Biogas [Botswana]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Sebego Reuben
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
Gase ya Boloko (Setswana)
technologies_1521 - Botswana
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Mulale Kutlwano
P/bag UB 00704 Gaborone
Botswana
Especialista MST:
Chanda Raban
University of Botswana
P/bag UB 00704 Gaborone
Botswana
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
University of Botswana (University of Botswana) - Botswana1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
19/02/2009
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Production of methane gas from cow-dung for use in house-hold cooking, heating and lighting in order to reduce fire wood demand
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
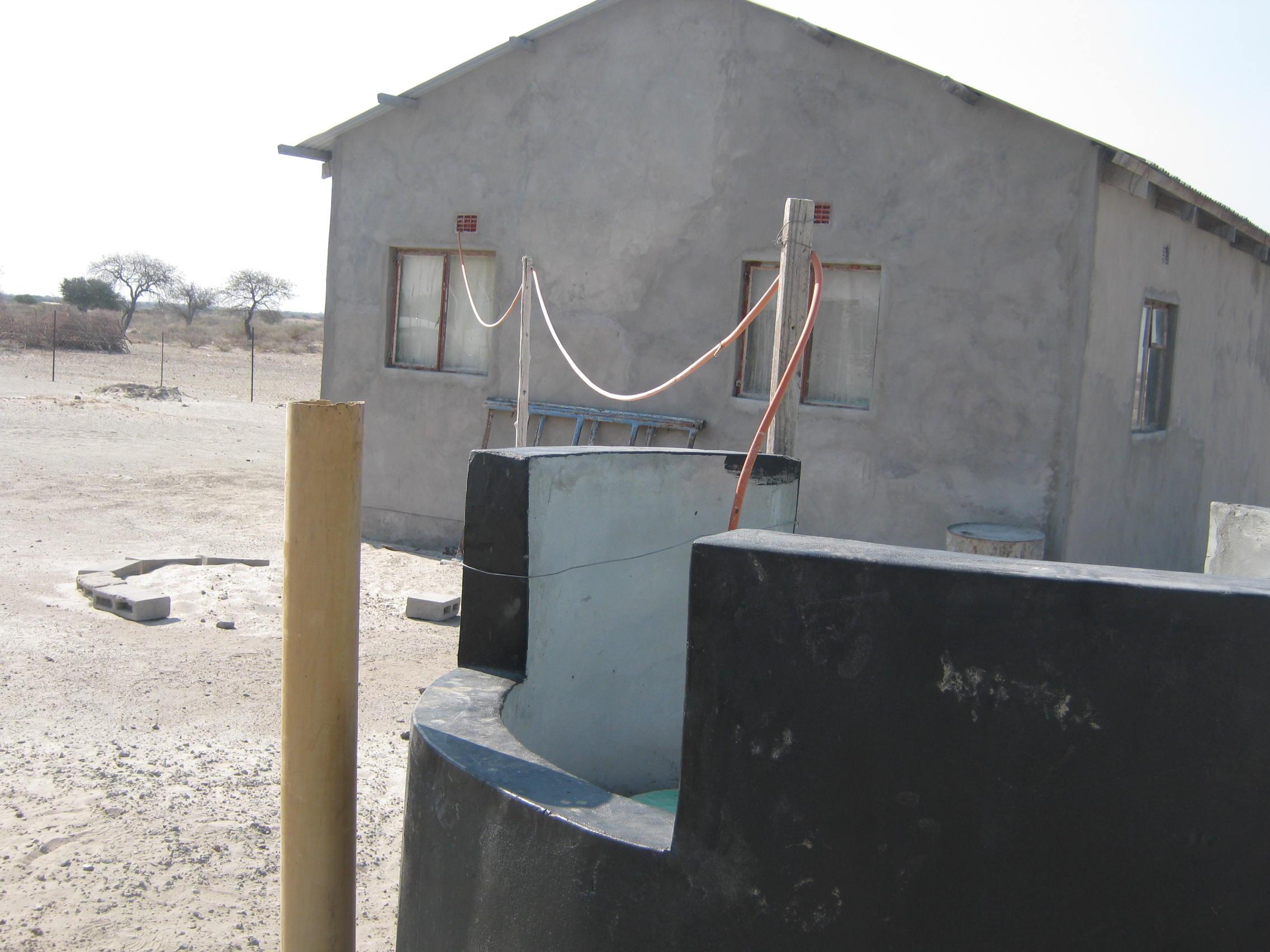
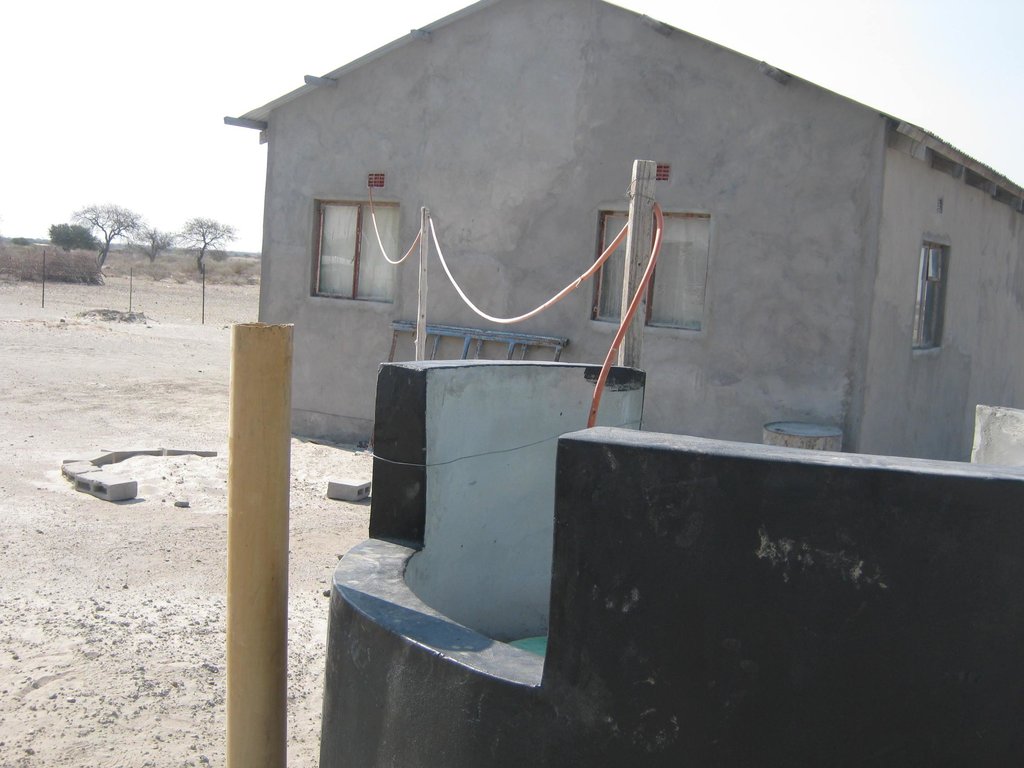
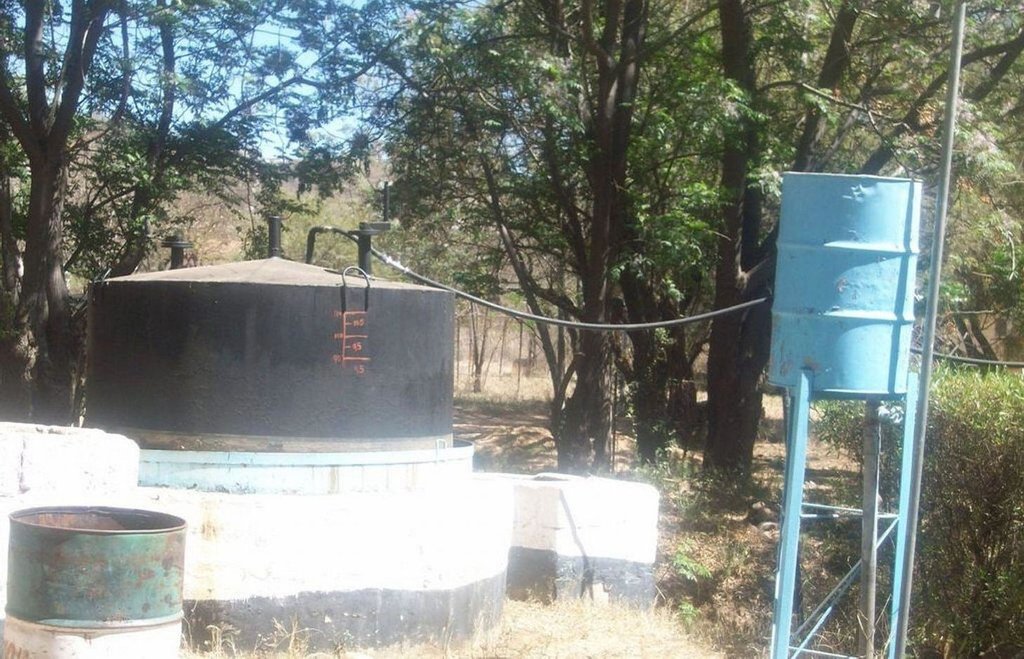
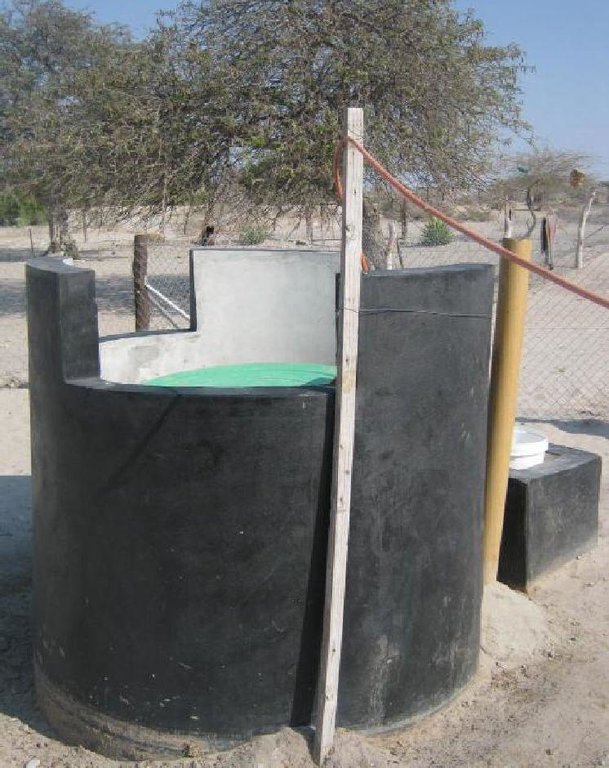
Biogas plant: The biogas plant can be constructed in several ways as long as it can provide a medium for the biological material be digested. Biogas is the name given to the gas that is produced during the decomposition of some organic waste specifically to produce methane gas. The gas is then captured in a storage tank (on site) to be used for household energy needs. In many parts of the world where this technology is used (including Botswana) the most common form of input material is cow dung making it more appropriate for rural environments.
Purpose of the Technology: Advantages: the technology offers two major advantages; first, at every level of use i.e. individual or institutional, savings in terms of energy is realized. The only costs that are borne are at installation, otherwise input of cow dung has a minimal cost of collection (if any at all). The second advantage is that there is reduced usage of fuel wood which translates into less cutting down of trees leading to reduced deforestation and degradation of land. A disadvantage is the initial investment which is significant for poor farmers.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Construction of the biogas plant: construction of the plant consists of three main chambers: namely, the Digester pit where all the microbiological reactions or decomposition of the material takes place. The digester has to be built to be air-tight with the released gas only escaping into the gas holder. The gas holder is connected to the digester by way of a pipe. Its main purpose is to collect all the gas that has been fermented. The mixing pit is the input chamber where the dung is mixed with water and fed into the digester. The amount and quality of water required for this is no constraint, even in this water stressed area. Construction the biogas plant has to be done according to specifications. A technical drawing of the plant is shown on page 3. The purpose of the technology is to use it for house-hold energy (for cooking, lighting and running appliances).
Natural / human environment: In Botswana the technology was introduced by the Rural Industries Innovation Center which is a government funded research institution. Despite the existence of this company for many years, the uptake has been very low due to poor marketing and extension services and lack of financial assistance to poor farmers.
Biogas is suitable either for a farm, cattle post or rural setting where the inputs (cow dung) are easily available. But there are possibilities of experimenting with other bio-degradable materials in major centres where cow dung is not readily available.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Botswana
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Southern District
Especifique más el lugar :
Kanye village
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The technology is promoted by a government funded NGO, but has its origins outside the country
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- conservar el ecosistema
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Cultivos asociados (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles), incl. agroforestería
- Agro-silvopastoralismo
Principales productos/ servicios:
Major cash crop seasonal cropping:
Major food crop seasonal cropping:
Major other crops seasonal cropping:
Main products semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Beef cattle, goats, sheep, donkeys, chicken
Main products ranching: Beef cattle
Forest products and services: fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing of the commons, droughts, saline water and over-harvesting of fuelwood for cooking, heating leading to deforestation and land degradation
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Overgrazing of the commons, droughts, saline water and over-harvesting of fuelwood for cooking, heating leading to deforestation and land degradation.
Grazingland comments: Biogass technology is not applied in the Boteti area at the moment, only at DESIRE test site.
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: specific tree species are felled for fuelwood even though people are supposed to take only fallen-dead wood
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Mixed cropping is the traditional practice but government extension advice promotes monocropping which the majority find expensive and risky.
Type of grazing system comments: Biogass technology is not applied in the Boteti area at the moment, only at DESIRE test site.
Constraints of settlement / urban
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Comentarios:
Water supply: Also post-flooding
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 179 Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar
Densidad del ganado (si fuese relevante):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- tecnologías de eficiencia energética
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0 m2.
This technology is basically on a point location, even though it is to benefit a wider area in terms of conservation
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S11: Otros

medidas de manejo
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
Comentarios:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bs: reducción en la calidad y composición/ diversidad de las especies
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (harvesting of fuelwood for cooking, sometimes live trees are harvested.), land tenure (Area is communal grazing land)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Trees are cut for bush fences), droughts (The study area is prone to droughts), poverty / wealth ((lack of alternative livelihood sources))
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
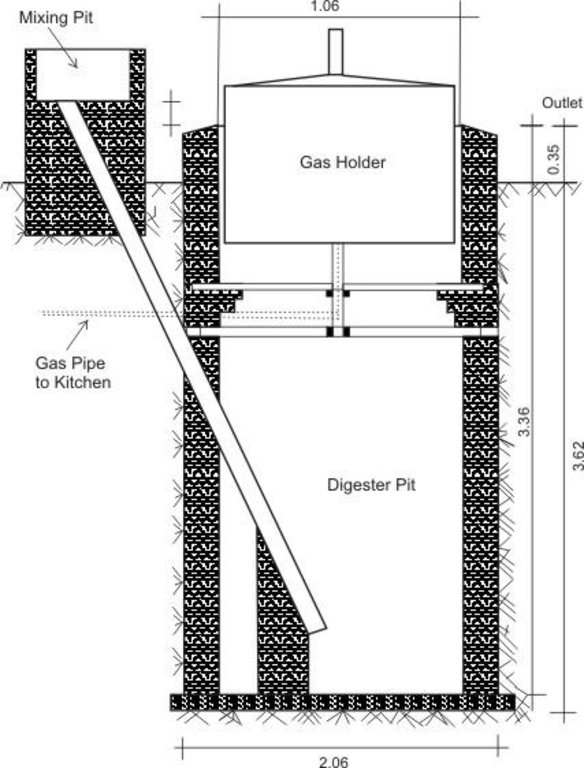
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
The diagram shows the technical layout of a biogas plant; showing the position of the main components: Digester, Gas holder, Mixing pit, and outlet. Cow dung & or kitchen waste (except bones) is mixed with water to form a sludge. This sludge is fed into the digester pit where decomposition and fermentation takes place. As the sludge ferments, methane gas is produced. Methane is a combustible gas and can therefore be used for cooking and lighting. Specially designed gas stoves and lanterns may be required as the gas would not be purified and hence ‚thicker‘ than commercially produced gasses. However, the design can include a water filled pipe bend (u shaped) between the gas holder and outlet pipe. The water in this pipe would help to purify the gas before it is fed to the household appliances. The gas holder tank floats in water, through which the gas bubbles escape and methane gas collects into the floating tank. An outlet through which decomposed material leaves the plant is necessary. Old sludge would float and be removed through this opening (Diagram drawn by G. Koorutwe, Department of Environmental Science, University of Botswana).
Location: Mopipi. Boteti Sub-District
Date: 05/10/11 (revised)
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Skilled technician is needed for installation)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: reduction of wood exploitation
Secondary technical functions: promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), enhancement of tree growth
Structural measure: Digestion pit
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3.38
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2.06
Structural measure: Gas holder
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.6
Construction material (other): bricks, pipes, cement, iron sheets
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Use of biogass for cooking would lead to reduced cutting of wood for cooking
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Pula
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
6,5
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
1.08
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction | Manejo | N/A |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Labour | Tank | 1,0 | 198,0 | 198,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Tank | Tank | 1,0 | 615,0 | 615,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Bricks | Tank | 1,0 | 77,0 | 77,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Cement | Tank | 1,0 | 123,0 | 123,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Plumbing material | Tank | 1,0 | 154,0 | 154,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Earth | Tank | 1,0 | 31,0 | 31,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 1198,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.5 month(s)
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Filling up with cow dung and water | Manejo | 1 Day |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipo | Cow dung | Tank | 1,0 | 33,0 | 33,0 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 33,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Costs were calculated for labour and material based on the real cost of construction at the Mopipi Site.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Material, labour and equipment used in construction are the most determining factors affecting the costs (installation cost is US$ 1198).
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Seasonal summer rains, approx six months dry (LPG = 75-179)
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: subtropics. Sub-tropical climate. Semi-arid with dry winters (LPG=75-179 days).
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Altitudinal zone: 501-1000 m a.s.l. (Part of the Makgadikgadi basin)
Slopes on average: Flat (ranked 1, mainly low lying land of lucrustrine (pans) formation) and gentle (ranked 2, gently sloping (plains))
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil depth on average: Shallow (ranked 1, generally soils are 40cm deep, underneath is a calcrete layer at about 40cm deep) and deep (ranked 2, some sandy area away from pans e.g. the Gidikwe Ridge )
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked 1, away from pans/river/flood plain = main soil type) and fine/heavy (ranked 2, sticky when wet in the depression)
Soil fertility: Low (ranked 1, sandy areas (Arenosols)) and medium (ranked 2, in flood plains of the Boteti river)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (ranked 1, low on sandy areas/soils) and topsoil organic matter (ranked 2, on the flood plains for molapo farming)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (ranked 1, very good on sandy soils) and medium (ranked 2, flood plains are medium)
Soil water storage capacity: Very low (ranked 1, on sandy soils) and medium (ranked 2, on flood plains)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
> 50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Ground water table: >50m (ranked 1, for Boreholes) and 5-50 m (ranked 2, wells in the Boteti River bed)
Availability of surface water: poor/none (dry season-unreliable river flow/rainfall)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatement required, salty water in most areas, ranked 1) and unusable (sometimes too salty even for livestock consumption, ranked 2)
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- elevada
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Biodiversity: High (several game reserves (protected areas) nearby, ranked 1) and low (grazing areas with arable agriculture, ranked 2)
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
- muy rico
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- tracción animal
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: There is no difference, as this is mainly a family thing or institutioanal like in schools and community halls
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are very rich and own 50% of the land (Cattle farmers).
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (Most inhabitants).
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land (Subsistance farm).
Off-farm income specification: Saves money for buying commercial gas and electric power. Helps conserve the forests. Limited off-farm income opportunities for everyone including non-adopters of the technology.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (mostly donkeys for draught power)
Market orientation of annual cropping production system: Mixed (subsistence/commercial) Could be used/produced for domestic and commercial purposes.
Market orientation of grazing land production system: Subsistence and commercial/market
Market orientation of forest production system: Mixed (subsistence/commercial) in both cases use of biogas is approppriate
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- gran escala
Comentarios:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology on grazing land
1000-10000 ha (ranked 1, cattle farmers in ranches and cattle posts)
15-50 ha (ranked 2, subsistence farmers)
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology on cropland:
50-100 ha (ranked 1)
2-5 ha (ranked 2, on average)
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- comunitaria/ aldea
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
Comentarios:
The SLM can be used by anybody - not specified to any group. Dual grazing rights is a problem (private ranchers can also use the commons).
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Assuming large scale removal of dung, there could be reduction in animal manure available for crop production
generación de energía
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
As farmers would have to purchase fertilizer as animal manure becomes scarce
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
With biogas no labour for fuelwood collection. Time and effort previously used for firewood collection is freed
Impactos socioculturales
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
mitigación de conflicto
Comentarios/ especifique:
Future conflict over fuelwood resources would be averted. In case of no ownership of cattle.
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Comentarios/ especifique:
Less demand on the time and labour of women and the girl child who are the main collecters of fuelwood
Gender related issues
Comentarios/ especifique:
Where taboos exist for women harvesting dung from kraals (livestock enclosure); this could constrain adoption along gender lines
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
Provides cheaper and alternative source of energy. Reduces workload for fuelwood collection for women and the girl child.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to reduced plant cover
Suelo
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
More trees certaily provides soil cover. But problems possible when plant cover is reduced as a result of less manure
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced soil fertility with distance from water points/kraals
salinidad
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to redused animal manure
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Trees would have more density or cover
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Wood collectors target specific species
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
Large scale adoption of biogas production may introduce air pollution. Also unpleasent smell around the village.
Otros impactos ecológicos
Concentration of nutrients (dung)
Comentarios/ especifique:
Cow dung will be reduce around water points and kraals
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
sedimentos transportados por el viento
daño a campos de vecinos
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
| temperature decrease | no muy bien |
Comentarios:
Biogas technology may be limited under extreme cold conditions whereby fermentation may be limited by cold temperatures.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
Very costly to set up, if no government aid. It is however very good for long term water provision.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
10
Comentarios:
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: A very insignificant number of individual farmers have used this technology
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The technology has mostly been used where the Research institution has installed in farmers' properties. Only in very few instances around the country have individuals installed it for themselves.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There seems to be very little marketing of biogas in the country
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
Problems of diminishing firewood species are reduced. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Because it is not every or all species that is used for firewood, the targeted species are quickly diminished |
|
Cost of getting firewood is reduced How can they be sustained / enhanced? Distance to wood collection places are ever increasing hence users have to buy from truck or donkey cart owners |
|
More time is freed How can they be sustained / enhanced? This especially applies to children (of school going age) in that they would have more time for their home works. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Low maintenance and inputs are required for this technology How can they be sustained / enhanced? There is need for promotion of the technology |
|
The structures to be put in place are very basic How can they be sustained / enhanced? There is need for the government to subsidize farmers in installing biogas plants, especially in the rual areas. |
|
Good for rural households where firewood is used extensively. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve income of rural families so that they could afford the technology |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Too expensive for poor farmers to adopt without assistance | Donor/government subsidies |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Brown, V. J., 2006. BIOGAS: A Bright Idea for Africa. Environ Health Perspectives. 114(5), pp. A300–A303.
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
internet
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Dayal, M., Vimal, O.P., Singh, K.K., 1989. Biomass gasification in India — DNES activities. Biomass, Volume 18, issues 3-4,pp. 197-204
¿Dónde se halla disponible? ¿Costo?
http://www.ganesha.co.uk/Articles/Biogas%20Technology%20in%20India.htm
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos