Pasture management of a communal grazing land [Tayikistán]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Malgorzata Conder
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
technologies_1555 - Tayikistán
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuizaNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
CARITAS (Switzerland) - Suiza1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
25/09/2012
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Pasture management of a communal land through daily rotation
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
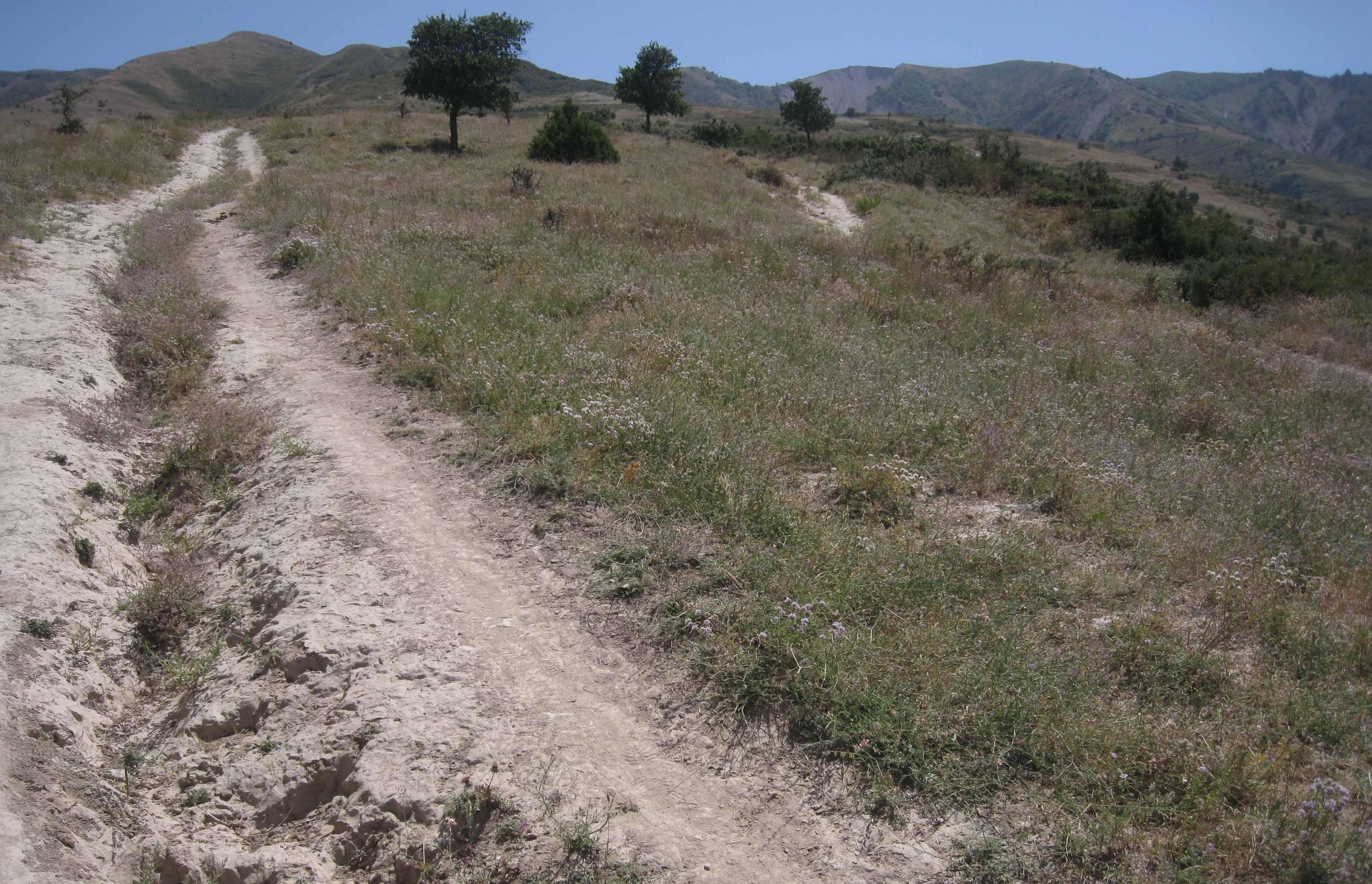
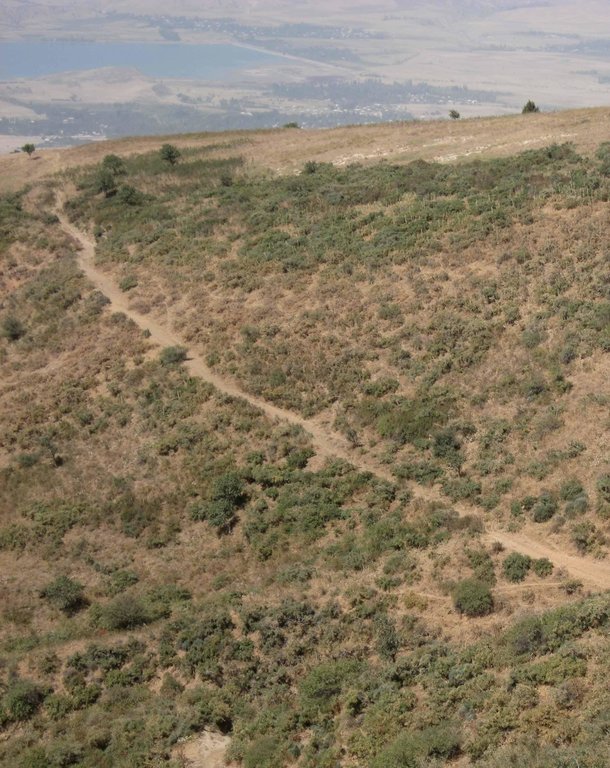
The total area of the pasture accounts for 300 – 500 ha. The pasture is property of the Doshmand village but it includes also some private properties, mainly potato and wheat crops. After the harvest, livestock is also grazing on these crops. Eighteen households are currently using the pasture with a total of 150 cows and 500 small animals. Additionally, three groups of herds from other villages graze irregularly on this pasture mainly on the lateral parts as it is less guarded by the villagers. The interviewee estimates that over 1000 cows, goats and sheep are coming from other villages. Other herds cross this pasture when migrating to or coming back from the summer pasture in spring and autumn, respectively. Nevertheless Doshmand residents claim that this intrusive grazing is accepted as “every animal has to be fed”. This shows the need of a pasture management not only on village but also on watershed level.
During Soviet time the inhabitants of Doshmand were forced to migrate to the valley. In 2003, the resettlement of the ancient location started with two families. Simultaneously, the pasture management was established and joined by each family who resettled. The controlled area is divided in 4 subparts. The herd switches daily within them. Every household looks after the herd for a day, which results in a rotational cycle of 18 days. There are no fixed and regular meetings for pasture management within the village pasture. However, two subsequent herders communicate to know where the herd has been grazing and where to graze the next time.
Purpose of the Technology: Purpose of the rotational grazing is to graze on one subpart, while the three other areas are resting. This reduces the impact of grazed and trampled areas per subpart and allows the growth and recovery of the vegetation in the other parts.
The task of herding is shared among the families. The rotational grazing is organized orally and freely, why it’s not sure if that approach is strictly binding. Discussions about pasture management rise only in case of need.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Doshmand village got the pasture in a good condition at the time of establishment. Vegetation cover was high. The only investment consisted in building a water point for the livestock. A further investment was to buy a water pipe and dig out a channel for the pipe to conduct the water from the water point to the village. Money was collected by the families and many villagers were involved in digging the channel.
No further input was and is required except coordination between the herders.
Natural / human environment: The pasture of Doshmand village is located in the middle and upper zone of the watershed. Thanks to the distance to other settlements, the pasture is less affected by overgrazing than other communal pastures in the watershed. Nevertheless, the pasture is heterogeneously grazed, with some areas which are difficult to access even for livestock and hence abundant vegetation. Other areas, especially those situated next to the village show a more bare vegetation cover.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tayikistán
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
Especifique más el lugar :
Muminabad
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- conservar el ecosistema
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierra de pastoreo
Tierras de pastoreo extensivo:
- Semi-nomadismo/ pastoralismo
- rotational grazing
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Erosion
Overgrazing
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): increase of unpalatable vegetation
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Grazingland comments: Mainly summer pasture, normally no grazing from November/ December to February/ March
Type of grazing system comments: Mainly summer pasture, normally no grazing from November/ December to February/ March
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 160Longest growing period from month to month: April-Sept
Densidad del ganado (si fuese relevante):
> 100 LU /km2
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- pastoralismo y manejo de tierras de pastoreo
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- 1-10 km2
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 4 m2.
The Vakil (village representant) was not sure about the area, between 300 to 500 ha.
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas de manejo
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
Comentarios:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wo: efectos de degradación fuera del sitio

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo
- Bs: reducción en la calidad y composición/ diversidad de las especies
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects, Pc: compaction, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing, land tenure (communal grazing land also used by other communes)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
Comentarios:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
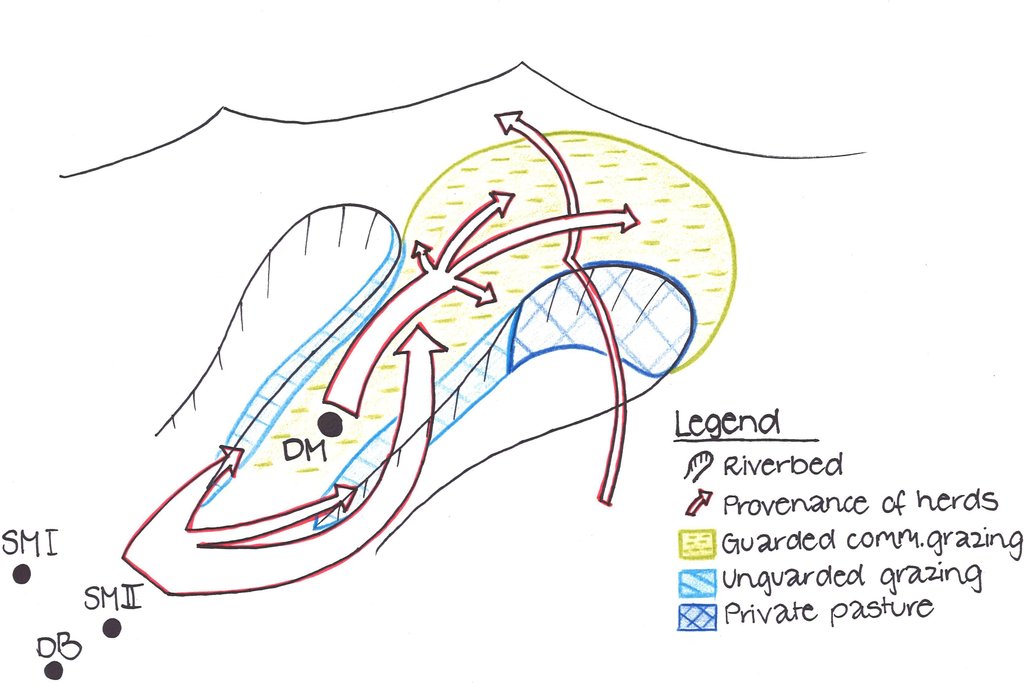
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
Livestock from Doshmand village (DM) is grazing in the four subparts of the communal pasture. Livestock from other villages, located in the valley Sarmadoni I (SMI) and II (SMII) and Dehibaland (DB), can invade the guarded and unguarded communal pasture of Doschmand. In spring and autumn also other livestock crosses Doshmand's pasture when migrating to or leaving the summer pasture.
Location: Chukurak watershed. Muminabad, Khatlon
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Rotational grazing at village level
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- dólares americanos
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
12.40
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Coordination with villagers and herders | Manejo | Reestablishment of village |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Coordination with villagers and herders | - | 1,0 |
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Consultation with village herders | Manejo | If needed |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Consultation with village herders | - | 1,0 |
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
There are no costly factors, the most important input is a good planning, coordination and consistent execution of the rotational grazing system.
The installation of a waterpoint would be needed but it is a very costly installation.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Annual rainfall (1,001-1,500 mm): Totally 800mm: 700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season (At 1200mm asl, weather station Muminabad)
Annual rainfall (1,501-2,000 mm): Precipitation increases 60mm per 100m of altitude in average. Here up to 1600mm.
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Thermal climate class: temperate
LPG from April until September
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Slopes on average (steep): Some flanks up to approx. 40%
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- elevada (>3%)
- media (1-3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Topsoil organic matter (high): On some flanks with high vegetation cover, which are difficult to access by livestock
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is low near the villages and high on mountain slopes (off-village)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Water quality (untreated) is also for agricultural use only (irrigation)
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- elevada
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- subsistencia (autoprovisionamiento)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- grupos/ comunal
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
Around 3 ha, if 7.7 pers/household of totally 2350 ha pasture
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- arrendamiento
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
Comentarios:
Land ownership is based on the land user certificate conferred by the government
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de forraje
producción animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Not the whole pastureland can be grazed at once
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
disponibilidad de agua para ganado
calidad de agua para ganado
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
instituciones comunitarias
Livelihoods and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
Strenghtening of the community sense and awareness through increased coordination for rotational grazing between villagers. Higher fodder availability leads to healthier livestock.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
escurrimiento superficial
evaporación
Suelo
humedad del suelo
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
compactación de suelo
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
riesgo de incendio
Otros impactos ecológicos
Hazards towards adverse events
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
colmatación río abajo
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | no muy bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | no muy bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no muy bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | no se sabe |
Comentarios:
Conduct the rotational grazing even more strictly
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
neutral/ balanceado
Ingresos a largo plazo:
ligeramente positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
neutral/ balanceado
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
Si tiene la información disponible, cuantifique (número de hogares y/o área cubierta):
NA
Comentarios:
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Effort is made to introduce more rotational grazing on cummunity level in the region with institutional support.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| No big input, coordination between farmers exists anyway |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
In a rotational grazing system at village level every family is responsible for the sustainability of the pasture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Give more responsability and co-determination to individuals |
|
High establishment potential as rotational grazing do not demand any costs, except coordination and organization on village level How can they be sustained / enhanced? Disseminate the idea of rotational grazing also on watershed level |
|
Ecologic benefits as high vegetation cover, less erosion etc. can be achieved without monetary investment How can they be sustained / enhanced? Spread knowledge of long-term effects by rotational grazing |
|
Being a pasture of a big area extent in the uphills, the good quality of the pasture plays an important role for all the settlements and cultivations downstream How can they be sustained / enhanced? Raise the awareness about the upstream-downstream interrelation in the watersheds |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| In reality, rotational grazing is not executed strictly enough | Stricter separation of the subparts needed |
| Herds from other villages graze in the same pasture | Strenghten coordination of grazing between and within villages |
| Some flanks show high vegetation because they are not accessible for livestock and not because of the rotational grazing |
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos