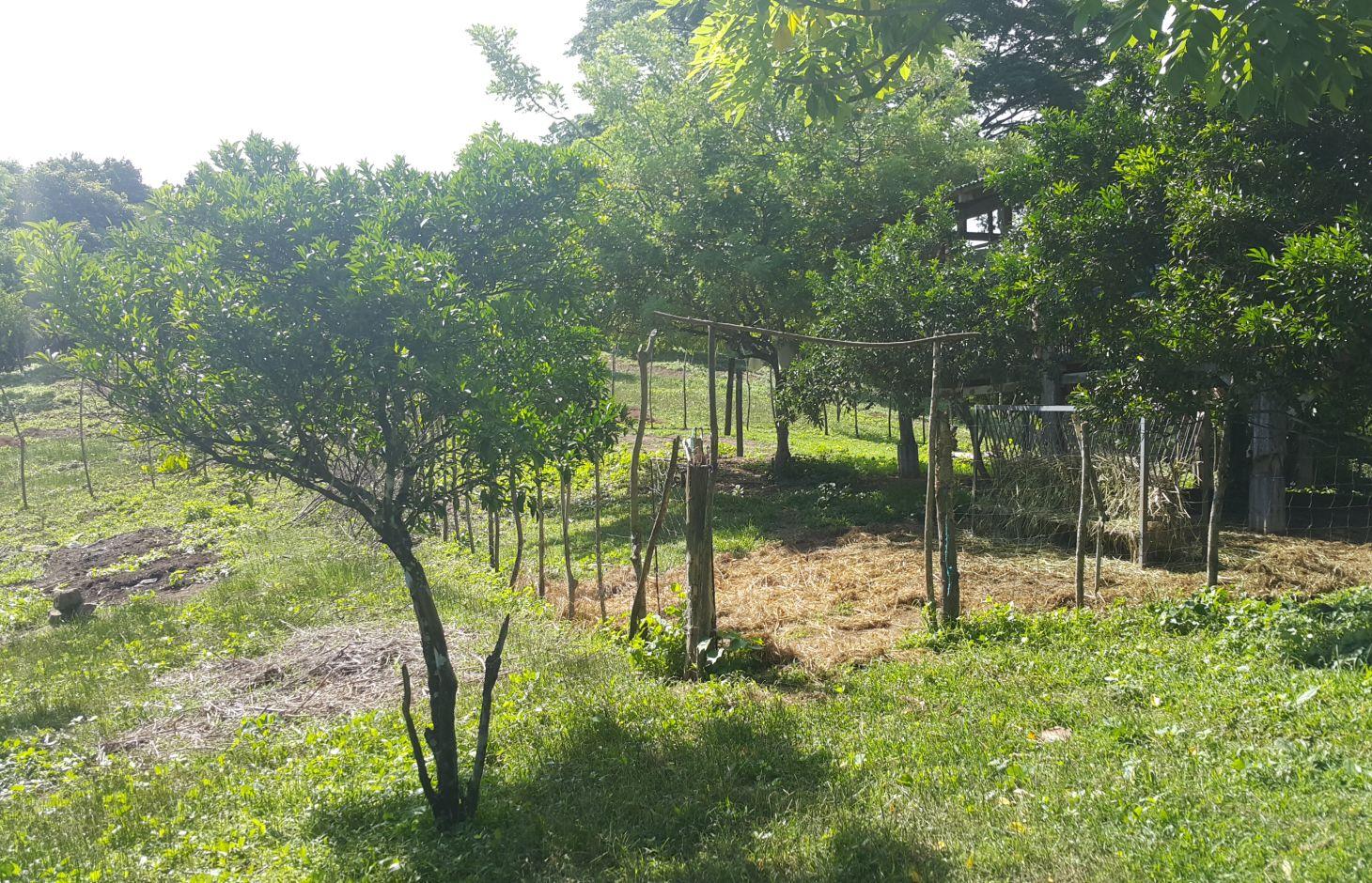
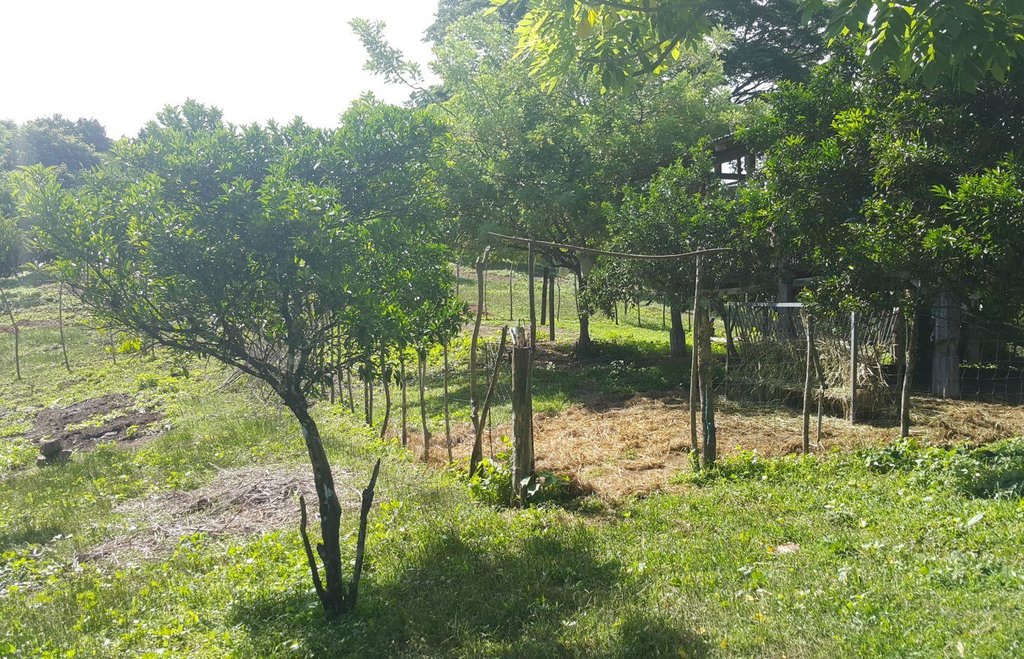
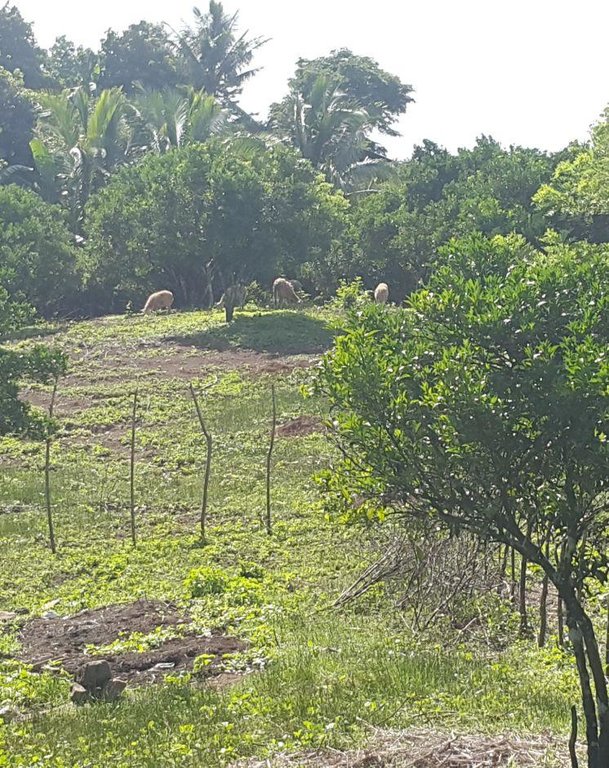
Improved pasture under citrus [Filipinas]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
Pastulan sa ilalim ng dalanghitaan (Filipino)
technologies_1321 - Filipinas
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
Especialista MST:
Rojales Jose
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Filipinas
Especialista MST:
Calonge Arsenio
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Filipinas
Especialista MST:
Millare Kirby
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Filipinas
Especialista MST:
Quinto Jasmin
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Filipinas
Especialista MST:
Gultiano Wilfredo
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Filipinas
Especialista MST:
Cornes Jennelyn Mae
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Filipinas
Especialista MST:
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - Filipinas1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
29/06/2016
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST

Soil Conservation Guided Farm System [Filipinas]
Soil Conservation Guided Farming System (SCGFS) is a land use management approach that integrates technologies: terracing, agro-pastoral technology, multi-storey cropping, and contouring within the socio-economic and bio-physical limitations of upland areas for optimum development of soil and water resource in a sustainable manner.
- Compilador: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
It is a farming system that integrates the growing of fodder crops under plantation crops.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
It is an integration of livestock and agronomic crop production of incorporating small ruminants in an existing citrus plantation. This technology was based on the private initiative of the farmer where he adapted it from other land users. He further improved it through study of reading materials and ad hoc monitoring of his environment.
Purpose of the Technology: After the adaption of the technology, the land user observed a decrease in the infestation of aphids. The land user observed and concluded that the decline in the aphids infestation was due to the presence of the small ruminants in the area. The small ruminants forage on grasses that were continuously growing, year-round, in the plantation area. The foraging of grasses improved the micro-environment of the plantation crop, which contributed to the decline and almost total eradication of aphids in the area, as observed by the land user. This promoted natural farming and improved the biodiversity.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The area was first established as a citrus plantation inter-cropped with Vigna unguiculata, Cucurbita maxima, and Ipomoea batatas, as cash crop during the vegetative stage of the citrus crop. As the small ruminants increased in number, the land user decided to do “controlled grazing” by dividing the area into 3 paddocks. During lean days of forage grasses, the land user practices “cut-and-carry” system of feeding. In addition, the manure of the small ruminants serves as a source of organic fertilizer for the citrus and other crops grown by the land user.
Natural / human environment: Aside from the eradication of the aphids on the citrus crop, the technology aided in the financial needs of the land user. It increased the land user’s income by an increase in the fruits bore by the crop and the increase in the number of the small ruminants. The land user sells or sometimes suppliers of citrus fruit and goat meat would go to the area to do wholesale buying. As for the community near the area, they to benefit from the area, by wholesale buying the citrus fruit and be the one selling it to the market. The technology does not only contribute to the livelihood improvement of the land user but also to the community.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Filipinas
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Bulacan
Especifique más el lugar :
City of San Jose Del Monte
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
- experience from other farm land user
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
8 years
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
Cosechas principales (comerciales y de subsistencia):
Major cash crop:
Citrus

Tierra de pastoreo
- Silvo-pastoralism
Especies y productos animales principales:
Goat and sheep grazing in combination
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Possibility of pollution in the area. The land user might have applied pesticide to the citrus crops to control the pest, but the land user did not mention of it. Application of herbicide to control the growth of grasses within and outside the area.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Without land conservation, there was an occurrence of pest in the citrus plants.
Mixed: (eg agro-pastoralism, silvo-pastoralism): silvo-pastoralism, goat and sheep grazing in combination
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Ms: Silvo-pastoralism
Si el uso de la tierra ha cambiado debido a la implementación de la Tecnología, indique el uso de la tierra antes de la implementación de la Tecnología.
Cropland: Cp: Perennial (non-woody) cropping
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Comentarios:
Water supply: rainfed, rainfed
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: July to November
Densidad del ganado (si fuese relevante):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- manejo de agricultura—ganadería integrada
- manejo integrado de pestes y enfermedades (incl. agricultura orgánica)
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.08 m2.
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas agronómicas
- A1: vegetación/ cubierta del suelo

medidas vegetativas
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes
Comentarios:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación del suelo encarados con la Tecnología

degradación biológica
- Bp: incremento de pestes/ enfermedades, pérdida de depredadores
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bp: increase of pests / diseases, loss of predators
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (intercropping planting), droughts (time frame of drought)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (grazing of small ruminants), overgrazing (no. of small ruminants), change in temperature (dry season time frame)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación del suelo
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación del suelo
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Third goal: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
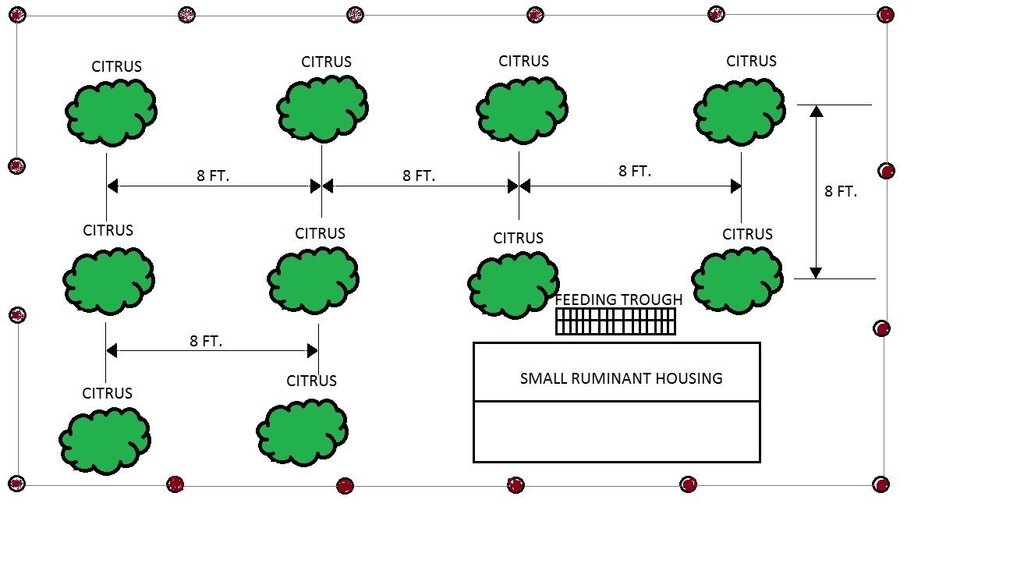
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
Citrus plants are evenly distributed in the area, with a planting distance of 8 feet by 8 feet. The ground cover are forage grasses for the small ruminants.
Location: Barangay San Roque. San Jose Del Monte, Bulacan
Date: 06/29/2016
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (technical assistance from agricultural advisory from other aspect in land degradation)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (land user is open minded with the technology introduced)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, increase of surface roughness, increase of infiltration, reduction in wind speed, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: pole sitao-squash-sweet potato/citrus
Agronomic measure: intercropping (1st Year)
Material/ species: pole sitao/citrus
Quantity/ density: 2,000/188
Agronomic measure: intercropping (2nd year)
Material/ species: squash/ citrus
Quantity/ density: 2,000/188
Agronomic measure: intercropping (3rd year)
Material/ species: sweet potato/ citrus
Quantity/ density: 8,800/188
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: goat manure
Quantity/ density: 5,000 kg
Remarks: .5 per square meter
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Philippine Peso
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
47,5
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
5.26
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | rotational grazing | Vegetativas | rainy season |
| 2. | cut-and-carry feeding system | Vegetativas | dry season |
| 3. | Buying pole sitao | Agronómicas | |
| 4. | Buying sqaush | Agronómicas | |
| 5. | Buying citrus | Agronómicas |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 10,52 | 10,52 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 3160,0 | 3160,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 48,0 | 48,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Hog wire | ha | 1,0 | 397,89 | 397,89 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 3616,41 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
Life span of products:
Pole Sitao - 1 year
Squash - 1 year
Citrus - 50 years
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 10,52 | 10,52 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 10,52 | |||||
Comentarios:
The above costs usually occurs during the dry season when forage grasses are scarce. Lean months of availability of forages grasses are from the months April to June. This is the time the cut-and-carry method is applied and the start of the maintenance/recurrent cost.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Cut-and-carry method of feeding the small ruminants during lean months of forage grasses.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especifique el promedio anual de lluvia (si lo conoce), en mm:
2382,00
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Indique si la Tecnología se aplica específicamente en:
- situaciones cóncavas
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Landforms: Ridges (concave)
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil fertility is: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is: Good
Soil water storage is: High
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
solo para uso agrícola (irrigación)
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Género:
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: It is the countries socio-cultural model, where men is the one working and the women stay at home. According to the land user it is the women who is record keeper.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
10% of the land users are average wealthy.
Off-farm income specification: off-farm income provides additional income to the land user during the dry season.
Market orientation: Subsistence (small ruminants are bought by the land user)
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Cantidad antes de MST:
3,000 kilograms
Cantidad luego de MST:
8,000 kilograms
producción animal
Cantidad antes de MST:
5
Cantidad luego de MST:
5
diversidad de producto
manejo de tierras
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Cantidad antes de MST:
30,000
Cantidad luego de MST:
80,000
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
carga de trabajo
Otros impactos socioeconómicos
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
It gave an opportunity to the neighbors of the land user to work at the field, with pay. Thus, an added income to the neighbor of the land user. According to the land user, he was able to send his children to a decent school for a quality education. It also gave the land user another source of income by purchasing a jeepney used as a public transportation through the increased income from the SLM technogy he adapted.
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
The increased in the income of the land user contributes to the food security of the family
situación de salud
Comentarios/ especifique:
Daily chores of herding the small ruminants contributes to the good over health of the land user
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Rotational grazing and "cut-and-carry" style of feeding contributed to the possible overgrazing which is contributor to erosion
mitigación de conflicto
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Comentarios/ especifique:
The land user allows the member of his community to harvest some fruits and sell them to the market without the land user asking for something in return.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
calidad de agua
escurrimiento superficial
Comentarios/ especifique:
Rotational grazing and "cut-and carry" style of feeding contributes to the reduction in surface runoff, grasses are maintained on the soil surface
drenaje de agua en exceso
nivel freático/ acuífero
evaporación
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface reduced soil in any form
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
compactación de suelo
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
Comentarios/ especifique:
Manure of the small ruminants contributes to nutrient recycling
salinidad
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Manure of the small ruminants contributes to the increased in soil organic matter content
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
especies invasoras extrañas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Incorporation of small ruminants in the farming system which aid in the maintenance of grasses within the plantation area, helps improve the microclimatic condition inside the plantation area that further reduced alien species invasion
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Comentarios/ especifique:
Incorporation of small ruminants in the farming system which aid in the maintenance of grasses within the plantation area, helps improve the microclimatic condition inside the plantation area that further increased biological pest/disease control
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
riesgo de incendio
velocidad de viento
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface improves soil tilth which further improves infiltration capacity
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
Comentarios/ especifique:
Manure of the small ruminants improves the soil tilth, an improved soil tilth improves the buffering/filtering capacity of the soil
sedimentos transportados por el viento
Comentarios/ especifique:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface reduces erosion due to wind
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | no se sabe |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | no se sabe |
| tormenta de viento | no se sabe |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | no muy bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no se sabe |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | no se sabe |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 90-100%
Comentarios:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Decreased in occurrence of pest |
| Increased land user's income |
| Helped the land user's neighbor by profit sharing during harvest of the citrus fruits |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Less labor input How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve the varietal species of the forage grass |
|
Decreased in occurrence of pest How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain the existing micro environment |
| Rotational grazing |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| There was an inbreeding of the small ruminants | Putting another small ruminants of good genetic quality |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Variety of forage grass is of low quality in terms of crude protein content | Planting of improved variety with a high crude protein content |
| Species of small ruminants are not of good genetic quality in terms of meat quality | Putting of species with a good genetic quality in terms of meat produce |
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Soil Conservation Guided Farm System [Filipinas]
Soil Conservation Guided Farming System (SCGFS) is a land use management approach that integrates technologies: terracing, agro-pastoral technology, multi-storey cropping, and contouring within the socio-economic and bio-physical limitations of upland areas for optimum development of soil and water resource in a sustainable manner.
- Compilador: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos