiden
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights hindered a little the approach implementation The land is owned by the state and prior to starting the work there was a conflict over where the boundaries lay. Adjacent private landowners illegally claimed a part of the land but withdrew their claims before the rehabilitation work started. The existing land ownership and land use rights hindered the implementation of the approach at the beginning.
conocimiento de MST, acceso a apoyo técnico
- impiden
Limited knowledge of appropriate SWC technologies and limited technical know-how to implement them
Treatment through the SLM Approach: On-site training and exchange visits organised to demonstration sites
3. Participación y roles de las partes interesadas involucradas
3.1 Partes interesadas involucradas en el Enfoque y sus roles
- usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales
Planning, implementing SLM activities and protection. Men and women worked equally. About 450 villagers participated in the rehabilitation activities. Women's participation was a little higher, they provided 56% of the labour.
- especialistas MST/consejeros agrícolas
- ONG
Technical and logistics support
- gobierno nacional (planificadores, autoridades)
Si varias partes interesadas estuvieron involucradas, indique la agencia principal:
Initiation and implementation by local youth club representing land users. Technical and logistics support by national specialists
3.2 Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales en las distintas fases del Enfoque
| Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales | Especifique quién se involucró y describa las actividades | |
|---|---|---|
| iniciación/ motivación | interactivo | Local youth club approached PARDYP for technical help during a meeting. |
| planificación | interactivo | Public meetings organised to share responsibilities. Land users took responsibility for land preparation, planting, protection, grazing control, and overall management of planted species. Men and women performed planned activities together. Construction of eyebrow pits done mostly by men. Filling o |
| implementación | auto-movilización | Self-mobilised group under leadership of youth club implemented the activities; technical guidance during implementing period provided by project |
| monitoreo y evaluación | interactivo | Survival of planted species, effect of eyebrow pits, performance of species and check dams were monitored/observed. Results shared in public meetings and reported to the project |
| Research | ninguno |
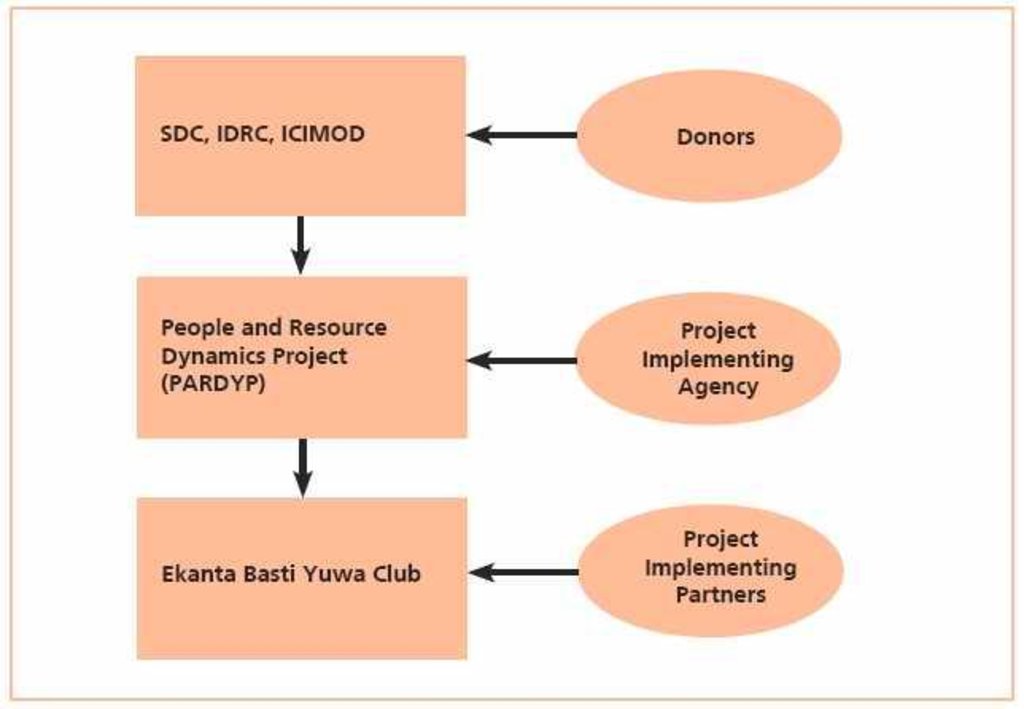
3.3 Flujograma (si estuviera disponible)
Descripción:
PARDP project donors and implementing partners: SDC: (Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation); IDRC (Internat. Development Research Centre); ICIMOD
Autor:
Dhakal Madhav
3.4 La toma de decisiones en la selección de Tecnología(s) MST
Especifique quién decidió la selección de las Tecnología/ Tecnologías a implementarse:
- principalmente por especialistas MST en consulta con usuarios de tierras
Explique:
A local youth club (Ekantabasti youth club) has initiated rehabilitation activities on the degraded communal land since May 2004. The youth club approached PARDYP for the technical assistance.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. Villagers took the responsibility for planting, protecting, and overall management of the planted species. PARDYP arranged planting materials and technical support
4. Apoyo técnico, fortalecimiento institucional y gestión del conocimiento
4.1 Construcción de capacidades / capacitación
¿Se proporcionó la capacitación a usuarios de tierras/ otras partes interesadas?
Sí
Especifique quién fue capacitado:
- usuarios de tierras
Forma de capacitación:
- áreas de demostración
Temas avanzados:
On-site training sessions were organised for establishing the eyebrow pits, contour hedgerows, gully treatments, and check dams and their maintenance.
4.2 Servicio de asesoría
¿Los usuarios de tierras tienen acceso a un servicio de asesoría?
Sí
Especifique si servicio proporcionado se realizó:
- en los campos de los usuarios de tierras
Describa/ comentarios:
Name of method used for advisory service: Rehabilitation of degraded land thorough demonstration and training; Key elements: On site training, Demonstration, Exchange visits and public meetings; After implementing the technology, a number of exchange and interaction, audio visual presentation, and monitoring programmes were carried out as a scaling up strategy.
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Trained human resources can continue the activities.
4.3 Fortalecimiento institucional (desarrollo institucional)
¿Se establecieron o fortalecieron instituciones mediante el Enfoque?
- sí, moderadamente
Especifique el nivel o los niveles en los que se fortalecieron o establecieron las instituciones:
- local
Especifique el tipo de apoyo:
- construcción de capacidades/ entrenamiento
Proporcione detalles adicionales:
Technical training was provided to local youth club.
4.4 Monitoreo y evaluación
¿El monitoreo y la evaluación forman parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Comentarios:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: soil type and texture
technical aspects were regular monitored through measurements; indicators: performance of planted species and their survival rates
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: preferred tree species and closing the area for grazing
economic / production aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: seed and grass production
no. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations; indicators: participation in maintaining planted species and structures
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: The users increased the size of the eyebrow pits and dug new pits and extended the hedgerow lines to fill in gaps; but the overall approach was not changed.
4.5 Investigación
¿La investigación formó parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Especifique los temas:
- tecnología
Proporcione detalles adicionales e indique quién hizo la investigación:
Research was not a major focus of the approach although the performance and survival rates of planted species, and performance of eyebrow pits and connecting drainage trenches were regularly observed.
Research was carried out on-farm
5. Financiamiento y apoyo material externo
5.1 Presupuesto anual para el componente MST del Enfoque
Si no se conoce el presupuesto anual preciso, indique el rango:
- < 2,000
Comentarios (ej. fuentes principales de financiamiento/ donantes principales):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (SDC, IDRC, ICIMOD): 90.0%; local community / land user(s) (materials and tools for training): 10.0%
5.3 Subsidios para insumos específicos (incluyendo mano de obra)
- agrícola
| Especifique qué insumos se subsidiaron | En qué grado | Especifique los subsidios |
|---|---|---|
| semillas | From projects own seed bank | |
| Seedlings | parcialmente financiado | Some locally arranged and some from forest departm |
Si la mano de obra de usuarios de tierras fue un insumo sustancial, ¿fue:
- voluntario?
Comentarios:
Land users involvement was fully voluntary, they worked together in a cooperative spirit to improve their common degraded land.
5.4 Crédito
¿Se proporcionó crédito bajo el Enfoque para actividades MST?
No
6. Análisis de impacto y comentarios de conclusión
6.1 Impactos del Enfoque
¿El Enfoque ayudó a los usuarios de tierras a implementar y mantener Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
An organized land users' group was formed, and awareness on SLM increased.
¿El Enfoque mejoró cuestiones de tenencia de tierra/ derechos de usuarios que obstaculizaron la implementación de la Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Project requested the users to solve the problem before rehabilitation work, users community and private land users solved the issue by measuring area of the community land. An authorized technician from the government office helped solving the issue.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The approach adopted during rehabilitation activities is quite standard and is taken by many other land management and community development projects.
6.2 Motivación principal del usuario de la tierra para implementar MST
- conciencia medioambiental
reduction of soil erosion
- mejoramiento estético
to maintain greenery.
6.3 Sostenibilidad de las actividades del Enfoque
¿Pueden los usuarios de tierras sostener lo que se implementó mediante el Enfoque (sin apoyo externo)?
- incierto
Si respondió no o incierto, especifique y comente:
Land users planned to upscale the technology and its related approach to rehabilitate the degraded areas of their community forest but it hasn't happened yet.
6.4 Fortalezas/ ventajas del Enfoque
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Suitable technologies were shared and valuable knowledge given during the rehabilitation work (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue this incorporating new ideas) |
| Community institution strengthened, and some money (US$ 17) raised by selling grasses and grass seed within two years of rehabilitation. Money used for social activities (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: As above) |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Site visits and focus group discussion meetings were effective for disseminating and scaling up the approach (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue these initiatives on a regular basis to strengthen land users??? involvement in SLM activities) |
| Among total participants, women's participation was higher. User committee was made up of just women (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue this) |
| The local youth club played a key role in rehabilitation activities - a key factor for sustainability and continuity (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: More local institutions should be identified and involved.) |
| This is a bottom-up approach with the rehabilitation activities purely demand driven. Farmers' priorities for tree species to be planted were identified in a participatory way (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue by including new priorities) |
6.5 Debilidades/ desventajas del Enfoque y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Research was not a main focus of the activity, and not enough options were explored. | Explore and test more options |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Collaboration with government line agencies was lacking | Rehabilitation work should be carried out involving all main stakeholders |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
7.2 Referencias a publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management, Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. Kathmandu: ICIMOD
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
ICOMOD
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Gully plugging using check dams [Nepal]
Small dam structures constructed across erosion gullies
- Compilador: Nicole Guedel
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos