Gully Rehabilitation [Kenia]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Kithinji Mutunga
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
technologies_1488 - Kenia
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Kiio Jacqueline
MOARD
Kenia
usuario de la tierra:
Kirimi Patrick
MOARD
Kenia
Especialista MST:
Gitau Mary
MOARD
Kenia
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - Italia1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
26/04/2000
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Erosion control by use of physical barriers and vegetative materials
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
The innovation comprises control of gully erosion by use of constructed barriers (check dams) combined with vegetative materials. The end result is a stabilized gully that is prevented from advancing further. The system also involves fruit trees/banana establishment and fodder grass planting for structure stabilization. Establishment of the technology involves excavation of pits, planting fruit trees/bananas and grass cuttings.
Purpose of the Technology: This is a structural measure that is vegetated for stabilization. Its purpose is to rehabilitate a gully bed, through control of concentrated runoff by reduction of slope length and both trapping of runoff and sediment harvesting. The productive use of the innovation is mainly for perennial crops (fruit trees and
bananas) and for fodder production.
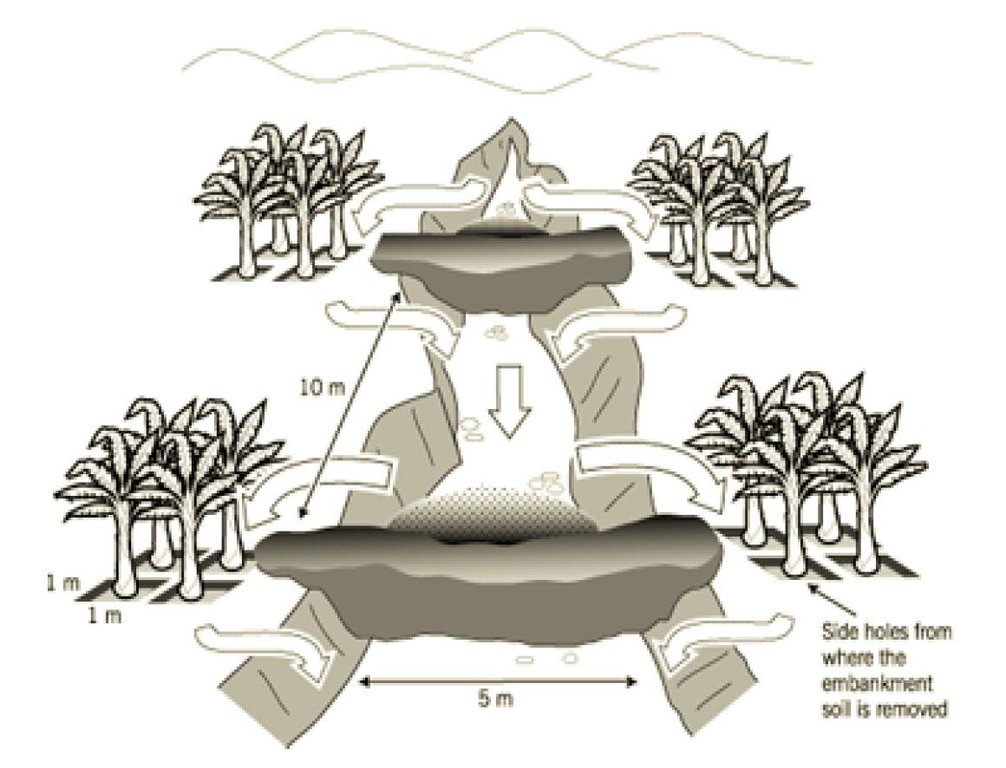
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Earth check dams are constructed in the gully, using borrow spoil from square pits in the walls of the gully (see diagram). The earth embankment of the dams are then stabilized with grass. Pawpaws are planted on the original gully floor. Initially the innovator left the pits empty: now she plants bananas in them.The 5 check dams, each 1 m or more in height, are spaced at about 10 m apart in the gully. The excavated pits are about 1 m x 1 m wide and 1 m deep. Four pits are dug separately on each side of each check dam. Makarikari grass (Panicum coloratum var. makarikariensis) is used for stabilization, while bananas and pawpaws are planted within the rehabilitated area. When it rains, runoff generated from the neighbouring plots upstream flows down and is slowed by the check dams. The runoff passes around both wings of each embankment, filling and flowing through the pits. Sediment is trapped in the pits. Excess runoff flows on to the second embankment, then through the
second set of pits and so on. Only during heavy rains does water pass through and out of the system, though its velocity is reduced. Thus the gully heals slowly with time and vegetation becomes established. Regular maintenance work is required, involving repair of broken sections from time to time, using
manual labour with a panga, shovel and jembe. Also of importance is manure application every season to the planted areas before the rains to sustain fertility and thus productivity.
Natural / human environment: Kalekye Mutua is a single household head in her mid thirties. Although she has no partner to help support her three children, she manages quite well through farming her 6 hectares of land - where she grows various crops and keeps a few local cattle. She had a small trading venture but has recently abandoned
this. Kalekye is not amongst the poorest in Mwingi, but represents a number of female-headed households who prosper through hard work and enterprise. In fact she even employs labourers part-time to help with the farming activities.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Kenia
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Eastern Province
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace más de 50 años atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- como parte de un sistema tradicional (> 50 años)
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
farmers own intiative
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): soil erosion, overgrazing, declining soil fertility
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): low yields
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 60 Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Dec Second longest growing period in days: 75 Second longest growing period from month to month: Mar - May
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- cobertura de suelo/ vegetal mejorada
- cosecha de agua
- diversión y drenaje de agua
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentarios:
a very small portion of the individual farm is covered by the technology
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas

medidas estructurales
- S3: Acequias graduadas, canales, vías fluviales
Comentarios:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
Gully under reclamation: note flow of runoff
Kenya
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Fruit trees / shrubs species: pawpaws
Perennial crops species: bananas
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 5.00%
Construction material (earth): Local soil excavated from pits on the side of the gully
Construction material (other): Grass for stabilization Makarikari grass prefeered
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 8%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
kenya shillings
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
70,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
2.14
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | digging banana holes | Vegetativas | dry season |
| 2. | acquisition of grass cuttings | Vegetativas | dry season |
| 3. | acquisition of banana cuttings | Vegetativas | before |
| 4. | planting of grass and bananas | Vegetativas | onset of rain |
| 5. | manure application | Vegetativas | before the rains |
| 6. | Excavation | Estructurales | Dry season |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | repair of broken structures | Vegetativas | after rains /seasonally |
| 2. | weeding | Vegetativas | during rains /twice /season |
| 3. | banana prunning | Vegetativas | after rains /biannually |
| 4. | manure application | Vegetativas | dry season /annually |
| 5. | Repair of broken sections | Estructurales | during /after rains/seasonally |
| 6. | Stabilization with grass | Estructurales | during rains/when required |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
Comentarios:
1100 banana/ fruit trees holes/ha
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
slope, soil type, timeliness of operation
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
1% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
4% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
25% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
40% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: the are few members of the household who are in formal employment
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de forraje
área de producción
Ingreso y costos
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
Sale of bananas
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
escurrimiento superficial
Cantidad antes de MST:
60
Cantidad luego de MST:
10
Suelo
humedad del suelo
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
610
Cantidad luego de MST:
1
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- casos individuales / experimentales
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
1 household
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 90-100%
Comentarios:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Kalekye only started the innovation two years ago, and while there has been a policy of taking women’s groups to visit Kalekye, this is a relatively recent occurrence (starting approximately a year ago). Despite the visitors obviously being inspired, there have been no reports as yet of direct adoption of the technology.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Reclamation of land for production of fodder and bananas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Possible improvements would include planting improved fruit trees that are rapidly maturing and yield more: grafted mangoes for example |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| High labour requirements |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Farm Management handbook of Kenya Vol II
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
Ministry of Agiculture, Nairobi
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Kithinji M., Critchley W. 2001. Farmers' initiatives in land husbandry: Promising technologies for the drier areas of East Africa. RELMA Technical Report series no. 27
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos