Water retention polders to improve water management [Alemania]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Martin Maier
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
Polder zum Wassermanagement entwickelt durch lokale Experten (Nordsee Region)
technologies_1583 - Alemania
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Persona(s) de referencia clave
Especialista MST:
Kleyer Michael
michael.kleyer@uni-oldenburg.de
University of Oldenburg
Ammerländer Heerstraße 114, 26129 Oldenburg, Germany
Alemania
Especialista MST:
Karrasch Leena
University of Oldenburg
Ammerländer Heerstraße 114, 26129 Oldenburg, Germany
Alemania
Especialista MST:
Mayer Martin
martin.maier@uni-oldenburg.de
University of Oldenburg
Ammerländer Heerstraße 114, 26129 Oldenburg, Germany
Alemania
Nombre del proyecto que financió la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Book project: Making sense of research for sustainable land management (GLUES)Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
University of Oldenburg (University of Oldenburg) - Alemania1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
10/06/2015
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Water retaining polders to reduce flood risk due to heavy rainfall or runoff at high tide in embanked coastal lowlands. Delineation of the retention area and land use within the retention area was developed in a participatory process with local experts.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
In the 19th and 20th century land was reclaimed from the sea to make use of the exposed fertile soils for agriculture through a process known as ‘impoldering’. The reclaimed land is now characterized by intensive grazing and cropland. This is a region where agriculture is the most important form of land use. However, the land needs to be regularly drained. Given the expected increase in precipitation in winter due to climate change, the corresponding increase in freshwater discharge needs to be managed. Furthermore, the periods when natural discharge into the sea oc-curs are likely to decrease – because of rising sea levels also caused by climate change. Consequently, in winter and spring, greater quantities of freshwater will need to be pumped into the sea rather than discharged naturally at the low or ‘ebb’ tide. Specially embanked water retention polders will be required to temporarily impound water as part of a multifunctional approach to coastal zone management.
Purpose of the Technology: These retention polders could be a cost-effective alternative to expensive invest-ments in extra pumping capacities to prevent submergence of low-lying cultivated areas. The primary aim is to restrict floods to the retention polders when the drain-age network is overburdened and cannot deal with the predicted extra demands in the future. The high evapotranspiration from the open waterbody, and the reeds growing within, will also help with reducing the amount of water. During dry sum-mers, the water in the retention polder could also be put to creative use as a source of irrigation. Another potential advantage is that subsurface saltwater intrusion in the region could be prevented by the freshwater-filled polders. During extreme storm surges and in the rare case of breaches in the sea wall, the retention polders would serve as an extra line of defence by holding seawater.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: An embankment enclosing approx. 500 ha will be able to store up to 2,500,000 m³ of water. This will improve the drainage of an area of approx. 49,000 ha. The invest-ment for building this water retention area is high – but for the reasons stated it serves a necessary purpose at a cost which is lower than the alternative – increased pumped drainage installations. Maintenance costs will be lower than the drainage alternative as only the integrity of the embankment needs to be monitored regularly. Currently, agricultural land use within the polders is adapted to higher water levels and occasional flooding. Within the embanked area there will be a change from the current use of mainly crop land to extensive grazing, open water and reed stands.
Natural / human environment: Some parts within the retention polder will be used for agricultural purposes, while the wetter parts will be set aside. In these latter sections, undisturbed natural regen-eration will take place. A landscape comprising various different elements, without any extreme forms of intensive land use such as large areas of monocultures will be the result. Thus requirements for agricultural use and tourism will be addressed.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Alemania
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Germany, Lower Saxony
Especifique más el lugar :
Landkreis Aurich
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- 10-50 años atrás
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- durante experimentos/ investigación
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierra de pastoreo
Pastoreo intensivo/ producción de forraje:
- Cortar y llevar/ cero pastoreo
- Pastoreo mejorado
Especies y productos animales principales:
Main species cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: cows for milk
Main species improved pasture: cattle for milk and meat

Cultivos asociados (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles), incl. agroforestería
- Agropastoreo
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Flood events and droughts may substantially disrupt the contemporary land use in the future and lead to higher drainage costs and higher economic risks for agricultural production. This may reduce the ecological and economic viability of the current intensive and highly productive land use under a changing climate.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): There is no awareness of risks due to climate change in the land users point of view.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: cows for milk
Improved pasture: cattle for milk and meat
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Other: Oo: Other: wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): needs to be adapted to regular flooding
Constraints of recreation (landscape is used for recreation and tourism ): change in landscape due to retention area
Constraints of nature conservation area (protected sites): wetter conditions in retention area
Si el uso de la tierra ha cambiado debido a la implementación de la Tecnología, indique el uso de la tierra antes de la implementación de la Tecnología.
Mixed: Mp: Agro-pastoralism
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Comentarios:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: March to October
Densidad del ganado (si fuese relevante):
> 100 LU /km2
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- manejo de agua superficial (manantial, río, lagos, mar):
- protección/manejo de humedales
- Flood prevention
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 33.7 m2.
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas estructurales
- S5: Diques, hondonadas, estanques

medidas de manejo
- M1: Cambio de tipo de uso de la tierra
- M2: Cambio de gestión/ nivel de intensidad
Comentarios:
Main measures: structural measures
Secondary measures: management measures
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cs: salinización/ alcalinización

degradación del agua
- Hs: cambio en la cantidad de aguas superficiales
- Hg: cambio en nivel de aguas subterráneas/ nivel de acuífero
- Hq: reducción de la calidad de aguas subterráneas
Comentarios:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level, Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Main causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (Climate change, higher rainfall in winter, lower in summer), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Heavy rainfall in winter due to climate change expected), floods (Flooding due to heavy rainfall in winter)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Droughts due to less rainfall in summer (climate change)), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Sea level rise)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- prevenir la degradación de la tierra
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
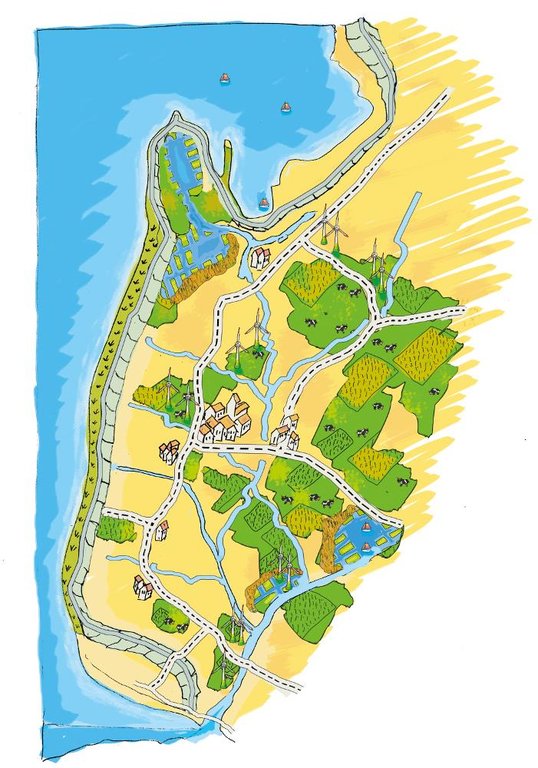
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
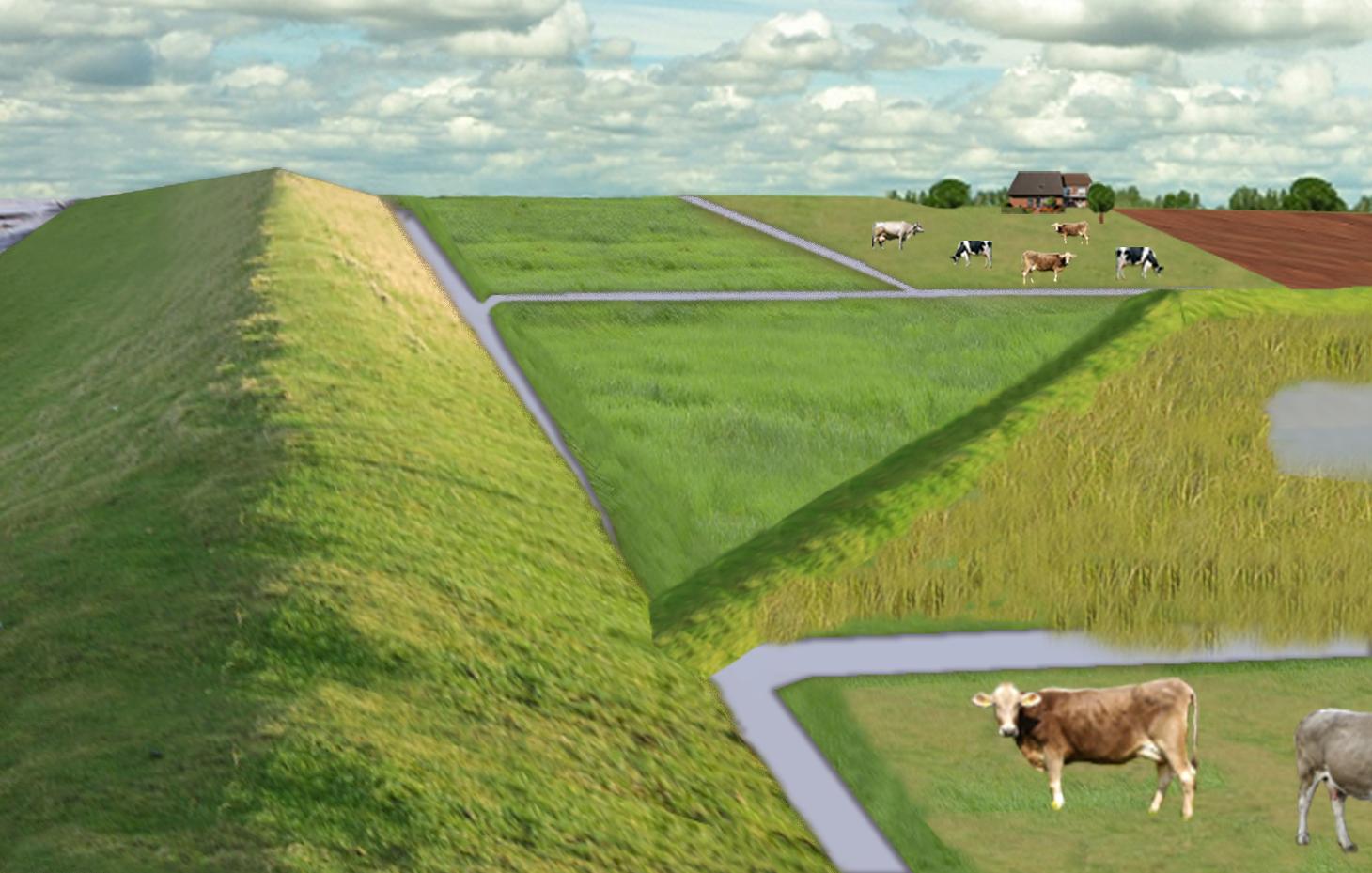
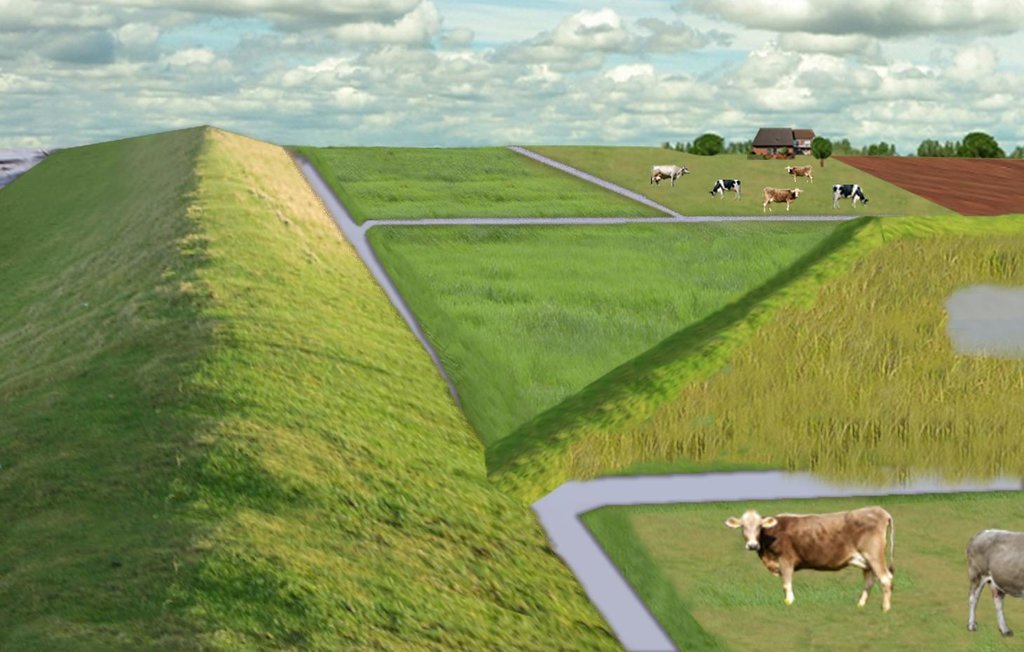
The figure shows the study region, located on the North Sea coast. The whole area is protected by a sea wall (grey). Crop fields (yellow), grasslands (green) and the drainage system (light blue) char-acterize the region. In contrast to T_GER001en and T_GER002en small water bodies (blue) surrounded by reeds (brown) act as water retention polders. Agricultural land use in some retention areas is adapted to the ground water levels and flooding frequencies. This results in parts of the retention areas being taken out of agricultural production and undisturbed development of natural habitats occurring. In other parts of the retention areas extensive grazing or reed farming will be practiced. This leads to a mosaic of different land uses in the landscape. Retention areas of 500 ha are able to store up to 2,500,000 m³ water. The height of the dams depends on the elevation of the landscape but in general a height of less than 2 m is sufficient.
Location: Krummhörn. County of Aurich, Lower Saxony
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (To generate income in the retention area (without existing agricultural methods))
Technical knowledge required for water board: high (To build a new adapted drainage system with retention areas)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Dam/ pan/ pond
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 13000
Construction material (earth): sand core and clay cover
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 2500000m3
Catchment area: 49000ham2
Beneficial area: 49000ham2
Other specifications: size of retention area (embanked area): 500.00 ha
Change of land use type: Within the retention area the conditions are wetter than before. Therefore the agricultural land use needs to be changed to an adapted land use.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Under the wetter conditions only a less intensive land use is possible, e.g. no crop fields but instead extensive grazing or cessation of agricultural land use.
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Euro
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
0,94
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
100.00
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Building of dams | Estructurales | during winter months |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Labour | Dam | 1,0 | 10000000,0 | 10000000,0 | |
| Equipo | Machine use | Dam | 1,0 | 4000000,0 | 4000000,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Earth | Dam | 1,0 | 112000,0 | 112000,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 14112000,0 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Control of dams | Estructurales | once a year |
| 2. | Maintenance of dams | Estructurales | once a year |
| 3. | Maintenance of drainage system | Estructurales | once a year (mean of many years) |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Labour | Dam | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | |
| Equipo | Machine use | Dam | 1,0 | 200,0 | 200,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Earth | Dam | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | |
| Otros | Maintenance per km ditch | Dam | 1,0 | 2270,7 | 2270,7 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 3070,7 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: digger, open truck
The main investment is based on a dam length of 13 km to build up the retention area of a size of 500 ha. The length of the drainage network for the whole watershed (retention area and the surroundings) is 1,134 km. Maintenance costs of drainage network are based on long term annual mean cost of 2,270.72 Euro per km including pumping costs.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The establishment costs are for the whole retention area (500 ha). The establishment period will be half a year.
Mainly the elevation in the region determines the costs as the height of the dams depend on the elevation. Typical heights are 1 m up to 2 m with a slope of 1:3.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- húmeda
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- elevada (>3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage/infiltration is meidum
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
< 5 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
solo para uso agrícola (irrigación)
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- comercial/ mercado
Ingresos no agrarios:
- 10-50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel relativo de riqueza:
- promedio
Individuos o grupos:
- empleado (compañía, gobierno)
Nivel de mecanización:
- mecanizado/motorizado
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
1% of the land users are very rich and own 1% of the land.
49% of the land users are rich and own 24% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
and own 25% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Many farmers do additional work in companies
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- gran escala
Comentarios:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha, 50-100 ha, 100-500 ha
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
energía:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Under wet conditions in the retention area a crop production is not possible any more.
producción de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
Under wet conditions in the retention area an intensive fodder production is not possible any more.
calidad de forraje
Comentarios/ especifique:
Under wet conditions in the retention area the optiomal fodder quality can not ensured any more.
riesgo de fracaso de producción
Comentarios/ especifique:
Regarding crops: The retention area is used for excess water and may be flooded during growing season.
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Only adjusted land use takes place, therefore the expenses are reduced nearly to 0.
ingreso agrario
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Comentarios/ especifique:
Due to land use adapted to the conditions the typical land use is not possible and a diversitfication will take place with reed mowing and extensive grazing in the retention area.
Otros impactos socioeconómicos
Intrusion by saline groundwater
Impactos socioculturales
oportunidades recreativas
Comentarios/ especifique:
Diversification of landscape by building the retention area will increase the attractivity for recreation and tourists.
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Comentarios/ especifique:
Less intensive land use results in more diversity and conservation of regional species and habitats.
mitigación de conflicto
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
'Regional belonging' and 'feeling of safety' are measured. The amount of increase is modelled and will be added here.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
Typical for the region are wet situations. These typical wet conditions are restored by cessation of drainage system within the retention area.
calidad de agua
Comentarios/ especifique:
Updwelling of saline groundwater is prevented by increased water level in the retention area.
nivel freático/ acuífero
Comentarios/ especifique:
By water in the retention are the recharge of groundwater will increase and prevent salinization.
evaporación
Comentarios/ especifique:
Instead of pumping water into the sea a higher amount is evapotranspirated naturally.
Suelo
humedad del suelo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Typical for the region are wet situations. These typical wet conditions are restored by cessation of drainage system within the retention area.
salinidad
Comentarios/ especifique:
By water in the retention are the recharge of groundwater will increase and prevent salinization.
materia orgánica debajo del suelo C
Comentarios/ especifique:
By wetter conditions the soil organic matter will be increased.
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
diversidad vegetal
Comentarios/ especifique:
By diversification of land use the number of species will be increased, especially due to extensive land use.
diversidad animal
Comentarios/ especifique:
By diversification of land use the number of species will be increased, especially due to extensive land use.
diversidad de hábitats
Comentarios/ especifique:
By diversification of land use the number of habitats will be increased.
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
Comentarios/ especifique:
Modelled is the global warming potential by gas emissions. Not yet clear if it is benefit or disadvantage. Model will show.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
disponibilidad de agua
corriente confiable y estable fluye en estación seca
Comentarios/ especifique:
Water stored in retention area can be used for irrigation during dry summer months.
inundaciones río abajo
Comentarios/ especifique:
Measured m3 of excess water in the catchment area, leading to floods or needs to be pumped. Exact values from modelling will be added as soon as possible!
daño a campos de vecinos
daños a infraestructura pública / privada
Reduced hazard towards adverse events
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | no se sabe |
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
negativo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
ligeramente positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
The benefits will be visible in an longer time frame. There will be benefits of the investments when considering sea level rise in the upcoming 100 years.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
Comentarios:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The SLM Technology is not implemented by land users but needs to be implemented in spatial planning of the federal state. We expect that there is a chance for implementation.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The SLM Technology was developed together with regional experts. It seems that the ideas developed, merge more often in their recent discussion and an implementation is likely.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
|
The retention area will supplement the drainage of the arable fields and pastures outside the retention area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Combine with other technical solutions for protection against flooding. |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Prevention of flooding during strong rainfalls and possibility to irrigate during dry periods How can they be sustained / enhanced? The larger the retention areas are the more water can be stored |
|
Prevention of salt water intrusion in the region How can they be sustained / enhanced? Fresh water in the retention areas prevents saline ground water from intrusion. Build polders in areas where saline ground water intrudes. |
|
Endangered species might obtain new habitats in the retention area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Extensive land use can help to optimize the habitats for endan-gered species and increase attractiveness for tourism. |
|
Through investments in building retention polders the very ex-pensive strengthening of the existing drainage system is no longer necessary. How can they be sustained / enhanced? By increasing the attractiveness for tourism alternative benefits for land owner can be generated. |
|
Multi-functional land use in the catchment and in the retention area How can they be sustained / enhanced? Support farmers with land in the retention area (e.g. financially or with additional agricultural land outside the retention area). Sup-port discussions between farmers’ associations and nature con-servation agencies. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The retention polders will change the landscape and this may reduce the value of the region for tourism | Include tourist concerns within the retention area (accessibility, information, attractiveness) |
| Endangered species might lose habitats when building up the retention polders | Do not build a retention area where endangered species live |
| Loss of livelihoods | Retention areas should be planned for parts of the landscape without settlements |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Loss of land for agricultural production | Create retention polders where the productivity is already low. Encourage alternative land use (for example reed production) in the retention polders. |
| High water levels (especially with changing levels) may generate high emissions of greenhouse gases. | Ground water levels should kept stable near to the soil surface. |
| Retention area is probably too small if pessimistic sea level rise predictions come true. | Increase size of retention polders. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.2 Vínculos a las publicaciones disponibles
Título, autor, año, ISBN:
http://www.comtess.uni-oldenburg.de/
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
http://www.comtess.uni-oldenburg.de/
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos