Jatropha curcas hedge [Etiopía]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Simon Bach
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
Agulo Keter
technologies_1524 - Etiopía
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Ayele Habtamu
+251 92 592 0594
Haramaya University
Haramaya University, P.O. Box 138, Dire Dawa, Ethiopia
Etiopía
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Haramaya University (HU) - Etiopía1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
30/04/2011
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Gully rehabilitation and hill stabilization with Jatropha hedges.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
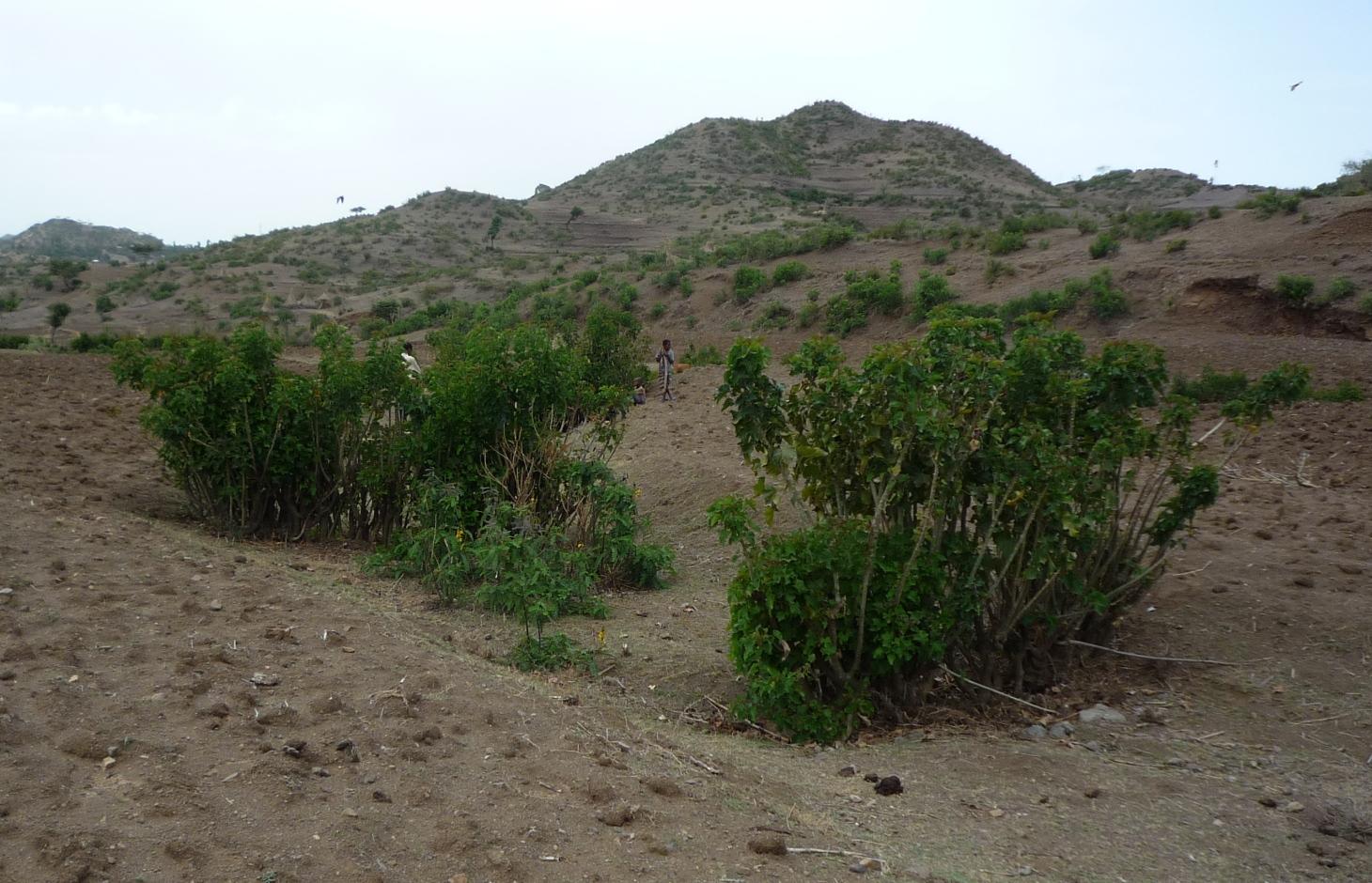
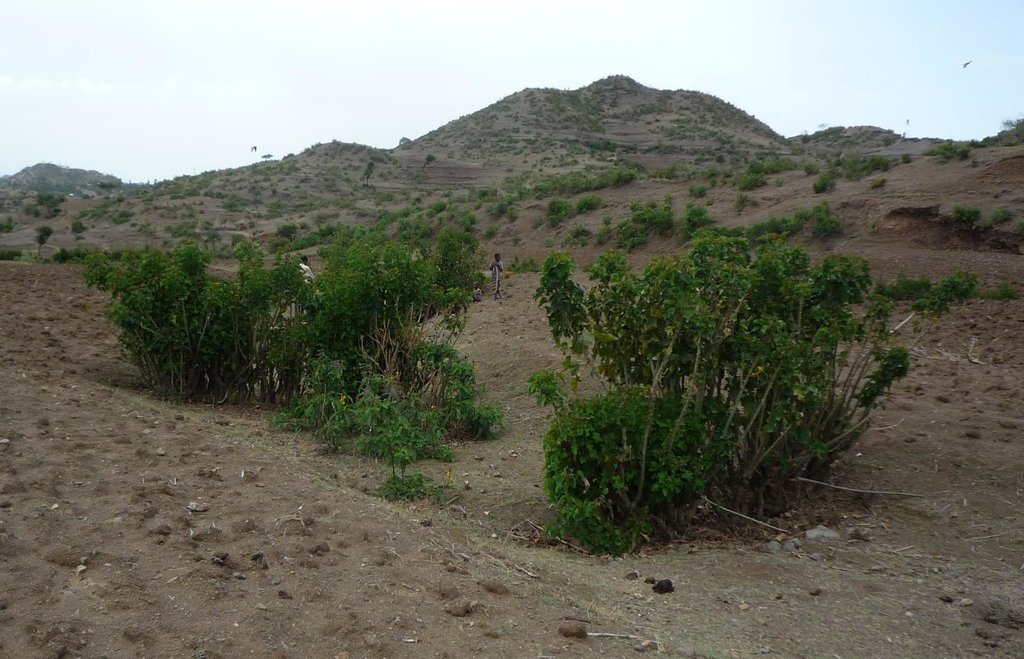
In the area around Bati in Ethiopia, Jatropha is used to stabilize hills ore to rehabilitate gullies. The technology was introduced during the last decade by local farmers on their plots. The advantage of Jatropha against other shrubs is that it is poisonous and therefore not browsed by animals. Additionally the seeds can be collected by household members and sold on the local market. The seed's oil can be used as a lamp oil or even for the production of bio-fuel.
Purpose of the Technology: Besides hedges and living fences, Jatropha is used for combating sheet or gully erosion. To stop erosion processes the Jatropha cuttings are planted across a gully or along hill sides to stabilize them in the same manner as check dams or terraces do. The plant is chosen because of its very tolerant character, rather high accessibility in the area and because it is easy to propagate by cuttings. Often Jatropha is used in combination with traditional stone check dams or terraces aiming for an increased stability of the technology itself. For that purpose Jatropha is planted in front of the stone walls or also on top of them.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In earlier times Jatropha was planted by seeds but nowadays, since there are a lot of plants in the area, propagation by cuttings is the more prominent form. Since the plants are pruned every year anyway, the cuttings are accessible almost in any case for free. At markets further away, the cuttings cost around one cent per piece. In order to rehabilitate a gully Jatropha cuttings are planted as near as possible in the selected area in a row across the gully. After rooting, the spaces between the plants are filled up with litter, shrubs or stones. In order to have a thick stem and avoid competition with crops, the plants are pruned every year. The thick main stems reach a height of approximately one meter which delineates the maximum height of possible soil collection. If the area behind the filled up gaps and the cuttings has silted up, the height is increased by adding new litter in the higher up gaps. In off farming season, the Jatropha seeds are collected and sold on the market to create additional income.
Natural / human environment: The case study site, Bati, lays in an semiarid climatic zone on 1600 m a.s.l. Rainfalls are erratic and the rain sum per year is between 500-1000 mm. The landscape is very hilly with rather steep slopes. The area has a high population density and growth. The agricultural sector is very dominant and lead by a lot of small scale farming with a lot of livestock and small plots of cropland.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Etiopía
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Ethiopia / Amhara Region
Especifique más el lugar :
Bati
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
Farmers are using Jatropha curcas since approximately 30 years in the research area in Bati mostly for fencing. Innovative farmers started using the plant for stabilizing existing physical structures (stone walls, terraces, gully check dams) or using it as a complete substitute for these physical structures.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cosecha anual
Cosechas principales (comerciales y de subsistencia):
Major food crop: Sorghum
Major other crop: Corn

Cultivos asociados (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles), incl. agroforestería
- Silvo-pastoralismo
Principales productos/ servicios:
Major food product: Cattle, goat, sheep, camel
Major other product: Chicken
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Deforestation, overgrazing, cultivation of erosion-sensitive areas or steep slopes.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Too much soil loss and land degradation, no vegetation cover and poor soil moisture.
Grazingland comments: Livestock is not fenced in. Children herd the animals and watch out that they do not browse through crop fields. In off-farming season crop residues are collected from the field and stored next to the field. Animals are allowed to eat the still remaining residues on the field. After that, the animals are fed by the collected crop residues.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Type of grazing system comments: Livestock is not fenced in. Children herd the animals and watch out that they do not browse through crop fields. In off-farming season crop residues are collected from the field and stored next to the field. Animals are allowed to eat the still remaining residues on the field. After that, the animals are fed by the collected crop residues. Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Comentarios:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 90 Longest growing period from month to month: June until September
Densidad del ganado (si fuese relevante):
> 100 LU /km2
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- medida de pendiente transversal
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.7 m2.
Size of the case study watershed.
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos

medidas estructurales
- S1: Terrazas
- S6: Muros, barreras, vallas, cercas
Comentarios:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie
- Wg: erosión en cárcavas
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation for the past 30 years.), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Wood collection for cooking and construction.), overgrazing (60% of the watershed area are cultivated - big grazing pressure on remaining land), other human induced causes (specify) (Cultivation of very steep slopes.), change of seasonal rainfall (Erratic rainfall.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (If there is rain, it is intensive.), population pressure (High population pressure.), poverty / wealth (Poor facilities.)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (Poor soil management practices and lack of awareness.), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Annual cropping.), droughts (The research area is considered rather dry.), land tenure (If the land is rented, it is poorly managed.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Poor access to fertilizer. Bad infrastructures.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of awareness for soil degradation.), Low productivity of the land (As a consequence seeking for new/larger areas to increase production.)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
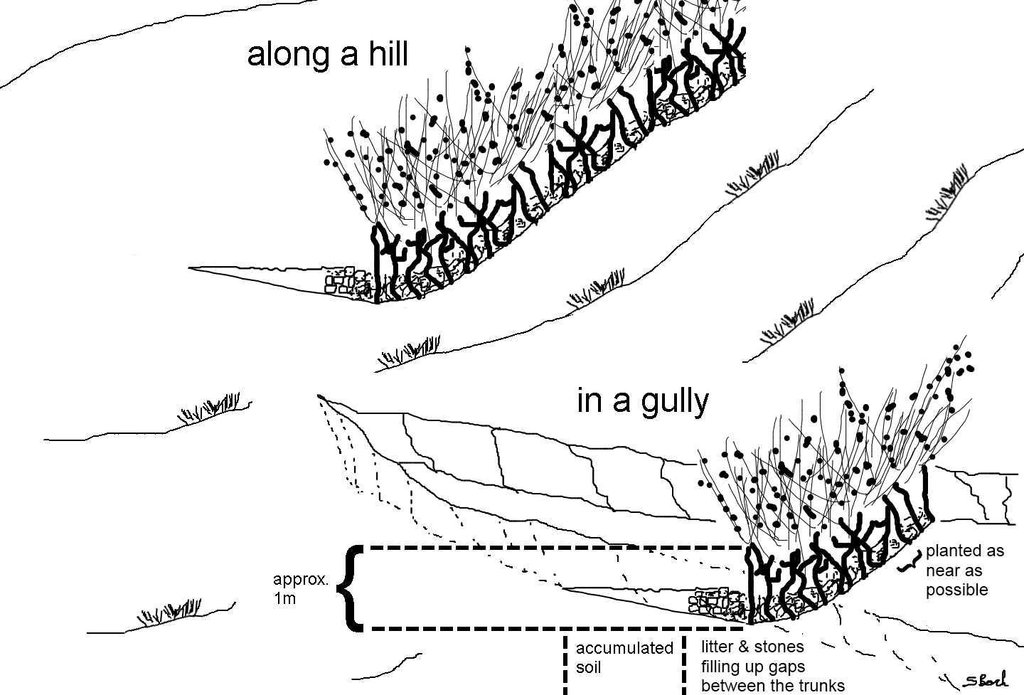
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
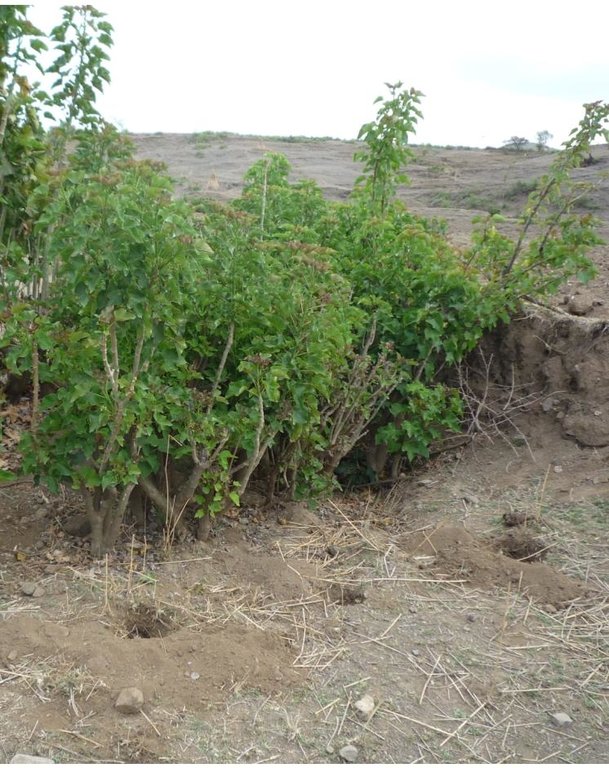
Jatropha hedges as they can be found in the region of Bati. Often the plant is used for gully rehabilitation. For that purpose it is planted (mostly by cuttings) with a minimal interval between each plant to create a barrier-like hedge. The gaps are filled up with litter or stones.
Approximately 1 m of soil can be collected by the trunk - above that height it is too thin. The Jatropha seed can create additional income besides the purpose of soil and water conservation. Often, the plant is used in combination with traditional technologies (terraces, stone walls) and planted on top or in front of these traditional structures to improve their stability.
Location: South of Bati. Bati Woreda, Amhara Region, Ethiopia
Date: 05.05.2011
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Planting takes place rather randomly in places of needs.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 10 per m
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): ~1m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): ~20m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Vegetative measure: filling material
Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Trees/ shrubs species: Jatropha curcas
Other species: Stones, shrubs, sticks - things that can be found and utilized to fill up gaps between each plant.
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Ethiopian Birr
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
16,82
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
1.00
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | One time initial sawing of Jatropha seeds (30 years ago). | Vegetativas | Initial. Wet season. |
| 2. | Cutting of the Jatropha cuttings (12.5 person days needed). | Vegetativas | dry season |
| 3. | Planting of the Jatropha cuttings (12.5 person days needed). | Vegetativas | dry season |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Seeding | person day | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Cutting of the Jatropha cuttings | person day | 12,5 | 1,0 | 12,5 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Planting of the Jatropha cuttings | person day | 12,5 | 1,0 | 12,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Tools for cutting | 500m | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seeds | kg | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 33,0 | |||||
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of Jatropha seeds (5 person days needed). | Vegetativas | Off farming season(Okt.) |
| 2. | Filling up the gaps with litter (5 person days needed). | Vegetativas | If necessary |
| 3. | Pruning of the Jatropha hedges (15 person days needed). | Vegetativas | Yearly before wet season. |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Collection of Jatropha seeds | Person days | 5,0 | 1,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Filling up the gaps with litter | Person days | 5,0 | 1,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Pruning of the Jatropha | person days | 15,0 | 1,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipo | Tools | Person days | 15,0 | 0,333333333 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construcción | Wood | 500m | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Material de construcción | Stone | 500m | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 30,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: saw, axe
Total costs of a hectare are calculated for a hedge of 100 m length every 20 m (500 m total hedge) in the year 2011. Tool prices were estimated and labor costs were calculated with a daily wage of 1$.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Rough topology in the area, questionable availability of construction materials if they are not found nearby.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Erratic rainfall (rainseason from June until September)
751-1000 mm ranked 1
501-750 mm ranked 2
Zona agroclimática
- semi-árida
Thermal climate class: tropics
LGP shorter than 90 days.
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (The study site is located at 1600m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1) and valley floors (ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Hilly (ranked 1), rolling (ranked 2) and steep (ranked 3)
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil depth on average: Very shallow (ranked 1), shallow (ranked 2)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Ground water table is unknown.
Availability of surface water: Only during rainy season
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, mostly groundwater)
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Relative to other parts of Ethiopia.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- rico
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- tracción animal
Género:
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 6%
1% of the land users are rich (Adopt the most of SWC technologies).
19% of the land users are average wealthy.
89% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Off-farm income has low importance.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (plowing by oxen, ranked 1) and manual work (ranked 2)
Market orientation: Mixed (subsistence and commercial) Goat/sheep are main meat source (in household or on market).
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
gullies are transformed to fields
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
improving soil moisture
diversidad de producto
Comentarios/ especifique:
selling the Jatropha curcas seeds
área de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
gullies are transformed to fields. Structure needs space but also gains space
manejo de tierras
Comentarios/ especifique:
gully is now flat land and traversable, structure as a new obstacle
generación de energía
Comentarios/ especifique:
Jatropha curcas seed oil as a biofuel
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua potable
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
alluvial soil is relatively fertile
ingreso agrario
Comentarios/ especifique:
new fields lead to higher productivity
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
selling the Jatropha curcas seeds
disparidades económicas
Comentarios/ especifique:
additional income by selling Jatropha seeds
carga de trabajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
slightly labor increase, establishment and maintenance work
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
additional space for new fields
instituciones comunitarias
instituciones nacionales
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
positive examples for other land users
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Comentarios/ especifique:
up -downstream problems may be solved
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
Accumulation of soil leads to new space for fields and additional food security or even income (if crop surplus is sold). Collection of Jatropha curcas seeds - they can be sold (additional income) or processed to oil (lamp oil etc.)
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
increased soil moisture
cosecha/ recolección de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
Jatropha curcas dam blocks water flow
escurrimiento superficial
Comentarios/ especifique:
increased infiltration, reduced flow velocity
nivel freático/ acuífero
Comentarios/ especifique:
increased infiltration
evaporación
Comentarios/ especifique:
maybe due to the Jatropha curcas canopy
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Jatropha curcas dam blocks water flow,. But additional groundwater may be logged
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Jatropha curcas canopy
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
alluvial accumulation behind the structure
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
increased rooting
compactación de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
increased rooting
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
Comentarios/ especifique:
Jatropha curcas leaves & litter
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Jatropha curcas leaves & litter
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
Jatropha curcas biomass
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
diversidad animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
especies benéficas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Jatropha curcas new habitat for worms etc
diversidad de hábitats
Comentarios/ especifique:
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Comentarios/ especifique:
new habitat for rodents etc.
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
impactos de inundaciones
Comentarios/ especifique:
flood controll by Jatropha curcas dams
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
little effect by additional plants
riesgo de incendio
Comentarios/ especifique:
Jatropha curcas wood is a bad fire wood
velocidad de viento
Comentarios/ especifique:
Jatropha curcas shrub as a wind breaker
Otros impactos ecológicos
Increased competition
Comentarios/ especifique:
Over water and sunlight
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
possibility of spring development
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
Comentarios/ especifique:
if a spring can develop
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
increased infiltration/reduced flooding
colmatación río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
trapping of the sediments by the structure
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
Comentarios/ especifique:
trapping of the sediments by the structure
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
Comentarios/ especifique:
increased infiltration
sedimentos transportados por el viento
daño a campos de vecinos
Comentarios/ especifique:
due to gully rehabilitation
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
Comentarios/ especifique:
due to gully rehabilitation
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no se sabe |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
Establishment needs a little time, although not very much. Maintenance work is very little needed and can be done if needed or in off-farming season. Establishment and mainentance costs are none or very little.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
De todos quienes adoptaron la Tecnología, ¿cuántos lo hicieron espontáneamente, es decir, sin recibir incentivos/ pagos materiales?
- 90-100%
Comentarios:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Local technology spread from farmer to farmer.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Completely based on farmer's initiative.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: A lot of farmer are adopting (or already have adopted) Jatropha curcas as a SWC technology in the region.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
Soil and water conservation are very important. Also the conservation of soil moisture. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Create farmer's awareness that SWC is very important for a sustainable land management. |
|
In combination, Jatropha curcas can also be used to stabilize traditional stone structuress (terraces, dams). These physical structures are not consideret very stable and need a lot of work to establish and maintain. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further research to improve physical structures, Jatropha curcas structures as well as their combination. |
|
The roots bind the soil and holding it together and help collecting additional soil that otherwise would be washed out. The root and the plant also help to slow down flowing water. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Research on how tolerant is the plant on flooding etc. |
|
Jatropha curcas is also a very good life fence that animals do not browse through because the leaves are poisonous. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Create awareness in the society that the plant is poisonous and should not be eaten. |
|
The seeds can be sold. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Creating and improving markets, infrastructures and technologies that need Jatropca curcas oil or biofuel. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Very low labor and money input for establishment and maintenance. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep the technology as simple as it is today. |
|
Easy to atopt in a wide range of environments (Jatroha curcas is a rather tolerant plant). How can they be sustained / enhanced? Additional research to improve knowledge of Jatropha curcas. |
|
Selling of the seeds is an additional income. If the seeds are crushed to oil it can substitute for example lamp oil that has to be bought. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve market situation and find technologies suitable to use Jatropha curcas oil or biofuel. |
|
The plant can be used in a wide range of rehabilitation purposes (gully rehabilitation, hill stabilization, improvment of micro climate etc.) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Create and maintain awareness of the farmers. |
|
If plantet on bare land only, the plant does not compete with food production. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sensitize the farmers that food is more important than gaining an extra income so they do not give up their fields for Jatropha seed production. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| If children eat the seeds they get sick. | Rise awareness that the plant is poisonous. |
| Plant competes for soil moisture. | Find a good compromise betweeen pruning and maximum toleratet shade as well as maximum soil moisture that can be taken by the plant to maximize yield. |
| Plant competes for sun light. | Find a good compromise betweeen pruning and maximum toleratet shade as well as maximum soil moisture that can be taken by the plant to maximize yield. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Jatropha curcas is an alien plant although it is used for more than 30 years in the region. | Research on the long term effects of Jatropha curcas in specific areas. |
| If the plant should reach maximum yields inputs have to be increased as well and it has to be planted on fertile soil (food competition). | Make shure people only use it as fence or as a SWC plant on bare land. |
| To avoid shading the plant is often pruned every year and the yield is therefore very small (economically irrelevant). | Find a good compromise betweeen pruning and maximum toleratet shade to maximize yield. |
| The plant is poisonous. People have to take care and children have to be sensitized. But acording to the farmers eating the leaves or the seeds leads to stomach ache and is not too dangerous. | Create awareness in the society that the plant is poisonous and should not be eaten. |
| Farmers plant and use Jatropha curcas quite randomly and without any specific approach. | The role of science: find the best practice. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Bach S. (2012) Potentials and limitations of Jatropha curcas as a multipurpose crop for sustainable energy supply and soil and water conservation - a case study in Bati, Ethiopia, using the WOCAT approach. Unpublished master’s thesis, Centre for Development and Environment, University of Bern.
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos