Catchment Approach [Kenia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: James Gatero Njuki
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli
approaches_2361 - Kenia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación del Enfoque
Especialista MST:
Nombre del proyecto que facilitó la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque (si fuera relevante)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ItaliaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación del Enfoque si fuera relevante)
Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development of Kenya (MoA) - Kenia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT :
Sí
1.4 Referencia/s al/los Cuestionario(s) de Tecnologías MST

Drainage Biofilter [República Checa]
Biofilters or “bioreactors” connected to agricultural tile drains are relatively inexpensive and space-saving measures with considerable potential to improve the quality of drainage water.
- Compilador: Antonín Zajíček

Grassing of Recharge Areas [República Checa]
Grassing recharge zones of agricultural drainage systems significantly improves the quality of drainage water. It can be a useful, effective and relatively cheap measure for improvement of shallow groundwater quality.
- Compilador: Antonín Zajíček
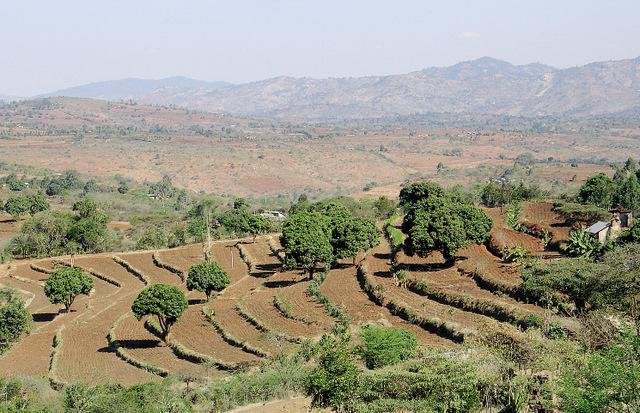

Les terrasses fanya juu [Kenia]
Terrasses en talus (remblais) associées à un fossé, le long des courbes de niveau ou selon une douce pente latérale. Le sol est rejeté sur la partie supérieure du fossé pour former le talus, souvent stabilisé par la plantation d’herbes fourragères.
- Compilador: Kithinji Mutunga
2. Descripción del Enfoque MST
2.1 Breve descripción del Enfoque
A focused approach to integrated land and water management, including soil and water conservation, where the active participation of the villagers - often organised through common interest groups - is central.
2.2 Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST
Descripción detallada del Enfoque MST:
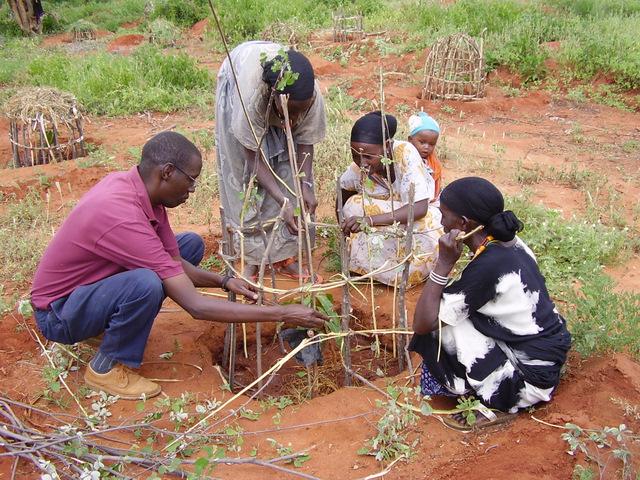
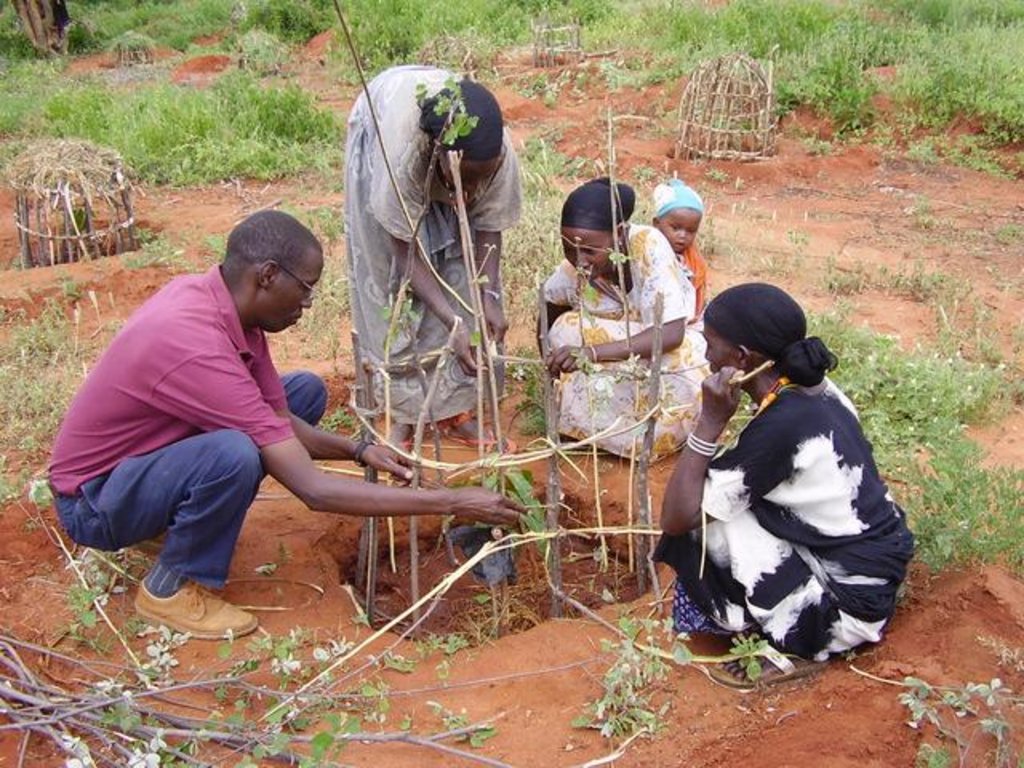
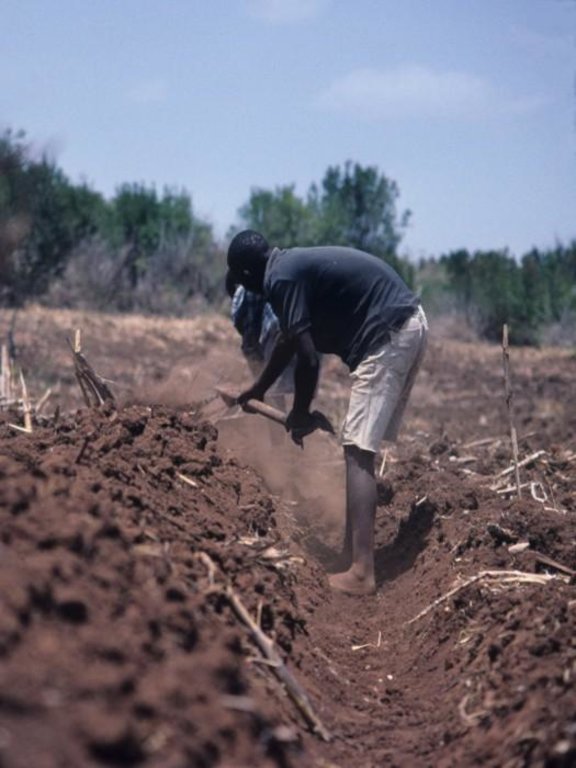
The catchment approach promotes sustainable land management systems by conservation of a defined area (so-called micro-environments) through the active participation of the communities living there. It was launched in Kenya in 1988 to achieve greater technical and social impact - and at a more rapid pace - than the previous focus on individual farmers. This case focuses on a single catchment in a subhumid area of Central Kenya. The emphasis is on structural measures - especially fanya juu terraces - but vegetative systems are promoted also. Other activities are supported such as spring protection, improved crop and animal husbandry, agroforestry, fodder production, fish ponds and others. The specific objectives are to stimulate the implementation of a variety of SWC measures leading simultaneously to improved production. Each approach area is defined by cultural/administrative boundaries rather than strict hydrological watersheds or catchments (as its name confusingly implies).
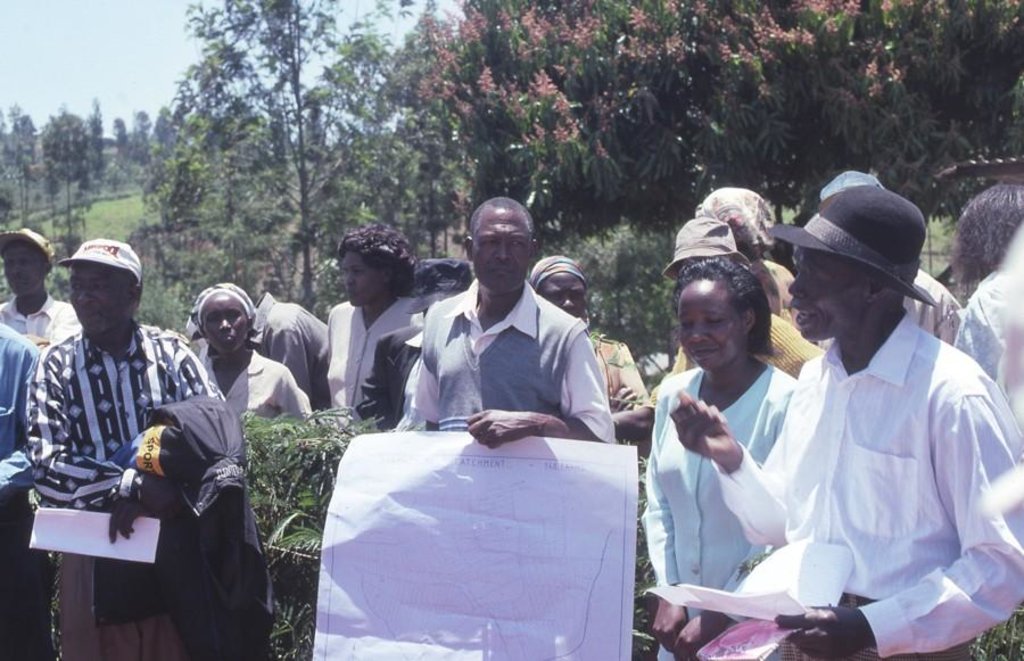
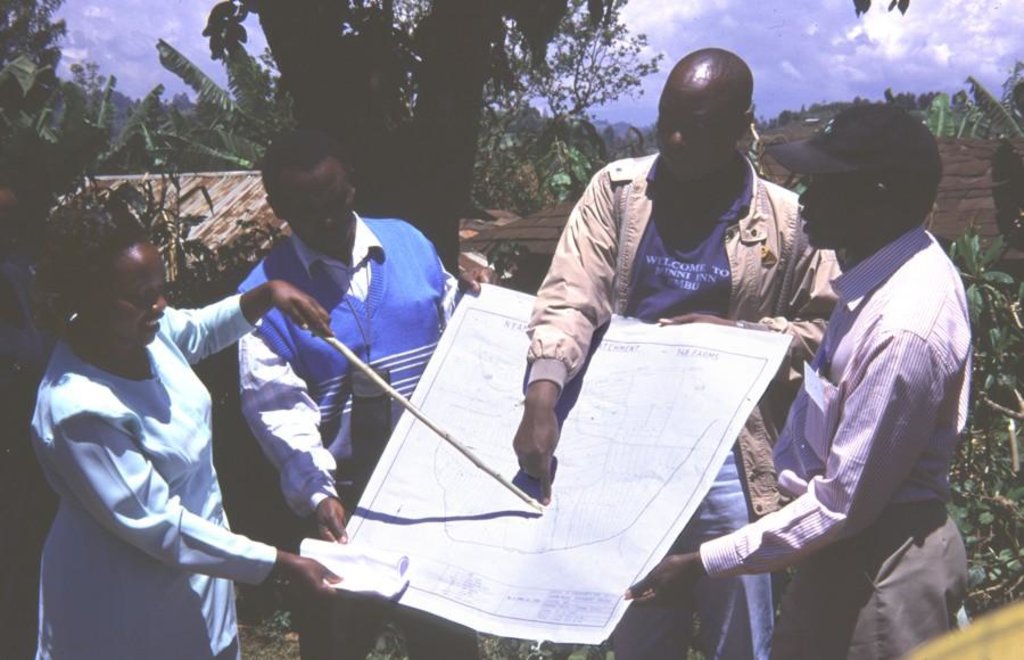
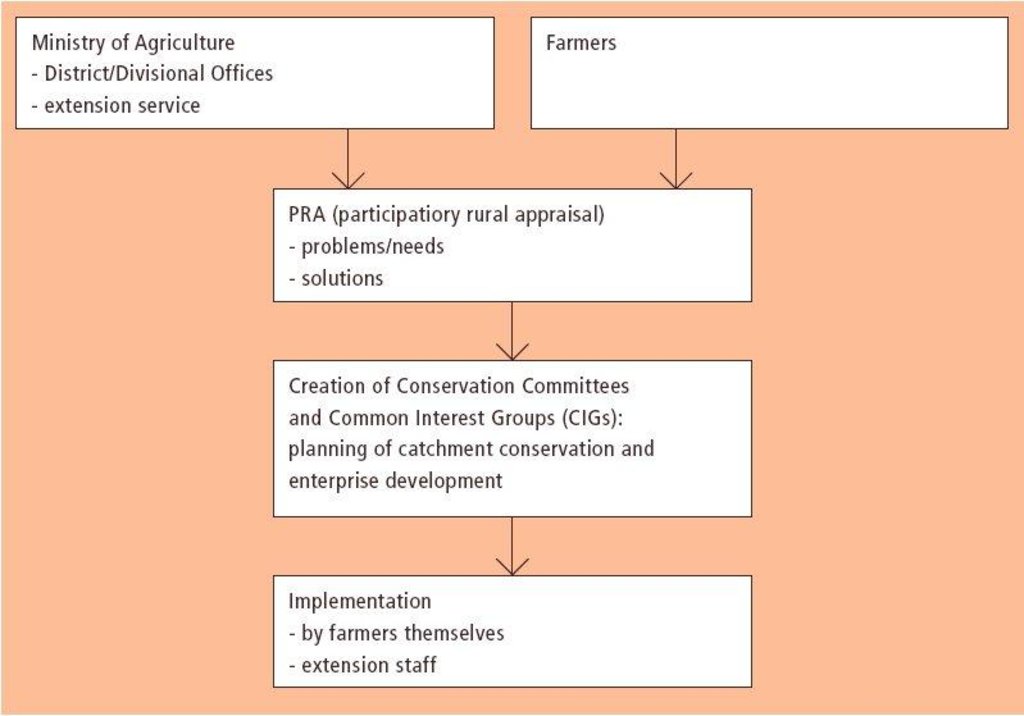
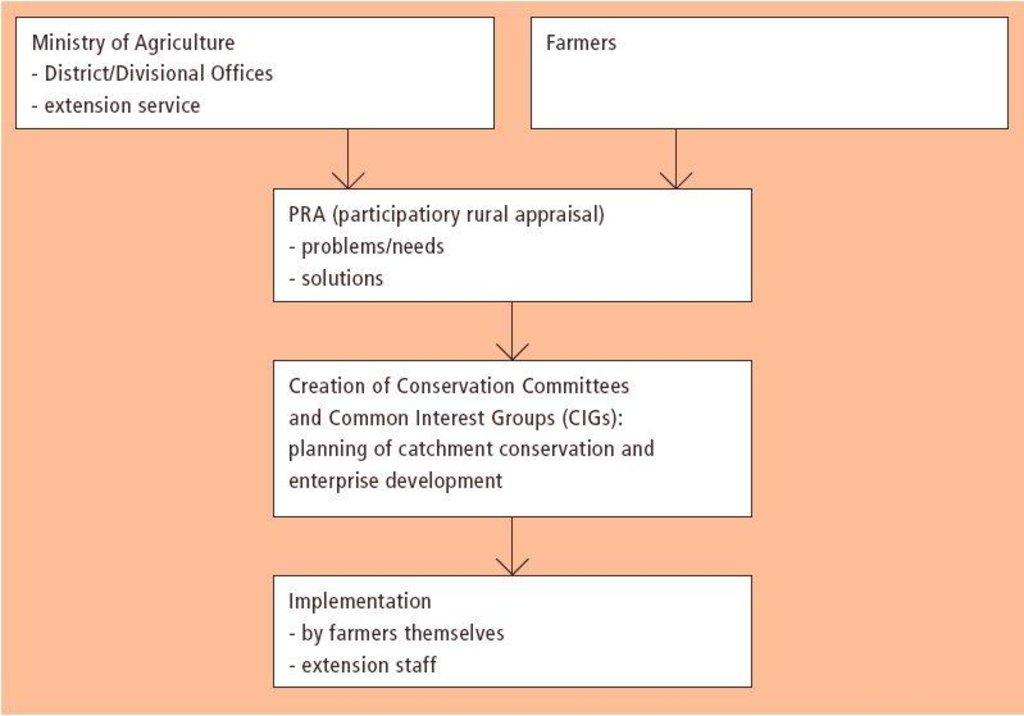
A conservation committee is elected from amongst the focal community before problem identification begins. Technical staff from relevant government and non-government agencies (NGOs) are co-opted onto the committee. The approach then involves participatory methods of appraisal and planning of solutions. Land users, together with the co-opted subject matter specialists, pool their knowledge and resources. Common Interest Groups (CIGs) are formed, with the aim of self-help promotion of specific farm enterprises. Training is given to the members of the CIGs by the Ministry of Agriculture. The farmers carry out the majority of the work themselves: monetary or other tangible incentives are few. The end result is the micro-environment (catchment area) conserved for improved production, and left in the hands of the community to maintain and sustain.
The catchment approach was developed under the National Soil and Water Conservation Programme - supported by (Swedish) Sida - and continues to be promoted as the Focal Area Approach (FAA) under the National Agricultural and Livestock Extension Programme (NALEP), which is again supported by Sida. However, under NALEP there is less emphasis on soil and water conservation than the previous programme, and more focus on promotion of productive enterprises.
The catchment approach is linked to cultural or administrative boundaries, rather than to hydrological watersheds. This emphasis on social units and integrated land management is becoming more common worldwide. In Kenya the approach is constantly evolving and has recently been renamed the 'Focal Area Approach'.
2.3 Fotos del Enfoque
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde el Enfoque fue aplicado
País:
Kenia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Central Province /Muranga District/Kangema divi
Especifique más el lugar :
Centre latitude:-0.721 Centre longitude:: 37.156
Map
×2.6 Fechas de inicio y conclusión del Enfoque
Indique año del inicio:
1987
Año de conclusión (si el Enfoque ya no se aplica):
2000
2.7 Tipo de Enfoque
- proyecto/ basado en un programa
2.8 Propósitos/ objetivos principales del Enfoque
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (The approach also included other activities like energy saving technologies and Agroforestry. It also involved collaboration with othe sectors like public health, fisheries, water. Also new technologies were introduced like water prospecting.) The main aims are to contribute to increased production among farmers and pastrolist through advise on sound land husbandry, conserve agricultural lands affected by erosion, create awareness on importance of soil conservation and introduce on-farm tree planting practices.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: lack of tangible and assessable impact of SWC activities, technically or socially, slow implementation of SWC, underlying problems of poverty, declining soil fertility, soil erosion and fuelwood shortage.
2.9 Condiciones que facilitan o impiden la implementación de la/s Tecnología/s aplicadas bajo el Enfoque
disponibilidad/ acceso a recursos y servicios financieros
- impiden
Lack of capital hinders farmers from investing in structures.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: farmers to work in group so that they can pool resources.
entorno institucional
- impiden
There was no institutional linkages to provide synergy
Treatment through the SLM Approach: collaboration forums through PRA were encouraged.
marco de trabajo legal (tenencia de tierra, derechos de uso de tierra y agua)
- facilitan
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately helped the approach implementation: Most land is individually owned, so there is no problem in that situation. Where land is rented, land users need to be persuaded to co-operate.
conocimiento de MST, acceso a apoyo técnico
- impiden
Lack of knowledge on better ways of conservation.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: training was carried out through courses, fielddays and demonstration.
3. Participación y roles de las partes interesadas involucradas
3.1 Partes interesadas involucradas en el Enfoque y sus roles
- usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales
Working land users were work equally divided between men and women. Groups consist out of both. Many joint activities but men and women still stick to some traditional gender-related agricultural activities. For example women often concentrate on food crops, men on cash crops. The poor resource group has been involved by participating in trainings, in election of catchment committee and during committee meetings.
- especialistas MST/consejeros agrícolas
- profesores/ niños en edad escolar/ estudiantes
- gobierno nacional (planificadores, autoridades)
Ministry of Agriculture, politicians
3.2 Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales en las distintas fases del Enfoque
| Involucramiento de los usuarios locales de tierras/ comunidades locales | Especifique quién se involucró y describa las actividades | |
|---|---|---|
| iniciación/ motivación | interactivo | public meetings; they were involved in making decisions on boundaries. |
| planificación | interactivo | rapid/participatory rural appraisal, public meetings, interviews/questionnaires; they were involved in providing information during the PRA and also the formulation of the community action plan |
| implementación | auto-movilización | responsibility for major steps; they were invoved in the actual work in the farms. implemented by community members |
| monitoreo y evaluación | pasivo | Mainly: interviews/questionnaires; partly: reporting; |
| Research | ninguno | only during trainings |
3.3 Flujograma (si estuviera disponible)
3.4 La toma de decisiones en la selección de Tecnología(s) MST
Especifique quién decidió la selección de las Tecnología/ Tecnologías a implementarse:
- principalmente usuarios de tierras con el apoyo de especialistas MST
Explique:
Land user driven (bottom-up). The choice on the technology to use is made primarily by the technical specialists based on the prevalent type of erosion on each farm and farmers preference.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists. Land user driven (bottom-up). The method of implementation is decided based on the farmers capabilities and resources at his disposal e.g. where labour is a constraint and finances limiting, biological conservation measures would be considered more.
4. Apoyo técnico, fortalecimiento institucional y gestión del conocimiento
4.1 Construcción de capacidades / capacitación
¿Se proporcionó la capacitación a usuarios de tierras/ otras partes interesadas?
Sí
Especifique quién fue capacitado:
- usuarios de tierras
- extensionists/trainers, school children/students (2), teachers (3)
Forma de capacitación:
- en el contexto de trabajo
- de agricultor a agricultor
- áreas de demostración
- reuniones públicas
- cursos
Temas avanzados:
including layout of measures; agroforestry; soil erosion and measures to control it; energy conservation; food preservation - as well as for specific farm enterprises. Carried out mainly through farm visits by Ministry of Agriculture agents.
4.2 Servicio de asesoría
¿Los usuarios de tierras tienen acceso a un servicio de asesoría?
Sí
Especifique si servicio proporcionado se realizó:
- en los campos de los usuarios de tierras
Describa/ comentarios:
Name of method used for advisory service: Catchment Approach: Formation of Conservation Committees. Implementation of techniques/technologies, Training on techniques/technologies, farm visits, field demonstrations, field days.
Advisory service was carried out through: Government's existing extension system (Both generalists and SWC specialists.) Extension staff: Mainly government employees.
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; There are extension staff posted at locational level who are well trained.
4.3 Fortalecimiento institucional (desarrollo institucional)
¿Se establecieron o fortalecieron instituciones mediante el Enfoque?
- sí, moderadamente
Especifique el nivel o los niveles en los que se fortalecieron o establecieron las instituciones:
- local
Especifique el tipo de apoyo:
- construcción de capacidades/ entrenamiento
4.4 Monitoreo y evaluación
¿El monitoreo y la evaluación forman parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Comentarios:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored through observations
technical aspects were ad hoc monitored through measurements
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored through observations
area treated aspects were regular monitored through observations
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored by 0 through measurements; indicators: None
management of Approach aspects were ad hoc monitored by 0 through observations; indicators: None
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: There have been few changes, but there is some enhanced collaboration between agencies, and - more income generating activities have been identified and implemented through common interest groups for crop production, marketing and livestock.
4.5 Investigación
¿La investigación formó parte del Enfoque?
Sí
Proporcione detalles adicionales e indique quién hizo la investigación:
Specific problems are researched as they arise. A strong research-extension linkage is being built up. Monitoring of the progress of the overall programme also takes place.
5. Financiamiento y apoyo material externo
5.1 Presupuesto anual para el componente MST del Enfoque
Si no se conoce el presupuesto anual preciso, indique el rango:
- < 2,000
Comentarios (ej. fuentes principales de financiamiento/ donantes principales):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (SIDA/trainnig, transport allowances etc): 70.0%; government (national - Office, personell): 20.0%; local community / land user(s) (Labour, materials): 10.0%
5.3 Subsidios para insumos específicos (incluyendo mano de obra)
- equipo
| Especifique qué insumos se subsidiaron | En qué grado | Especifique los subsidios |
|---|---|---|
| herramientas | Given to catchment committee for use in catchment | |
- agrícola
| Especifique qué insumos se subsidiaron | En qué grado | Especifique los subsidios |
|---|---|---|
| semillas | Tree seeds for group nursery establishment | |
Si la mano de obra de usuarios de tierras fue un insumo sustancial, ¿fue:
- voluntario?
Comentarios:
All labour is provided on a voluntary basis.
5.4 Crédito
¿Se proporcionó crédito bajo el Enfoque para actividades MST?
Sí
Especifique las condiciones (tasa de interés el apoyo, amortización, etc.):
This is not provided directly, though a savings and credit 'stakeholder kitty' revolving fund is being promoted and developed.
6. Análisis de impacto y comentarios de conclusión
6.1 Impactos del Enfoque
¿El Enfoque ayudó a los usuarios de tierras a implementar y mantener Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Intensified use of manures. The land user also adopted the construction of retention ditches. The improvements to SWC are moderate: these have been mainly through fanya juu and level bench terraces
¿El Enfoque mejoró cuestiones de tenencia de tierra/ derechos de usuarios que obstaculizaron la implementación de la Tecnologías MST?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
The approach through catchment committee was able to persuade the prople leasing land to undertake conservation measures.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
Spread has been limited to one Non-Governmental Organisation in this particular case study area.
- No
- Sí, un poco
- Sí, moderadamente
- Sí, mucho
6.3 Sostenibilidad de las actividades del Enfoque
¿Pueden los usuarios de tierras sostener lo que se implementó mediante el Enfoque (sin apoyo externo)?
- incierto
Si respondió no o incierto, especifique y comente:
Interventions are likely to continue and be maintained, but this depends on common interest groups continuing to function actively.
6.4 Fortalezas/ ventajas del Enfoque
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Much improved extension/training - research linkages have been forged (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue focussed training/strengthen research-extension linkage.) |
| New and productive farm enterprises have been promoted under the catchment approach alongside better SWC (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue to introduce/support where appropriate through Common Interest Groups.) |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Genuine community participation has been achieved under this approach (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue with participatory training.) |
| There is evidence of 'ownership' by the community which implies a feeling that what has been achieved is due to communal efforts and belongs to them (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Further training is more effective when benefits are appreciated in this way.) |
6.5 Debilidades/ desventajas del Enfoque y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Lack of material incentives like seeds and fertilizers | Assist the farmers with the credit. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| In many places there is a lack of availability of inputs | Provide better credit facilities for CIGs/farmers generally. |
| Technologies tend to be implemented uniformly, not site-specifically | SWC practices should be matched to each particular situation, eg structural measures such as fanya juu terraces should be promoted only where necessary, that is where agronomic and vegetative measures do not provide sufficient protection. |
| As yet uncertainty about continuation in specific areas if direct support stops after only one year | Don't abruptly terminate this support after one year: continue approach for at least two or three years in each catchment (approach area). |
| inadequate funding | Increase the funding. |
| Too small an area (of the country) is currently covered by NALEP | More staff required: more effective use of staff. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
7.2 Referencias a publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
The catchment approach is linked to cultural or administrative boundaries, rather than to hydrological watersheds. This emphasis on social units and integrated land management is becoming more common worldwide. In Kenya the approach is constantly evolving and has recently been renamed the 'Focal Area Approach'.
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Drainage Biofilter [República Checa]
Biofilters or “bioreactors” connected to agricultural tile drains are relatively inexpensive and space-saving measures with considerable potential to improve the quality of drainage water.
- Compilador: Antonín Zajíček

Grassing of Recharge Areas [República Checa]
Grassing recharge zones of agricultural drainage systems significantly improves the quality of drainage water. It can be a useful, effective and relatively cheap measure for improvement of shallow groundwater quality.
- Compilador: Antonín Zajíček

Les terrasses fanya juu [Kenia]
Terrasses en talus (remblais) associées à un fossé, le long des courbes de niveau ou selon une douce pente latérale. Le sol est rejeté sur la partie supérieure du fossé pour former le talus, souvent stabilisé par la plantation d’herbes fourragères.
- Compilador: Kithinji Mutunga
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos