Facilitation of community-based pasture management initiatives [Tayikistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Mizrob Amirbekov
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger
Mountain Societies Development Support Programme - Aga Khan Foundation
approaches_2444 - Tayikistán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación del Enfoque
Especialista MST:
Pachova Nevelina
Palm
Nombre del proyecto que facilitó la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque (si fuera relevante)
Sustainable Land Management in the High Pamir and Pamir-Alai Mountains (PALM Project / NCCR)Nombre del proyecto que facilitó la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque (si fuera relevante)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
Kyrgyzstan Mountain Societies Development Support Programme, Aga Khan Development Network (MSDSP KG) - Kirguistán1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT :
Sí
2. Descripción del Enfoque MST
2.1 Breve descripción del Enfoque
Initiation of community-based solutions to slow down pasture degradation, and to improve pasture use and management in three pilot Jamoats of upland Tajikistan.
2.2 Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST
Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST:
Aims / objectives: During the Soviet times land users in Tajikistan were allowed to keep very little livestock individually and this was mainly in the vicinity of rural settlements. The majority of the livestock were managed by collective agricultural farms, which utilised different seasonal pastures. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, the previously state-owned livestock was distributed among individual farmers, most of whom had limited knowledge and experience with pasture management (PM), and capacities to access the distant pastures used by the collective farms. As a consequence, the amount of livestock kept in the vicinity of rural settlements increased, leading to overgrazing and severe degradation of nearby pastures. In the framework of a project on sustainable land management in the Pamir-Alai region (PALM), funded by the Global Environment Facility (GEF), MSDSP facilitated the initiation of community-based solutions to the problem of pasture degradation at three pilot jamoats in Jirgital, and three in Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Oblast (GBAO).
Methods: 1. Awareness raising and capacity building of PM issues. 2. Integration of PM issues in village development plans. 3. Grant support and community co-financing for implementation of targeted measures. 4. Monitoring of the impacts of the implemented measures as a basis for up-scaling.
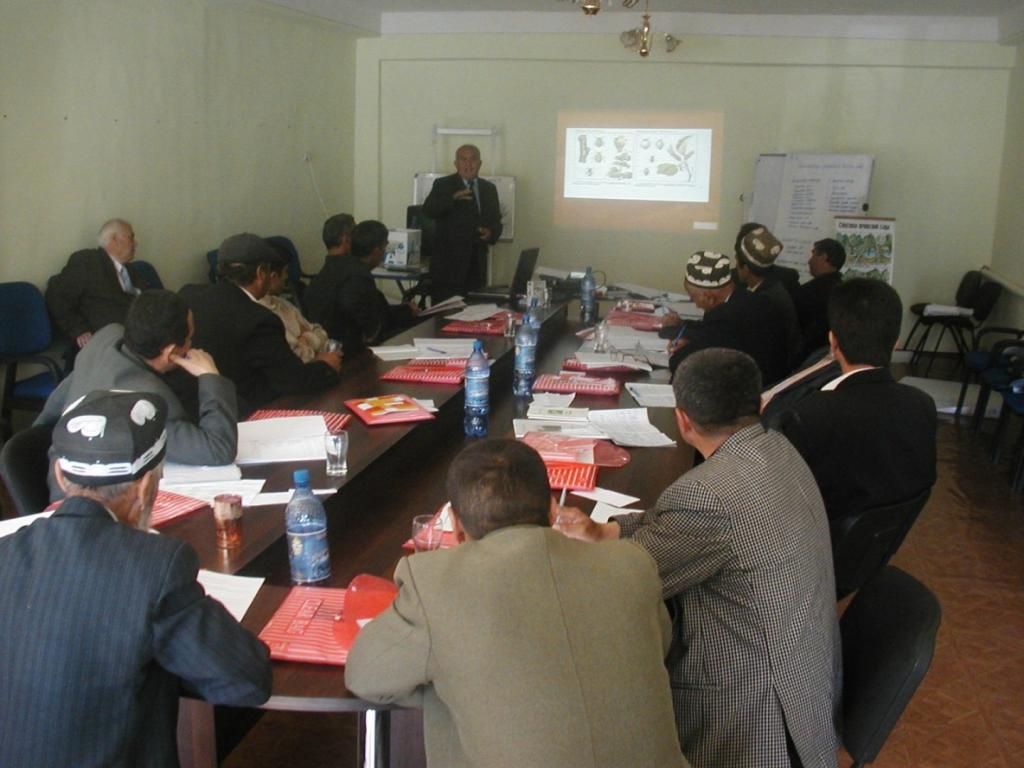
Stages of implementation: 1. National pasture management experts from the Pamir Biological Institute held a training of trainers (ToT) session for MSDSP facilitators and district specialists, who conducted follow-up training on PM at the pilot communities in 2009. 2. Pilot communities identified key problems related to PM in the process of Village Development Planning facilitated by MSDSP, and prioritised targeted measures for improved PM. 3. A set of micro-project proposals were developed based on the prioritised measures, which focused on (re-) construction of roads and bridges for improved access to pastures, and construction of stables during spring/autumn, as well as summer pastures. 4. Monitoring of the impacts of the implemented measures as a basis for up-scaling.
Role of stakeholders: Community members were engaged in identifying and implementing targeted measures for addressing pasture use and management issues. Jamoat level non-governmental organisations called Social Unions for Development of Village Organizations (SUDVOs), coordinated and supported the identification and implementation of the selected projects in several village organisations. Governmental agricultural extension agents were engaged in training, and consulted in the review process. MSDSP staff facilitated the overall process and engaged in monitoring progress with implementation. PALM project staff engaged in the review, monitoring and assessment of the impacts of the supported measures.
2.3 Fotos del Enfoque
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde el Enfoque fue aplicado
País:
Tayikistán
Especifique más el lugar :
Jirgatol
Comentarios:
Three pilot jamoats in the Jirgital region (Jirgital, Pildon and Yangishar), and three in Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Oblast (GBAO), (Shitharv, Vankala and Alichur) were covered by the approach
Map
×2.6 Fechas de inicio y conclusión del Enfoque
Indique año del inicio:
2009
2.7 Tipo de Enfoque
- proyecto/ basado en un programa
2.8 Propósitos/ objetivos principales del Enfoque
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (rehabilitation of rural infrastructure to improve access to pastures, pasture and livestock productivity, animal diseases)
The main aim of the approach was to initiate the improved use and management of pastures, by raising awareness and knowledge on issues regarding pasture degradation and sustainable pasture management, mobilising community action, and pilot-testing selected technologies and measures for improving pasture management in highly degraded areas.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: pasture degradation, overgrazing, restricted pasture area and too many cattle garzing, lack of infrastructure (bridges, roads, shelters), lack of knowledge about pasture management
2.9 Condiciones que facilitan o impiden la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
disponibilidad/ acceso a recursos y servicios financieros
- impiden
communities were lacking funds for infrastructure development and could therefore not invest in the construction of roads and bridges
Treatment through the SLM Approach: GEF funds were used to support communities in financing infrastructural improvements which allowed for more productive and sustainable use of available pasture resources
entorno institucional
- impiden
Lack of capacity to deal with pasture degradation problems
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Engagement of village organisations, and social unions of village organisations (SUDVO) in addressing pasture management issues at six pilot jamoats
marco de trabajo legal (tenencia de tierra, derechos de uso de tierra y agua)
- impiden
Limited clarity regarding responsibilities and lack of incentives for sustainable pasture management
Treatment through the SLM Approach: MSDSP and PALM project members recommended the development of a pasture management law that addresses those legal constrains
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately hindered the approach implementation there is no law about pasture management in Tajikistan, therefore it was difficult to regulate the process
conocimiento de MST, acceso a apoyo técnico
- impiden
technical knowledge about pasture management was lacking as during Soviet times people were not allowed to keep a lot of livestock
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Community members of village organisations and relevant government experts were trained in various issues of pasture management
3. Participación y roles de las partes interesadas involucradas
3.1 Partes interesadas involucradas en el Enfoque y sus roles
- usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales
Village organisations
Only 20% of the participants were women, since men are responsible for managing the livestock, while women are concerned with livestock products only
Elderly members of the communities were engaged in discussions on the possible solutions
- especialistas MST/consejeros agrícolas
Governmental agricultural advisors participated in the training.
- gobierno nacional (planificadores, autoridades)
Agrarian University in Jirgatol, Pamir Biological Institute
- pilot communities
3.2 Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales en las distintas fases del Enfoque
| Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales | Especifique quién se involucró y describa las actividades | |
|---|---|---|
| iniciación/ motivación | ninguno | |
| planificación | interactivo | Members of village organisations were involved in training and planning on pasture management, and actively participated in discussions |
| implementación | auto-movilización | The village organisations developed their own project ideas and submitted those proposals to MSDSP and other funders |
| monitoreo y evaluación | interactivo | Land users were engaged in the monitoring and evaluation of the impacts of the implemented projects |
| Research | interactivo | The Pamir-Biological Institute and the Institute of Botany under the Academy of Sciences were engaged in research and technical consultations |
3.4 La toma de decisiones en la selección de Tecnología(s) MST
Las decisiones para la selección de la/s Tecnología(s) fueron tomadas:
- pilot communities
Explique:
Community members were engaged in identifying and implementing targeted measures for addressing pasture use and management issues.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by pilot communities and facilitators. Community members were engaged in identifying and implementing targeted measures for addressing pasture use and management issues.
4. Apoyo técnico, fortalecimiento institucional y gestión del conocimiento
4.1 Construcción de capacidades / capacitación
¿Se proporcionó la capacitación a usuarios de tierras/ otras partes interesadas?
Sí
Especifique quién fue capacitado:
- usuarios de tierras
- personal de campo/ consejeros
Forma de capacitación:
- cursos
Temas avanzados:
Short training courses were provided for land user, field staff/agricultural advisors
4.2 Servicio de asesoría
¿Los usuarios de tierras tienen acceso a un servicio de asesoría?
Sí
- through trained experts
Describa/ comentarios:
Name of method used for advisory service: Engineering support and technical consultations
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities
4.3 Fortalecimiento institucional (desarrollo institucional)
¿Se establecieron o fortalecieron instituciones mediante el Enfoque?
- sí, mucho
Especifique el nivel o los niveles en los que se fortalecieron o establecieron las instituciones:
- local
Especifique el tipo de apoyo:
- construcción de capacidades/ entrenamiento
Proporcione detalles adicionales:
village organisations were trained
4.4 Monitoreo y evaluación
¿El monitoreo y la evaluación forman parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Comentarios:
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: changes in economic benefits for households before and after implementation of project
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: changes in vegetation coverage, edible grass species, etc.
area treated aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: Established at the start of project implementation
There were several changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Some areas were grazed although they should not have been, project staff then talked to the responsible people in the village to ask about the causes for this and to try and initiate changes in practice.
4.5 Investigación
¿La investigación formó parte del Enfoque?
Sí
- pasture management
Proporcione detalles adicionales e indique quién hizo la investigación:
Aimed at problem, option and impact assessment
Research was carried out on-farm
5. Financiamiento y apoyo material externo
5.1 Presupuesto anual para el componente MST del Enfoque
Si no se conoce el presupuesto anual preciso, indique el rango:
- 2,000-10,000
Comentarios (ej. fuentes principales de financiamiento/ donantes principales):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (PALM): 70.0%; national non-government (MSDSP): 30.0%
5.2 Apoyo financiero/material proporcionado a los usuarios de tierras
¿Los usuarios de tierras recibieron financiamiento/ apoyo material para implementar la Tecnología/ Tecnologías? :
No
5.3 Subsidios para insumos específicos (incluyendo mano de obra)
- infraestructura
| Especifique qué insumos se subsidiaron | En qué grado | Especifique los subsidios |
|---|---|---|
| caminos | parcialmente financiado | |
| bridges, shelters | parcialmente financiado | |
Si la mano de obra de usuarios de tierras fue un insumo sustancial, ¿fue:
- voluntario?
5.4 Crédito
¿Se proporcionó crédito bajo el Enfoque para actividades MST?
No
6. Análisis de impacto y comentarios de conclusión
6.1 Impactos del Enfoque
¿El Enfoque ayudó a los usuarios de tierras a implementar y mantener Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Reduced pressures on pastures in the vicinity of rural settlements
¿El Enfoque empoderó a grupos en desventaja social y económica?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Elderly herders with improved access to health facilities
¿El Enfoque mejoró cuestiones de tenencia de tierra/ derechos de usuarios que obstaculizaron la implementación de la Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
talks with the government were started to make way for a law on pasture management
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Strong interest by other communities but limited financial means for replication
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Improved access to fodder, reduced loss of livestock, etc
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The primary beneficiaries are the groups with a medium income
6.2 Motivación principal del usuario de la tierra para implementar MST
- producción incrementada
Increased pasture area and livestock productivity, reduced loss of livestock, reduced labour inputs
- conciencia medioambiental
Increased awareness of the degradation of pastures
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
Improved convenience, reduced conflicts over livestock tramping and grazing of croplands
6.3 Sostenibilidad de las actividades del Enfoque
¿Pueden los usuarios de tierras sostener lo que se implementó mediante el Enfoque (sin apoyo externo)?
- sí
Si respondió que sí, describa cómo:
The village organisations have the responsibility to teach their community members
6.4 Fortalezas/ ventajas del Enfoque
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Reduction of conflicts over resource use and strengthened social capital (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: utilise the improved social capital for addressing other pressing environmental and community development issues) |
| Improved income from livestock provides a strong incentive for sustaining the established infrastructure (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: a proportion of the obtained income should be reinvested in maintenance e.g. through collection of user fees ) |
| Improved environmental conditions in the vicinity of rural settlements, and reduced labour inputs into livestock breeding (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: capitalise on those environmental improvements through the development of alternative income-generating activities such as bee-keeping and eco-tourism that will limit the need for further increases in livestock numbers) |
6.5 Debilidades/ desventajas del Enfoque y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Improved access to new pastures and possible further increases in livestock numbers may lead to their degradation in the future | Community members and village organisations have to make sure that the new pastures are being used in a sustainable manner e.g. through controlled grazing and pasture rotation, designation of no-grazing areas in pristine forests in the vicinity of new pastures, etc. |
| The approach contributes to improve the well-being of the medium income groups of the communities in question, as accessing distant pastures is most often not a problem for the better-off, while the poor often have only limited or no livestock | use as part of the generated additional income in the community for support of poor households |
| The approach is economically beneficial but difficult to up-scale due to the high initial investment costs | identify appropriate mechanisms for stimulating replication through relevant legal and policy incentives or alternative financing |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos