State-controlled research territory for orcharding [Tayikistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Christian Wirz
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
approaches_2566 - Tayikistán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación del Enfoque
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suiza1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
20/08/2008
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT :
Sí
1.4 Referencia/s al/los Cuestionario(s) de Tecnologías MST

Combined cut-and-carry and fruit-production system with terraces [Tayikistán]
A combination of fruit- and nut-trees together with seminatural trees and shrubs on one side with grass-communities on the other side provide for a diversified production system.
- Compilador: Christian Wirz
2. Descripción del Enfoque MST
2.1 Breve descripción del Enfoque
Cultivation of an orchard with research activities and research staff with food for work.
2.2 Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST
Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST:
Aims / objectives: The main objective is to dispose of varieties of fruits that are adapted to different conditions. Another objective is to prevent degradation and test methods of rehabilitation and to spread this knowledge. The orchard was also implemented as a source of labour for 50 employees. In the last years it has become more important to acquire self-sufficiency by fruit- and hay-production, because wages cannot always be paid. And because of limited state-support in terms of fertilisers, pesticides and machines, the selling of tree saplings is important.
Methods: Work is subdivided into research, whereby the analysis of soils is carried out in laboratories, into conservation methods carried out by field staff and the brigadier himself (planting fruit and other trees, grafting fruit trees, planting and maintaining tree saplings, combatting pests and forbs) and harvest (of fruits and hay) that is carried out by all the employees and their families. The fruits are partly dried and sold.
Stages of implementation: After the terraces being built and the trees being planted in the early 1960ies, the orchard needed to be maintained: e.g. annually trees are substituted and fertilisers, manure and pesticides are applied. When trees are not grown, intercropping is possible. Since 1992 soils on the terraces, between the trees, are not tilled anymore, because rees are too high.
Role of stakeholders: The workers are initially employed for a clearly defined work such as tractor driver, research coordinator or research scientist. They execute orders given by their superiors. In the years after independance the strict subdivision is broken up and the research station is more independent. During civil war, when the district government was nearly inexistant, the land needed to be distributed among the employees, who were now land rentors and had to maintain their part of the orchard by themselves: It was the only way to protect the orchard from being destroyed, says the research coordinator.
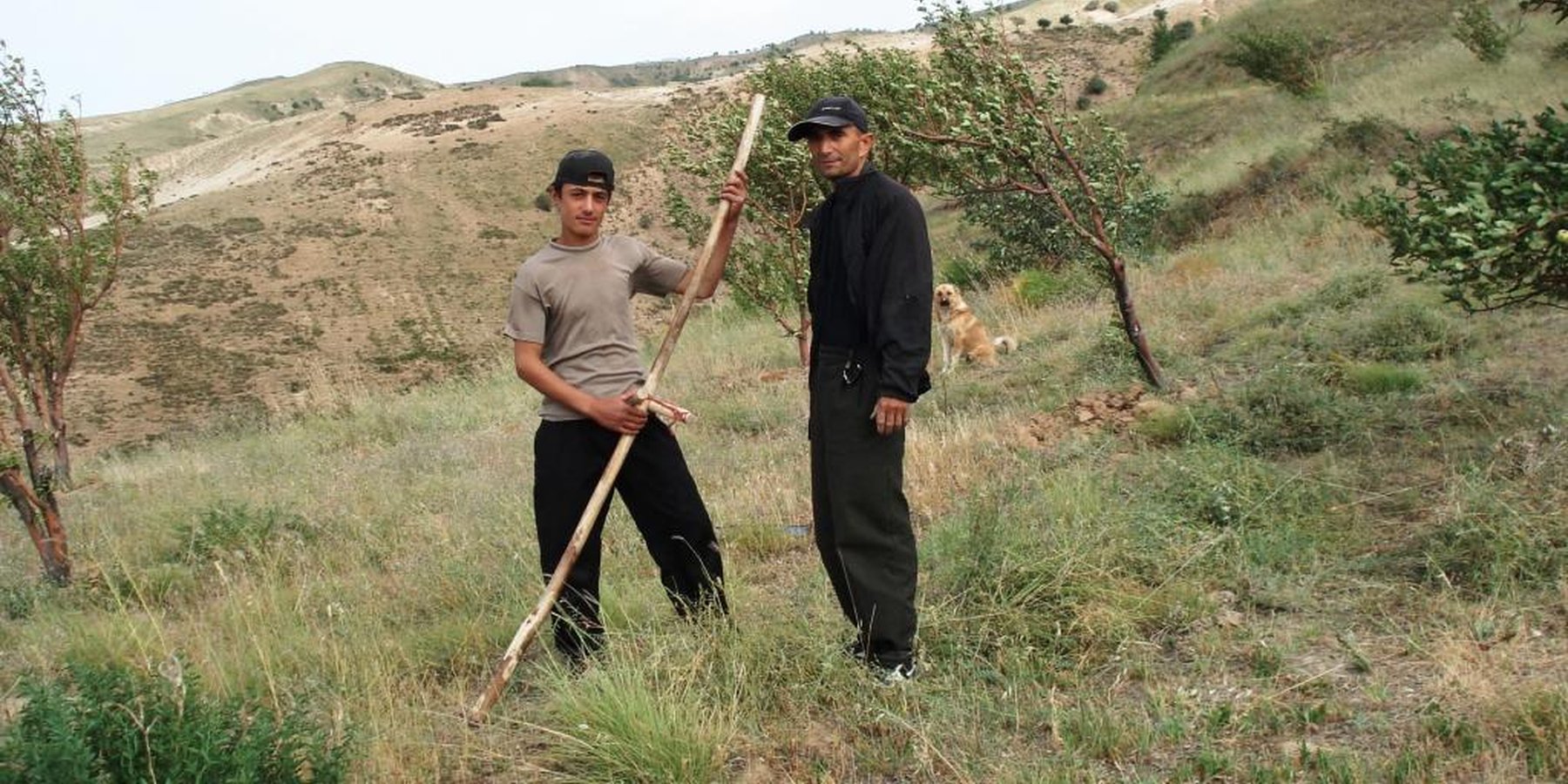
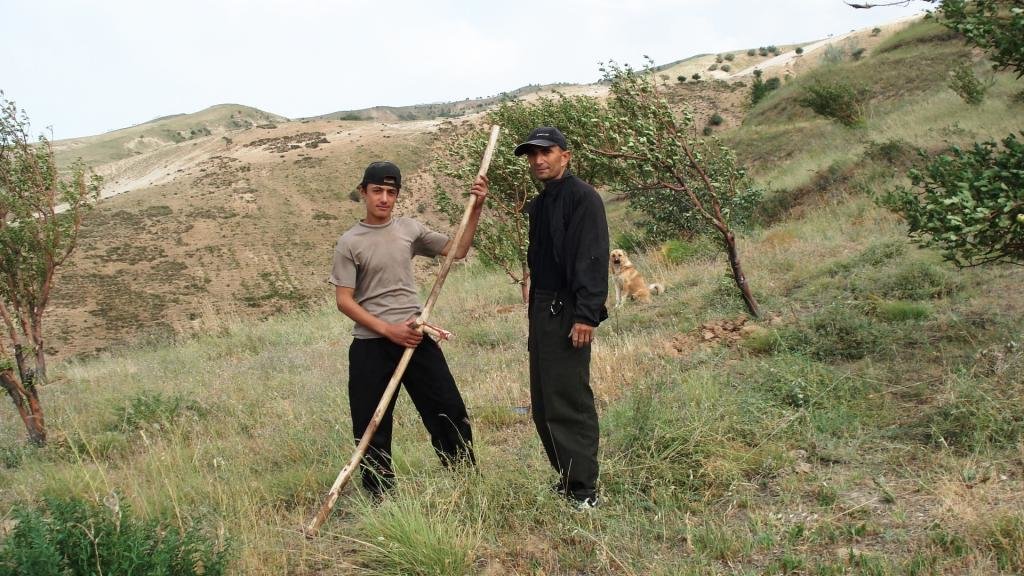
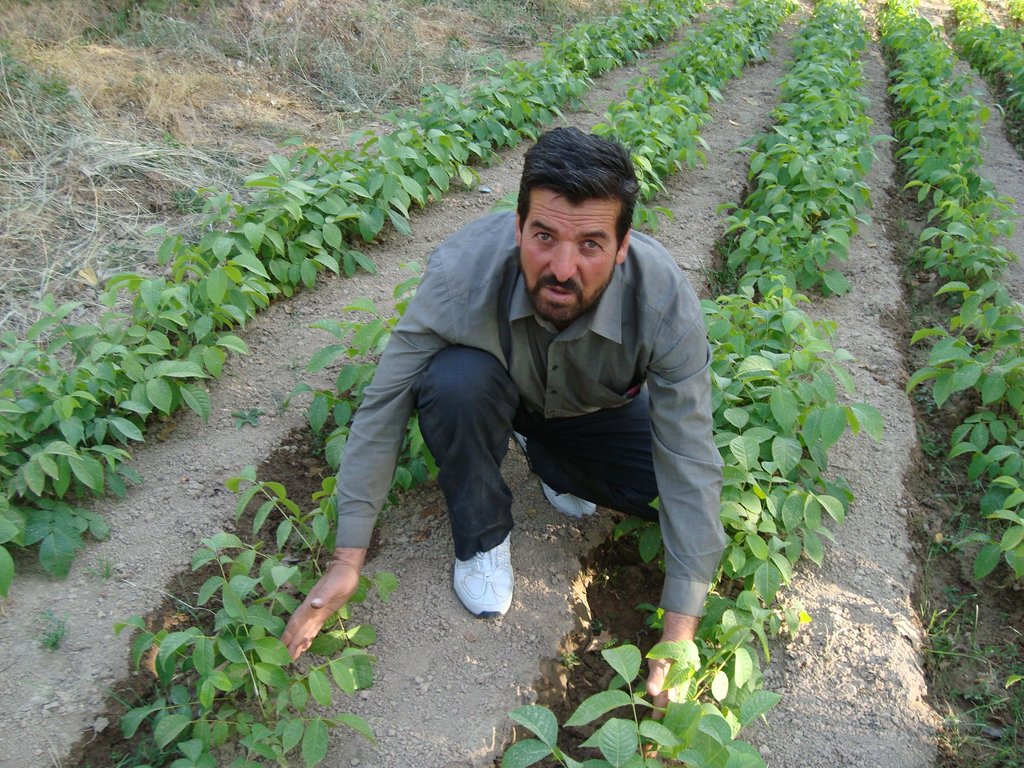
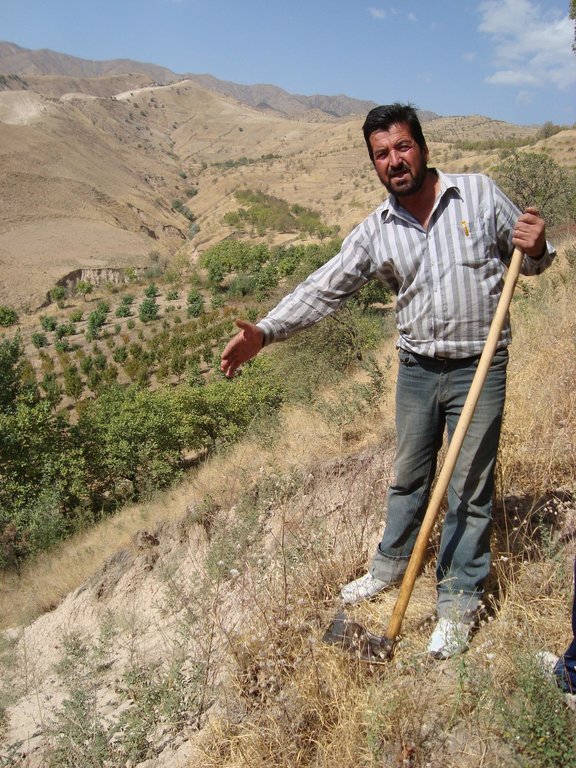
2.3 Fotos del Enfoque
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde el Enfoque fue aplicado
País:
Tayikistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Region of Republican Subordination
Especifique más el lugar :
Faizobod
Comentarios:
The research area is subdivided into two parts, one in the higher hills (around 1800-1900m) and one close to the village Karsang. Only the latter is assessed, even if the applied technology and the approach are similar for both locations.
Map
×2.6 Fechas de inicio y conclusión del Enfoque
Indique año del inicio:
1965
2.7 Tipo de Enfoque
- proyecto/ basado en un programa
2.8 Propósitos/ objetivos principales del Enfoque
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (In the last years production (of fruits and young trees) for market and self-sufficiency has increased.)
The field station should elaborate knowledge on fruit-production in steep areas. The knowledge gained on terraces would also be useful in the 1970ies, when forest administration was implemented and started to adopt and adapt the terrace technology. Research was in cooperation with other regions of Tajikistan and the URSS, e.g. good walnut varieties from Ukraine were imported and bred to make them adapted to local climate. From the very beginning it was important integrate and to create a surplus value for local population, be it jobs or knowledge on erosion prevention and fruit-production. In the last years it has become more important to spread conservation and production knowledge in favour of local population: Workshops are regularly organised, together with NGOs and with the own specialists, to make population share the gained knowlegde and apply it in their own orchards.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: The main focus was research on the productivity and stress-resistance (e.g. droughts) of different varieties of fruit-trees and vines under different climatic conditions. Another important objective is the elaboration of efficient terrace technology against erosion.There were also particular interests of political leaders such as vineyards for wine-production, a factor that is not important anymore in a country where the Islamic religion seems to be more important today than in Soviet times.
2.9 Condiciones que facilitan o impiden la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
marco de trabajo legal (tenencia de tierra, derechos de uso de tierra y agua)
- facilitan
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: Land belonged to the state in former USSR and the state initiated the project.
conocimiento de MST, acceso a apoyo técnico
- impiden
Topography (very steep slopes) difficult for mechanical use and dangerous for tractor drivers.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Terraces reduce slope and besides being a better wind-protection planting the trees diagonally to the main slope direction is a
3. Participación y roles de las partes interesadas involucradas
3.1 Partes interesadas involucradas en el Enfoque y sus roles
- usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales
Women are considered to be responsible for work in the household, even if they are sometimes the main field-workers today
- especialistas MST/consejeros agrícolas
by SLM specialists alone (top-down): Implementation and control of implementation. They are also encharged of research.
- gobierno nacional (planificadores, autoridades)
According to national and Soviet agricultural policies, the orchard was designed and organised.
Decision to implement research station (Academy of Science)
No women are found in a leading position of this research station.
3.2 Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales en las distintas fases del Enfoque
| Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales | Especifique quién se involucró y describa las actividades | |
|---|---|---|
| iniciación/ motivación | ninguno | |
| planificación | ninguno | |
| implementación | pasivo | Tractor-driver for terraces and field staff for tree-planting, land users' families for harvesting. |
| monitoreo y evaluación | ninguno | |
| Research | ninguno |
3.4 La toma de decisiones en la selección de Tecnología(s) MST
Especifique quién decidió la selección de las Tecnología/ Tecnologías a implementarse:
- solo por especialistas MST
Explique:
Different experts are the decision-makers, depending on the problem (e.g. type of fruits). This has stayed till today.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by SLM specialists alone (top-down)
4. Apoyo técnico, fortalecimiento institucional y gestión del conocimiento
4.1 Construcción de capacidades / capacitación
¿Se proporcionó la capacitación a usuarios de tierras/ otras partes interesadas?
Sí
Especifique quién fue capacitado:
- usuarios de tierras
- personal de campo/ consejeros
Forma de capacitación:
- áreas de demostración
Temas avanzados:
For land users it is interesting to learn specific technologies in fruit-production, e.g. how walnut saplings are maintained. For field staff it is interesting to learn from specialists how something is explained to different participants (young, old).
4.2 Servicio de asesoría
¿Los usuarios de tierras tienen acceso a un servicio de asesoría?
No
4.3 Fortalecimiento institucional (desarrollo institucional)
¿Se establecieron o fortalecieron instituciones mediante el Enfoque?
- no
4.4 Monitoreo y evaluación
¿El monitoreo y la evaluación forman parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Comentarios:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: Stress-resistance, depending on climate
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: Fruit harvest per tree.
There were few changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: With reduced crop harvests, partly due to lacking irrigation and partly to tall trees, cropping was stopped. Instead haymaking was focused.
5. Financiamiento y apoyo material externo
5.1 Presupuesto anual para el componente MST del Enfoque
Comentarios (ej. fuentes principales de financiamiento/ donantes principales):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (In the past government paid): 100.0%
5.2 Apoyo financiero/material proporcionado a los usuarios de tierras
¿Los usuarios de tierras recibieron financiamiento/ apoyo material para implementar la Tecnología/ Tecnologías? :
No
5.3 Subsidios para insumos específicos (incluyendo mano de obra)
- equipo
| Especifique qué insumos se subsidiaron | En qué grado | Especifique los subsidios |
|---|---|---|
| maquinaria | ||
- agrícola
| Especifique qué insumos se subsidiaron | En qué grado | Especifique los subsidios |
|---|---|---|
| semillas | ||
| fertilizantes | ||
Si la mano de obra de usuarios de tierras fue un insumo sustancial, ¿fue:
- comida por trabajo?
Comentarios:
There are fix employees with monthly salaries. But often, instead of salaries, people are paid in kind (i.e. the fruits for own use are substracted from the salary).
The government paid the whole implementation of the technology.
5.5 Otros incentivos o instrumentos
¿Se usaron otros incentivos o instrumentos para promover la implementación de Tecnologías MST?
No
6. Análisis de impacto y comentarios de conclusión
6.1 Impactos del Enfoque
¿El Enfoque ayudó a los usuarios de tierras a implementar y mantener Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Cover recovered on a nearby ex-cropland area, where the orchard technology was applied. It is especially the grazing-stop that triggered the change.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
In the 1970s the forest department began with state-organised reforesting and terracing. Nowadays land users visiting workshops in the research station adopt the orchard technology, but just for self-sufficiency.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Especially the employees could profit from their job, be it by payments in kind or by the wages. During civil war the decision to leave the cultivation of the orchards to local land users did not only
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The salaries allowed some land users to buy private livestock.
6.2 Motivación principal del usuario de la tierra para implementar MST
- producción incrementada
Especially in recent years workers have been relying more and more on harvests (fruits, hay).
- prestigio, presión social/ cohesión social
The employees made their living with this job.
- conciencia medioambiental
The brigadier was and is convinced that the ecosystem is maintained by the whole project.
6.3 Sostenibilidad de las actividades del Enfoque
¿Pueden los usuarios de tierras sostener lo que se implementó mediante el Enfoque (sin apoyo externo)?
- incierto
Si respondió no o incierto, especifique y comente:
Already today organisations carrying out workshops or training activities are asked to pay for it: food, paper and pens for the participants have to be organised.
6.4 Fortalezas/ ventajas del Enfoque
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| The strong focus on research helps improve the orchard. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Inputs from external experts (from Switzerland) could help improve the technology.) |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| It helps spread knowledge on an efficient conservation technology, especially on tree planting. |
| It permits land users to learn conservation methods and to make their living at the same time. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Giving the land users more decision capacities might strengthen their will to implement conservation.) |
6.5 Debilidades/ desventajas del Enfoque y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The chaos of war could have destroyed the orchard (people chopping trees illegally in a situation of no control). | The possibility of employees to rent land (land tenure assured) was the only possibility to save the orchard (as soon as the harvest goes to the land user, he has more interest to improve the land use). |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Research activities and the improvement of conservation technologies depend very much on the research coordinator. | Strengthening the position of land users would help make the system more sustainable on the long-term |
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Combined cut-and-carry and fruit-production system with terraces [Tayikistán]
A combination of fruit- and nut-trees together with seminatural trees and shrubs on one side with grass-communities on the other side provide for a diversified production system.
- Compilador: Christian Wirz
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos