Selective clearing and planting experiment to promote shrubland fire resilience [España]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Nina Lauterburg
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Deborah Niggli
Experimento para aumentar la resiliencia del matorral contra incendios (Spanish)
technologies_1579 - España
- Resumen completo en PDF
- Resumen completo en PDF para imprimir
- Resumen completo en el navegador
- Resumen completo (sin formato)
- Selective clearing and planting experiment to promote shrubland fire resilience: 4 de enero de 2017 (inactive)
- Selective clearing and planting experiment to promote shrubland fire resilience: 30 de julio de 2019 (inactive)
- Selective clearing and planting experiment to promote shrubland fire resilience: 1 de diciembre de 2021 (public)
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Valdecantos Alejandro
+34 609 183 599
a.valdecantos@ua.es
Fundación Centro de Estudios Ambientales del Mediterráneo (CEAM)
Parque Tecnológico Paterna. C/ Charles Darwin 14, 46980 Valencia, Spain
España
Especialista MST:
Baeza Jaime
jaime.baeza@ua.es
Fundación Centro de Estudios Ambientales del Mediterráneo (CEAM)
Parque Tecnológico Paterna. C/ Charles Darwin 14, 46980 Valencia, Spain. / Departamento de Ecología, Universidad de Alicante, Ap. 99, 03080 Alicante, Spain
España
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Catastrophic shifts in drylands (EU-CASCADE)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Centro de Estudios Ambientales del Mediterraneo (CEAM) - España1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
26/04/2013
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
The combination of clearing of fire-prone seeder species and planting of more fire resistant resprouter species directs the vegetation to later successional stages which increases the resilience to fires.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
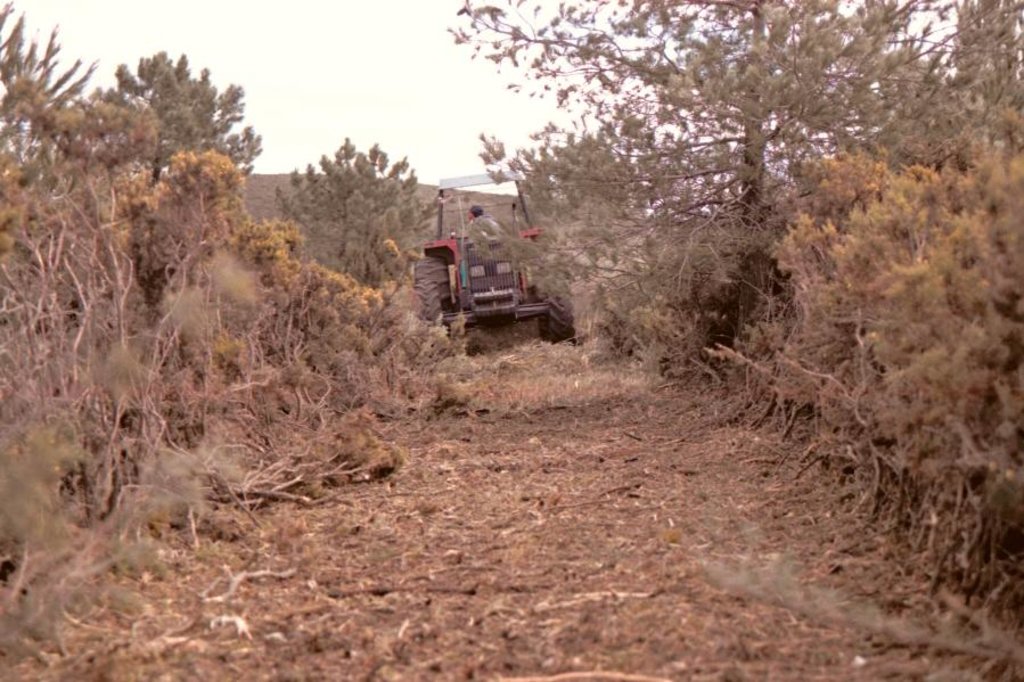
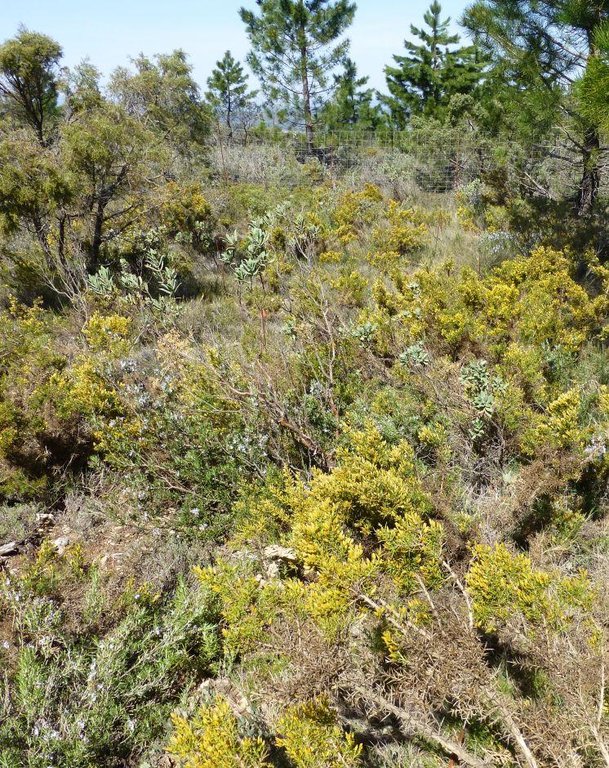
The forests and shrublands in Ayora experienced a series of disturbances in the past (such as deforestation and land use), which resulted in the degradation of the vegetation and the reduction of the resilience to fires. At present, there is a high fire incidence. Post-fire landscapes regenerated with a high and continuous fuel accumulation with few native resprouter species. Therefore appropriate vegetation management is crucial.
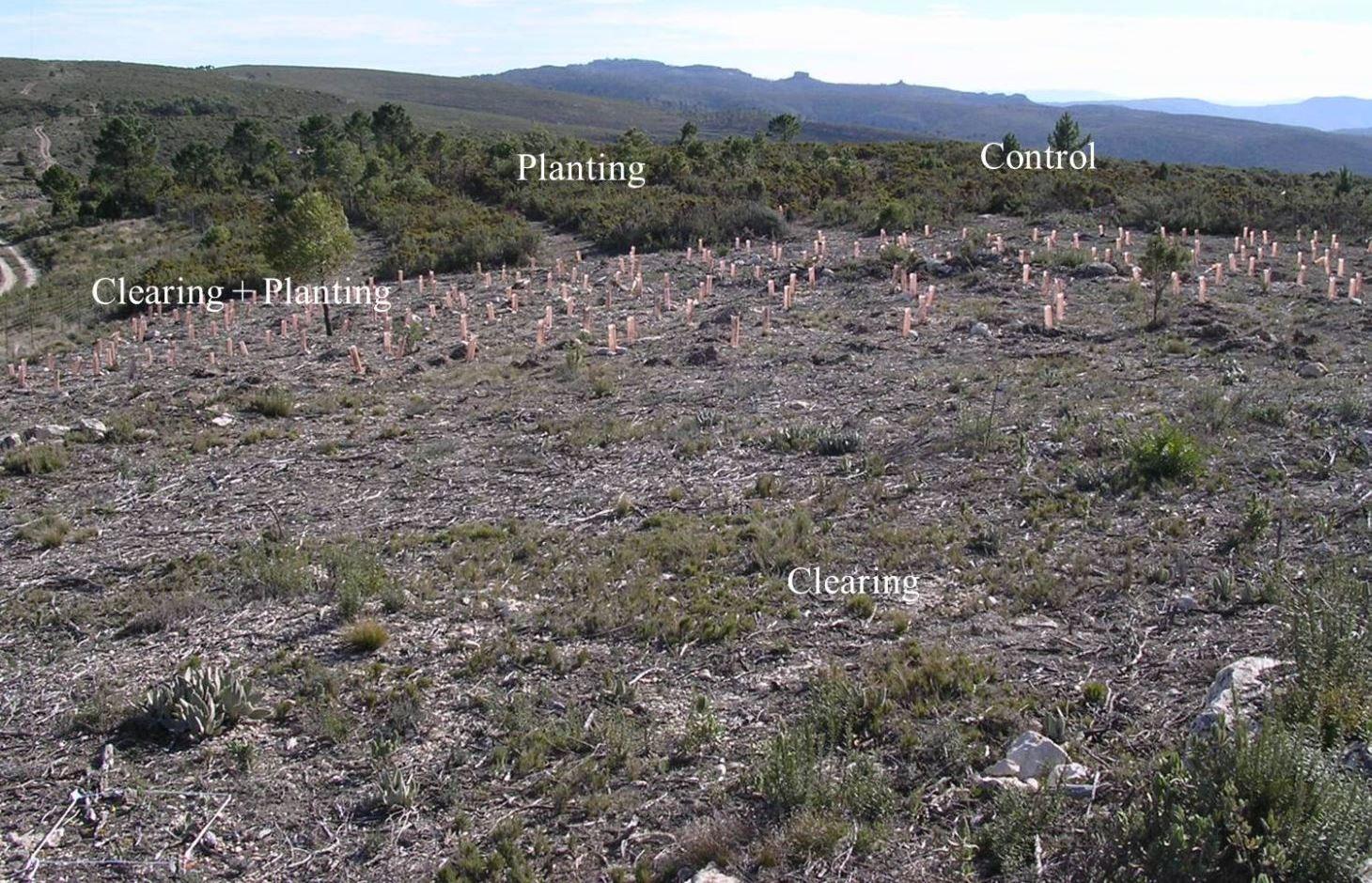
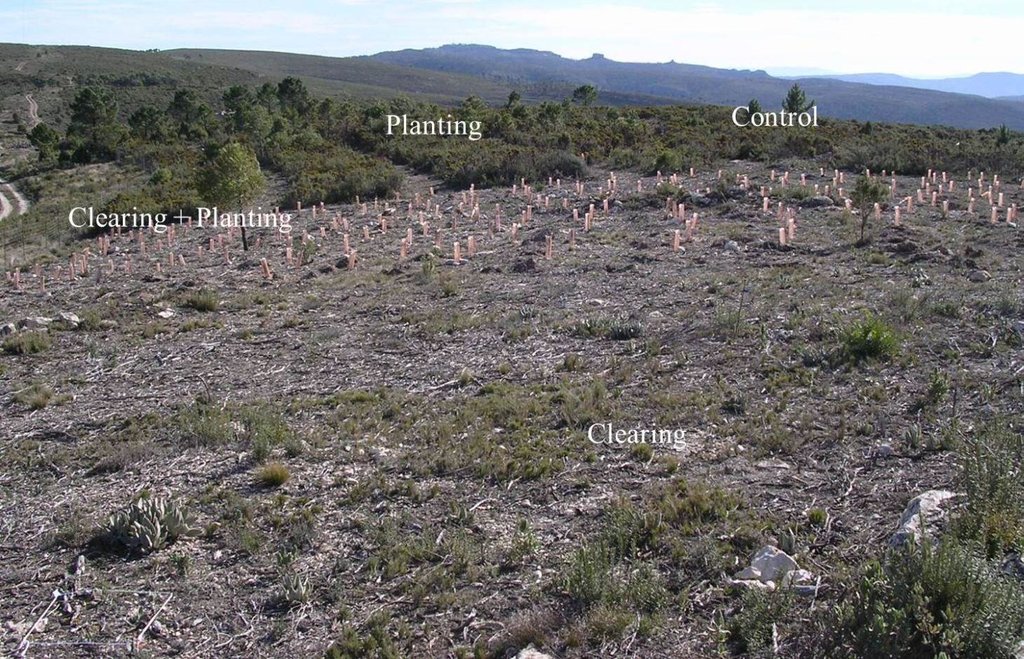
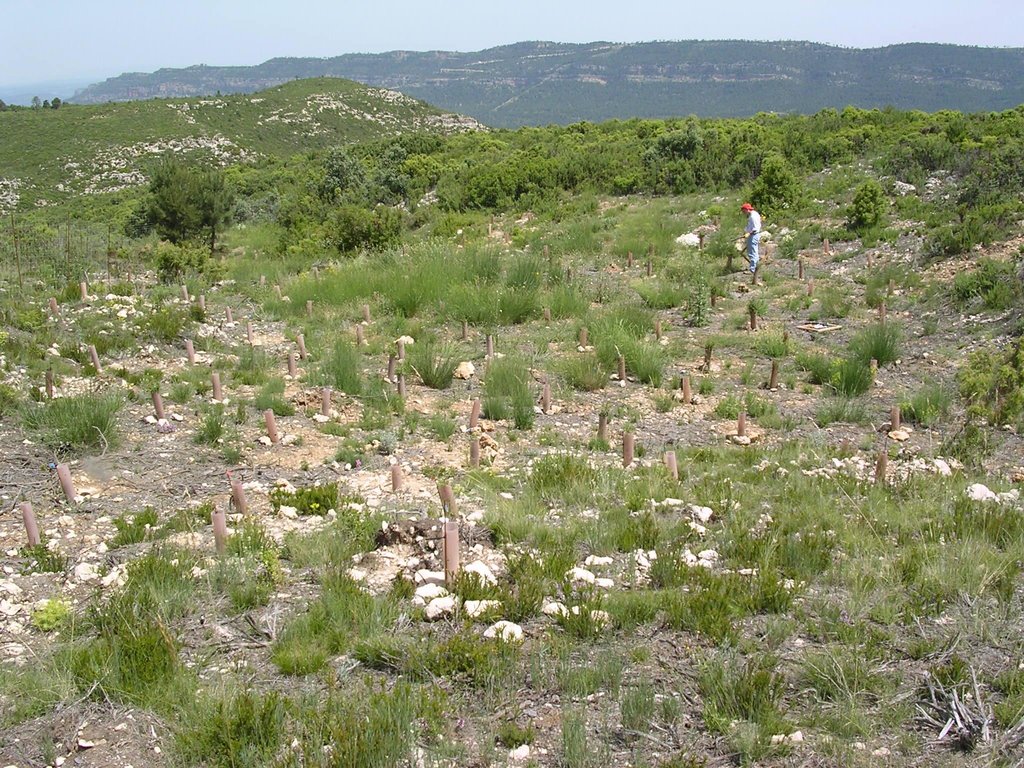
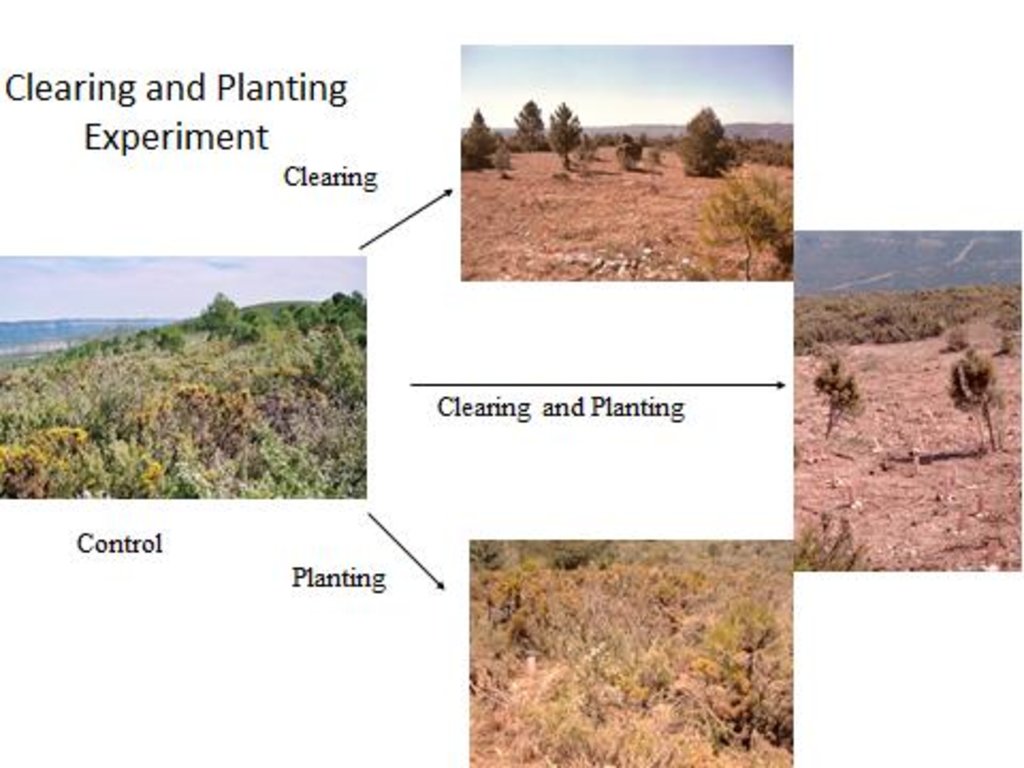
For management the major goals are to reduce the fuel load and its continuity and to increase the resilience of the vegetation to fires. Within this experiment carried out by CEAM (Centro de Estudios Ambientales del Mediterráneo, University of Valencia) different fuel management techniques were examined. They selected three study sites (Morera, Roñoso, Gachas) with a similar history of land use, vegetation composition, soil characteristics, and a typical post-fire scenario whith scarce occurrence of resprouter species. In each site, four plots were established to test the effect of the following management techniques: 1) control (no action), 2) clearing, 3) planting (within the shrubland) and 4) the combination of clearing and planting.
The main purpose of this experiment was to find out which management technique is the most appropriate to prevent fires and it was shown that the combination of selective clearing of fire-prone shrubs (fuel control) and planting of more resistant resprouter species can increase the resilience to fires and is therefore a suitable management practice. Compared to the other management techniques, there are some advantages. Clearing the vegetation (either by hand or mechanically) reduces the fire risk and enhances seedling establishment and growth. Furthermore, the cleared vegetation is chipped and applied in-situ as mulch, which protects the soil from erosion, reduces soil temperature and moisture loss, and enhances carbon conservation. Additionnally, selective clearing allows to preserve desired species and by planting resprouter species the natural processes can be accelerated. Once established, resprouter species persist for a long time which promotes an increase of the vegetation resilience.
In this documentation, only the combination of clearing and planting is evaluated since this action is considered as the most appropriate management practice.
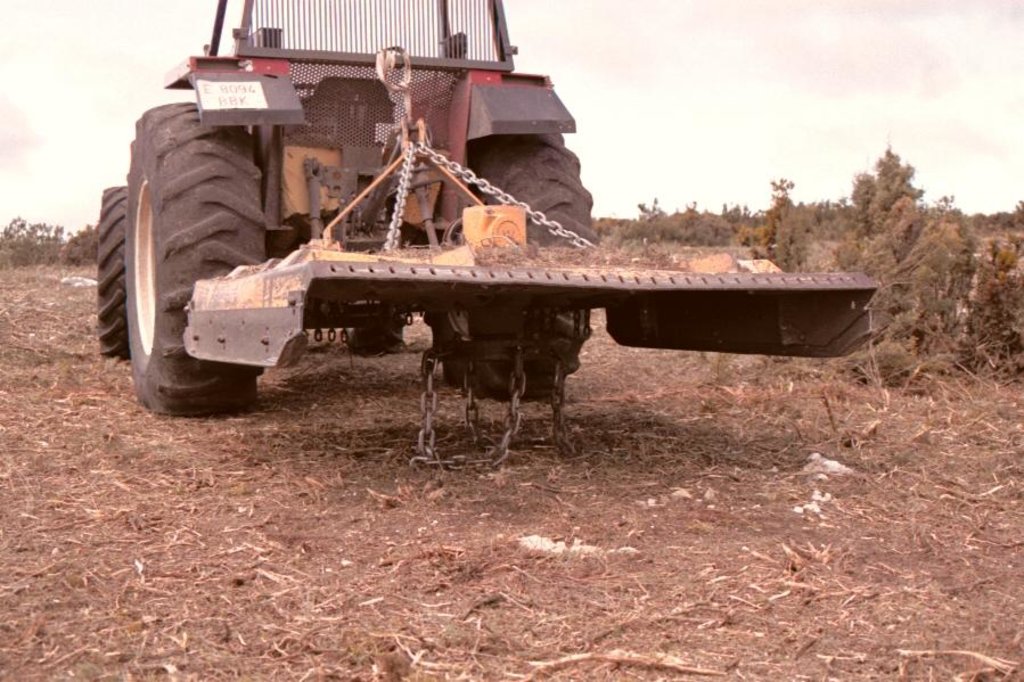
In each study site, the experimental area covered about 5000m2 (3 plots of 1000m2 each, one plot of 2000m2). To test the effect of the combination of clearing and planting, a clearing machine was used to clear a plot of 1000 m2 in all three sites. The few resprouting individuals such as Juniperus oxycedrus and Quercus ilex and also some seeder trees such as Pinus halepensis and Pinus pinaster were left standing. The planting holes (0.35 m2) were created with a tractor using a backhoe. The slash and brush chips generated by the clearing were reused in the planting holes as mulch which resulted in ecological benefits.
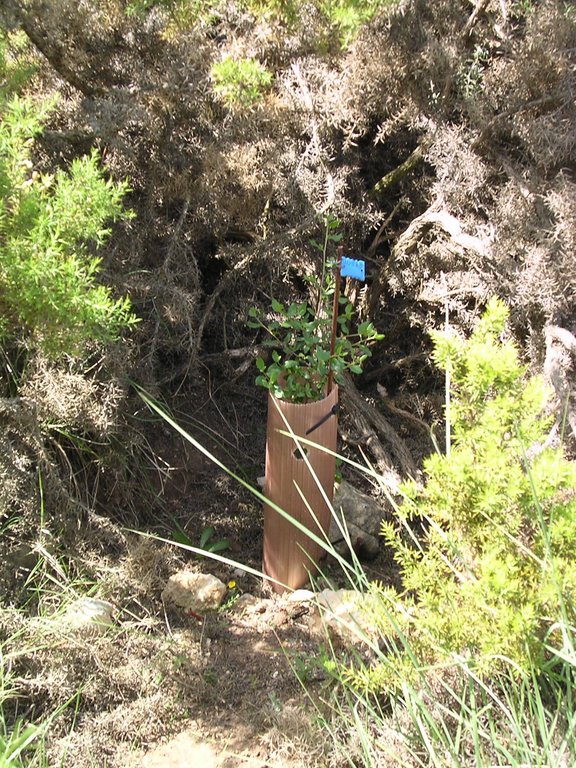
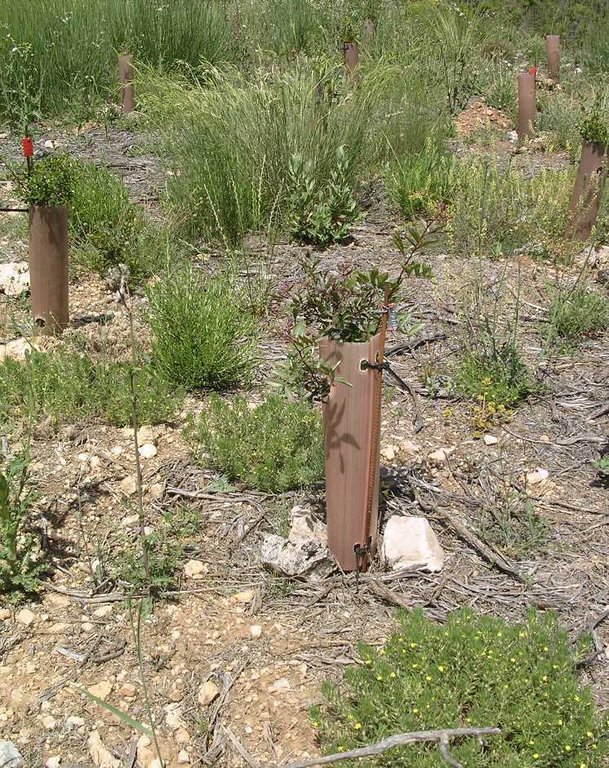
In February 2003, native resprouters of late successional stages with a low amount of dead fuel were planted, such as Quercus ilex, Rhamnus alaternus and Pistacia lentiscus, all protected by a plastic tree shelter to prevent browsing.
The seedlings were grown for 8 months in a nursery in Santa Faz (Alicante) and then transferred to a nursery in La Hunde (Ayora) one month before planting. The Regional Forest Services of Valencia provided seeds as well.
The region of Ayora is mountainous with a dry subhumid climate (~380 mm annual rainfall). The risk of fire incidence is at its highest from June to September when there are adverse conditions like drought, high temperatures and strong winds (mainly the winds coming from central Spain, called “poniente”). The population density is very low and there are only few job opportunities (e.g. marginal agriculture, grazing, hunting, beekeeping). Most of the inhabitants work in the nuclear power plant. Forest management could be a source for jobs.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
España
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Spain, Valencia
Especifique más el lugar :
Ayora
Comentarios:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Morera Centre latitude (N): 39° 07’ 17’’ Centre longitude (W): 0°57’11’’
Roñoso Centre latitude (N): 39° 07’ 22’’ Centre longitude (W): 0°57’56’’
Gachas Centre latitude (N): 39° 01’ 58’’ Centre longitude (W): 0°53’30’’
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- durante experimentos/ investigación
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
This research was carried out in the framework of the SPREAD project funded by the European Commission (2002-2005), in the year 2003.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- reducir el riesgo de desastres naturales
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Bosques
Bosques/ zonas boscosas (semi) naturales:
- Tala selectiva
Plantación de árboles, reforestación:
- Monocultivo variedad local
Productos y servicios:
- Madera
- Leña
- Frutos y nueces
- Otros productos forestales
- Pastoreo/ ramoneo
- Conservación/ Protección de la naturaleza
- Recreación/ turismo
- Protección contra desastres naturales
- wind mill parc, hunting
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): In Spain the prevalent dense shrublands (dominated by seeder species), which resulted from agricultural land abandonment and fire occurrence, contain a high fire risk because of both the high fuel loads and their continuity. Resprouter species have been removed in the past and are therefore scarce, whereas seeder species are abundant and increase the risk of fires.
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: As a management practice. The forest should be cut more frequently since there is a huge amount of fuel but there is no money for management.
Plantation forestry: Almost the whole forest in this region was planted. Furthermore, they also planted different species as a management practice.
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- manejo de bosques naturales y seminaturales:
- manejo de plantación forestal
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.015 m2.
The experiment was done in three different gorseland test sites with similar history of land use, vegetation composition and structure, and soil characteristics – Morera, Roñoso, Gachas. In each site, there were 4 plots (control, clearing, planting, clearing and planting). Each site has an area of approximately 5000 m2 (total area: 5000 x 3 = 15’000 m2)
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos
- V3: Desbroce de vegetación
- V5: Otros
Comentarios:
Specification of other vegetative measures: Introduction of fire resistant species
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

degradación biológica
- Bf: efectos nocivos de los fuegos
- Bs: reducción en la calidad y composición/ diversidad de las especies
Comentarios:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation in the past (removal of resprouter species), land abandonment, uncontrolled growth of fire prone vegetation, afforestations, forest fires), other human induced causes (specify) (change of vegetation composition to fire-prone shrubland), population pressure (Vast areas were deforested in the past for agriculture, important key species were removed. After land abandonment there was a lack of management strategies.), poverty / wealth (The current economic crisis in Spain leads to a lack of investment in forest management, therefore only a minor part of forests is managed), labour availability (In the past there was outmigration from the region to the big cities and therefore there was a lack of management)
Secondary causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (More variability in precipitation leads to a higher risk of fires), droughts (more fires during droughts), land tenure (The state is only allowed to apply management practices in public forest. The private forest is often not managed which increases the risk of fires and the resulting degradation), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (There were big fires in the past because of the lack of fire extinction media like water ponds, streets, transport media (this has been improved now)), education, access to knowledge and support services (Loss of knowledge, important for today’s fires: People (especially from the cities) are not aware anymore of the risk of fire. In the past people lived with the risk and knew how to prevent fires.), governance / institutional (Law to induce implementation of conservation interventions (ley forestal 3/1993). Before this law was implemented there were less conservation practices and therefore a higher fire risk)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
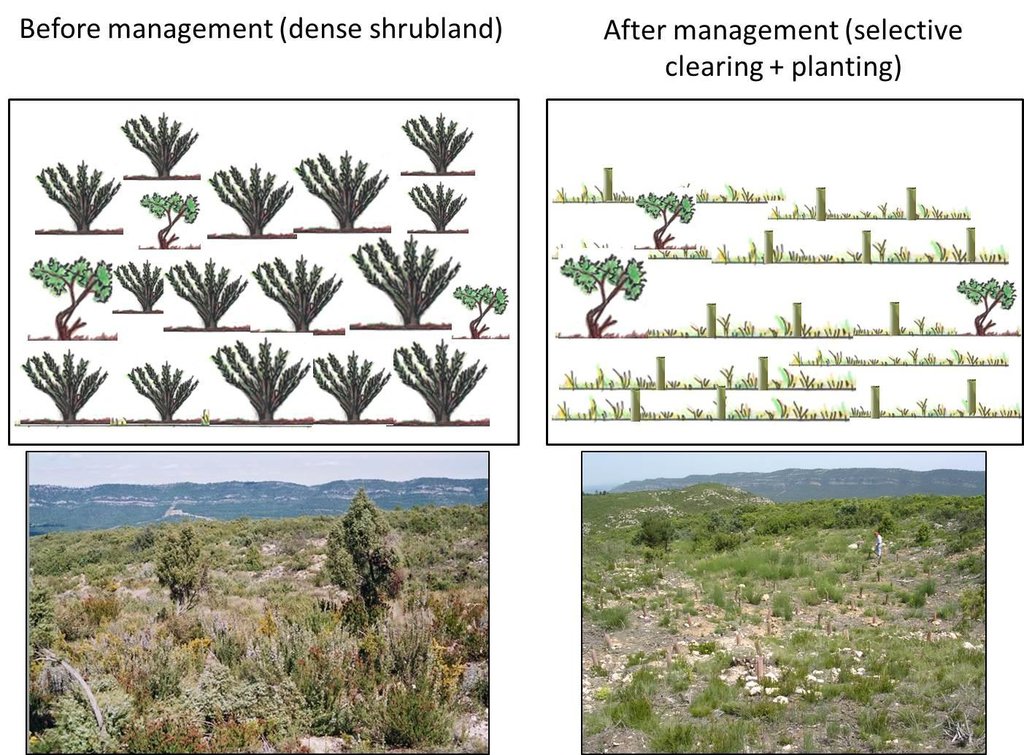
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
On the left, the situation before management is illustrated. Dense shrublands contain a high fire risk due to their high fuel amount and continuity. On the right, the situation after management is shown. The combination of selective clearing of fire-prone seeder species and planting of more fire resistant resprouter species (illustrated by tree shelters in the drawing) promotes shrubland resilience to fires.
Location: Ayora. Valencia, Spain
Date: 13-12-2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (The experiment was carried out by scientists (biologists) with a high technical knowledge.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (In case of upscaling this experiment to a local or regional level, the work could be carried out by land users with a low technical knowledge, with technical support of scientists and forest agents)
Main technical functions: control of fires, reduction of dry material (fuel for wildfires), Promotion of vegetation species and varieties (more fire resistant vegetation composition)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 1000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): <2m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): <2m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): <2m
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): <2m
Vegetative measure: Selective vegetation clearing
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: Planted species: Pistacia lentiscus, Quercus ilex and Rhamnus alaternus.
Other species: Removed species: Ulex parviflorus, Rosmarinus officinalis, Cistus albidus
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Euro
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
0,74
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
47.00
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting and chipping (in-situ) trees and shrubs (removed species: ulex parviflorus, rosmarinus officinalis, cistus albidus. Natural regenerated species which are not cleared: pinus halepensis, pinus pinaster, quercus ilex, juniperus oxycedrus) | Vegetativas | autumn/winter (when the vegetation activity is slowed down) |
| 2. | Planting (planted species: pistacia lentiscus, quercus ilex, rhamnus alaternus) | Vegetativas | autumn/winter (february 2003) |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipo | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 3089,0 | 3089,0 | |
| Equipo | tree shelters | ha | 1,0 | 945,0 | 945,0 | |
| Material para plantas | seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 4587,0 | 4587,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 8621,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.5 month(s)
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | There is no maintenance, but in case of maintenance they would do selective clearings (using machines) | Vegetativas | all 5-7 years in autumn/winter |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipo | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 446,0 | 446,0 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 446,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
The costs were calculated for the application of the technology (combination of clearing and planting) on one hectare. The costs can vary depending on the amount of vegetation which has to be cleared (site specific). The costs of the clearing amount to 1090 Euro per ha (1470 Dollar). The costs of the plantation (both labour and machines) are approximately 5300 Euro per hectare (7150 Dollar). But it should also be noted that the application of the selective clearing and planting on a vast continuous area is not the aim of this technology, but rather to apply the treatments on some selected spots to reduce the continuity of fire-prone seeder species and to increase the probability of dispersal of resprouter species (e.g. by birds). Therefore the costs would be lower than indicated here.
The currency rate (Euro-Dollar) was calculated on November 16th, 2013.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Slope (if the slope is steep, the work is much more difficult and takes more time), distance from a street (people can work less in a day if they have to walk far to clear/plant), vegetation density (it takes more time to clear a densely vegetated area).
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- media (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
5-50 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
pobre/ ninguna
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- mediana
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Individuos o grupos:
- empleado (compañía, gobierno)
Género:
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The experiment was done by biologists, all of them were men.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
- individual, con título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
- public/open access but organised (e.g. wood, hunting)
- public/open access but organised (e.g. wood, hunting)
Comentarios:
There is some public land, controlled by the state. But there is also some private land. The access to the public land is open but organized. Permission is needed from the government to cut trees, to build a house or to hunt. There are some private hunting areas for which the hunting association has to pay a fee.
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
More grasses for animals (game and livestock) in the cleared areas
calidad de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
Animals (especially goats) eat everything but they like more young grasses than shrubs
producción animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Game/wildlife and livestock are better because there is an increase in fodder quantity and quality
producción de madera
Comentarios/ especifique:
Production increases because there is less competition between species and more species planted. The wood/timber generated by the clearing can be used for biomass, fertilizers, pellets, firewood. A part of the wood is chipped in-situ and applied as mulch
generación de energía
Comentarios/ especifique:
Bioenergy (biomass)
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Less damage on the cultivated fields because the wild animals do not destroy the fields anymore and stay in the forest (because there is more grass available due to clearings).
Impactos socioculturales
oportunidades culturales
Comentarios/ especifique:
People appreciate the visual impact of a cleared forest with a high species richness. It has a high aesthetic value and offers recreational opportunities. Since the planted species are more fire-resistant this value can be sustained.
oportunidades recreativas
Comentarios/ especifique:
People appreciate the visual impact of a cleared forest with a high species richness. It has a high aesthetic value and offers recreational opportunities. Since the planted species are more fire-resistant this value can be sustained.
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
Local people know about the importance of conservation of the area and really like to have the forest protected of wildfires. They will learn about the relationship of planting later-successional species and the reduction of the fire hazard.
mitigación de conflicto
Comentarios/ especifique:
Less fires result in a decrease of the destroyed area, less money will have to be invested in restoration or fire extinction. Farmers, hunters,honey producers will experience fewer losses. Wild animals remain in the forest (more grasses after clearing).
situación de grupos en desventaja social y económica
Comentarios/ especifique:
The clearing and planting could create more job opportunities for unemployed people. This is especially important during the current economic crisis.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
evaporación
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to the mulch layer more moisture is stored in the soil and less water is lost by evaporation (the soil is covered).
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
More soil moisture because of less dense shrubland and mulch cover after clearing
cubierta del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Mulch layer
pérdida de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Less erosion because the soil is protected by a mulch layer.
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Mulch layer protects the soil from crusting.
ciclo/ recarga de nutrientes
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reintroduction of native species which disappeared due to removal by humans in the past.
diversidad animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
There might be more animals because of the fodder supply. Further, different species (e.g. birds) might be attracted by the reintroduced plant species.
control de pestes/ enfermedades
Comentarios/ especifique:
Mono-plantations are bad for the propagation of a pest. After clearing there is a decrease in competition, plants are in healthier conditions,less prone to diseases.Weak plants are eliminated which reduces the risk of pests (always weak plants affected).
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
Carbon sequestration, and less fires because the fire-prone shrubs are removed and more fire-resistant trees and shrubs are prevalent
riesgo de incendio
Comentarios/ especifique:
The fire risk is reduced in the long term because by clearing fire-prone and planting more fire-resistant species the vegetation is redirected towards later successional stages (ecosystem more resilient against fires).
velocidad de viento
Otros impactos ecológicos
germination of competing seeds
soil surface temperature
Comentarios/ especifique:
Mulch layer
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | no muy bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| temperature decrease, snow, frost | no muy bien |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
muy positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
Short term returns are slightly negative because the management practice is expensive and until the trees reach a mature state, there are not many returns (in terms of wood and biomass). In the long term this management practice has very positive results because it increases the resilience to fires and can be seen as a sustainable management of fire-prone areas. Additionally, wood and biomass can be extracted. The idea is not to apply any maintenance in the first 10 years after the establishment.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
Comentarios:
There is no adoption trend since this was only an experiment, but maybe there will be the possibility to upscale this technology in a regional project.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| Almost all villagers prefer a managed forest. It has a high aesthetic and recreational value. Through the application of this technology the awareness of the risk of wildfires would probably increase. |
| Shepherds and farmers benefit from forest clearings. There are more young grasses in the forest which provides fodder for livestock. Also wild animals benefit from this food supply which in turn hinders them to destroy cultivated fields of the farmers. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
After fires, the natural landscape regenerated with a high and continuous fuel amount and a scarce occurrence of native resprouter species. It is crucial to apply management actions to reduce the fire hazard. The experiment demonstrated that it is possible to accelerate the post-fire vegetation response (which promotes ecosystem resilience). |
| Planting of resprouting species in post-fire areas can accelerate the natural process. Clearing of the vegetation reduces the fire risk, but this treatment may also enhance seedling establishment and growth. |
| The slash and brush chips generated by the clearings can be reused in the planting holes. This mulch layer protects the soil surface and reduces both the soil surface temperature and the germination of competing seeds while increasing the soil moisture content, especially in the driest periods. |
|
The combination of clearing and planting resprouting species seems to be an appropriate option for managing these areas because, once established, the resprouting species persist for a long time and lead to an increase of the ecosystem resilience. |
| Social and economic benefits for the locals. Especially during the economic crisis the forest management is an important source for jobs. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The management activities are expensive and labour-intensive. The state does not invest much money in prevention of forest fires but focuses more on fire extinction. | More investment in prevention of forest fires is required and this management practice could increase the ecosystem resilience against fires in the long term in a sustainable way. This would also generate jobs. This technology implies a combination of techniques (selective clearing and planting). Costs may be reduced by implementing individual techniques but positive results may also be reduced. |
| The technology could result in a reduction of the animal production because grazing should be restricted after planting to ensure the growth of the planted seedlings. | Since the technology would not be applied over vast areas but only locally on some plots, the fodder supply would probably still cover the needs of the animals. |
| Depending on the site, some soil may be exposed to erosion due to mechanical clearing. | Mulching with brush chipping can minimize or even solve this problem. |
| After clearing, an increase in wind velocity might occur. | The planted trees will grow which will again result in the reduction of this problem. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con especialistas/ expertos en MST
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
Valdecantos, A., Baeza, M.J., Vallejo, V.R. (2009): Vegetation management for promoting ecosystem resilience in fire-prone Mediterranean shrublands. Restoration Ecology 17, 3: 414-421.
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos