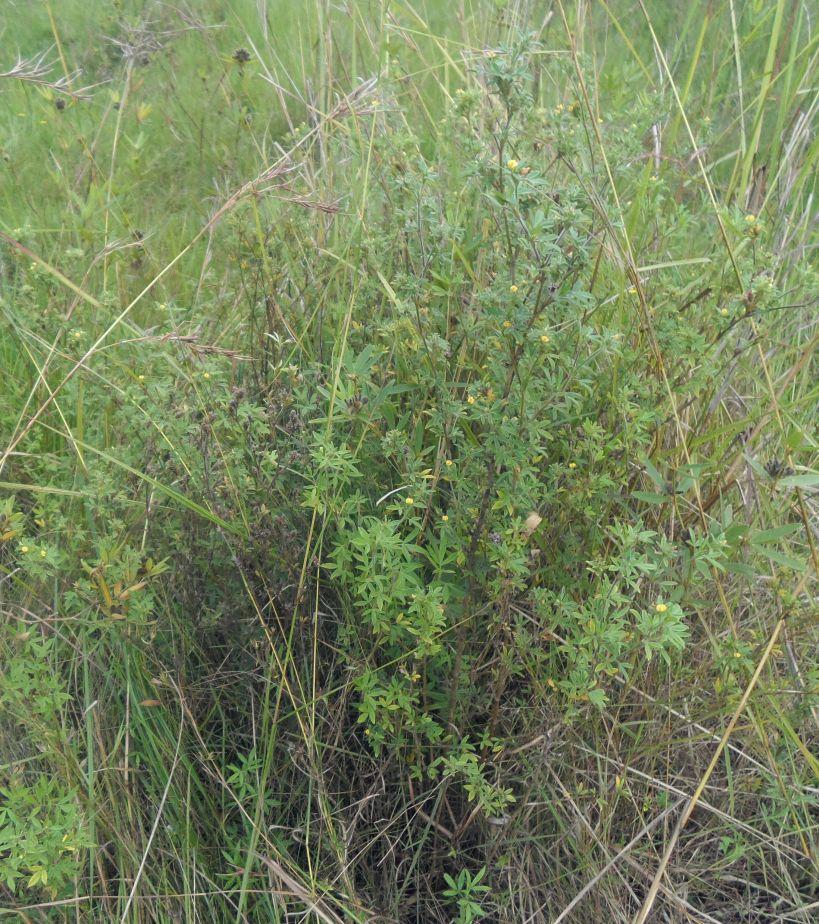
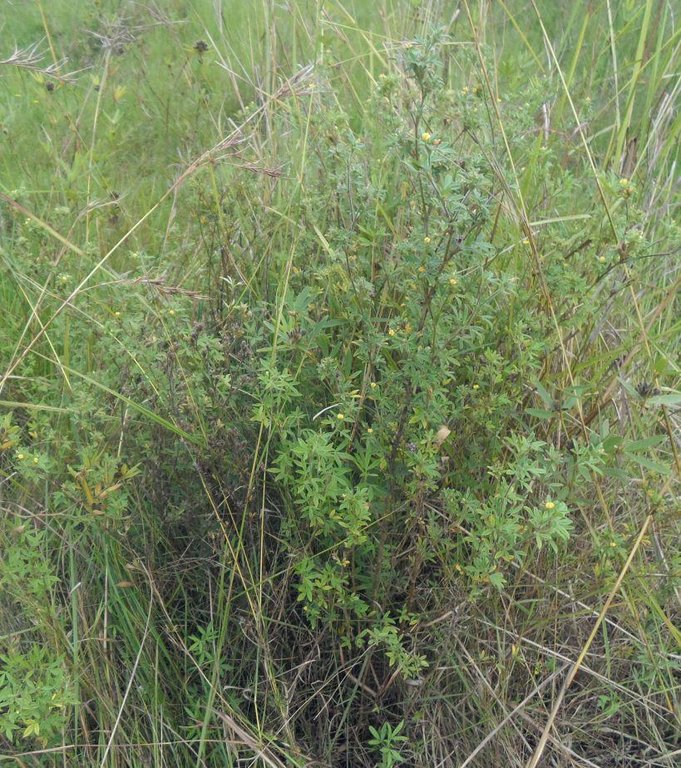
Area enclosures for protection of riverine ecosystem and regeneration of cut and carry materials. [Tanzania, República Unida de]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: ALLAN BUBELWA
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
Eneo lililotengwa na kwa ajili hifadhi ya mto na kuvuna malisho na matandazo
technologies_1607 - Tanzania, República Unida de
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Member of the district council:
Egidius Pancras
Missenyi Disrict Council Kagera Tanzania
Tanzania, República Unida de
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - Tanzania, República Unida deNombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - Tanzania, República Unida de1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
03/06/2014
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
1.4 Declaración de la sostenibilidad de la Tecnología descrita
¿La Tecnología aquí descrita resulta problemática en relación a la degradación de la tierra, de tal forma que no puede considerársela una tecnología sostenible para el manejo de la tierra?
No
1.5 Referencia al (los) Cuestionario(s) de Enfoques MST
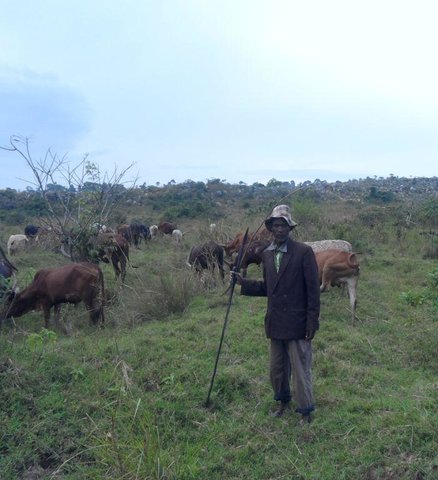

Active participation of herder leader (WAKONDO) in management … [Tanzania, República Unida de]
Prevention and mitigation of the grazing land and riverine ecosystems through mandatory grassroots meetings, law enforcement and active participation and empowerment of herder leaders’ (masters of the most resource destructive group)
- Compilador: ALLAN BUBELWA
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Area enclosures for protection of riverine ecosystem and purposeful regeneration of mulching and pasture materials for cut and carry
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
Area enclosure is done in low grazing range lands of average slope 2 – 5%. Enclosure is done by demarcating the fragile land that has direct impact to the riverine ecosystem. The land is exposed to degradation through overgrazing and soil compaction by livestock, bush fire, river bank erosion and reduced quality of pasture spps. Demarcation is done by planting trees in identified area situated about 300 meters from the riverine buffer zone. The preferred plants are Ficus thonigii. The average space between trees is 2 meters. Physical enclosure is supported and enhanced by use of protective bylaws. Reseeding of nutritious pasture species is also done and the area is left under protection for growth and regeneration of mulch, pastures and other vegetation to take place. The common pasture species reseeded are Leucaena spp, cannavaria brazile, clitoria tenatea, sesbania sesban, stylothensis, cajanus cajan, chloris gayana, branchalia spps . Direct grazing is prohibited and mulch and pasture materials are accessed through controlled and organized cut and carry.
Area enclosure is meant for rehabilitation of the riverine ecosystem and prevention of further degradation. Mulch and high nutritious pasture materials that are accessed through organized cut and carry procedures improve crop and animal productivity and have both direct and indirect impact to diversification of income sources and thus play significant role in putting the triple win solution into reality.
Purpose of the Technology: Purpose: 1) To improve vegetative cover, reduce soil erosion and prevent and rehabilitate degradation of the riverine ecosystem 2) Ensure sustainable availability and accessibility of mulch and nutritious pasture that are need for increased crop and livestock productivity 3) Promote use of environmental friendly exploitation of land resources (i.e. mulch, pasture, grass carpeting and other materials) and 4) Promote direct and indirect diversification of income sources.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment and recurrent activities includes: area identification and measurement; slashing and land preparation for boundary tree planting and pasture reseeding; collection of planting materials and planting along defined boundaries for demarcation; procurement of seed and reseeding of nutritious and palatable pasture species; selective weeding; area reshaping and gap filling.
Natural / human environment: Bio-physically the area is semi natural grassland with grasses and shrubs trees. The technology is a combination of management and vegetative measure (area enclosure, demarcation using ficus thonigii and reseeding of nutritious pasture). Climatic zone is sub humid with 210 length of growing period (LGP). Slope category is gentle lying between 2-5%. Soil texture is fine heavy (clay) with medium soil depth.
Social economic wise the area is dominated by handy tools typology of mechanization. Production system is mixed (both for subsistence and commercial purposes). Inputs used includes tools (hand hoe, machete, sickles, spade and mattock), light and heavy labour, pasture seeds and tree planting materials with average annual costs of 1084.3 USD per hectare. Land ownership in technological area is communal.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Tanzania, República Unida de
Región/ Estado/ Provincia:
Tanzania/Kagera
Especifique más el lugar :
Missenyi distict/Minziro ward/Minziro village
Map
×2.6 Fecha de la implementación
Si no se conoce el año preciso, indique la fecha aproximada:
- hace menos de 10 años (recientemente)
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- mediante la innovación de usuarios de tierras
- mediante proyectos/ intervenciones externas
Comentarios (tipo de proyecto, etc.):
The technology is a result of the recent SLM participatory dialogues made between land users and SLM specialist (external experts). In these dialogues both endogenous and technical knowledge based were given equal weight and were combined in a complementary manner. Land users alos were empowered to take self initiative and ownership of the decision making process.
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- conservar el ecosistema
- preservar/ mejorar biodiversidad
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierra de pastoreo
Tierras de pastoreo extensivo:
- Nomadismo
- Semi-nomadismo/ pastoralismo
Pastoreo intensivo/ producción de forraje:
- Cortar y llevar/ cero pastoreo

Cultivos asociados (cultivos/ pastoreo/ árboles), incl. agroforestería
- Silvo-pastoralismo
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion due to downstream run off exacerbated by loss of vegetation cover due to bush fire and soil compaction caused by overgrazing, degradation of the riverine ecosystem caused by River bank erosion, land bareness and exposure to direct sunlight and excessive unproductive loss of both green and blue water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): River pollution, erosion of the river bank, land bareness and reduction of mulching and pasture materials.
Nomadism: People with large herd of animal move with their animals in search of adequate pasture
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Exercised with people with few stock.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: done by farmers who usuall keep dairy goats and cattles.
Grazingland comments: Area enclosure is largely meant to control land degradation of the riverine ecosystem through overgrazing by people who own large number of stocks at the same time promote organized, sustainable and environmental friendly exploitation of the fragile land lands (e.g. controlled cut and carry rather than direct grazing in the riverine ecosystem).
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Provisión de agua para la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología:
- de secano
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: September to December Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May
Densidad del ganado (si fuese relevante):
50-100 LU /km2
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- veda de zona (detener uso, apoyar la restauración)
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Especifique la difusión de la Tecnología:
- distribuida parejamente sobre un área
Si la tecnología se halla difundida homogéneamente en un área, indique el área aproximada que cubre:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentarios:
Includes enclosed and demarcated area closer and around the riverine ecosystem.
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V2: Pastos y plantas herbáceas perennes

medidas de manejo
- M7: Otros
Comentarios:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Specification of other management measures: Area enclosure to promote vegetative regeneration and organized use
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wr: erosión de riberas

deterioro físico del suelo
- Pc: compactación

degradación biológica
- Bc: reducción de la cobertura vegetal del suelo

degradación del agua
- Hs: cambio en la cantidad de aguas superficiales
Comentarios:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Compaction due to overstocking, accerated runoff and erosion.), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Reduction of mulching and pasture materials), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Rampant bush fire), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Un0rganize exploitation of mulching materials), overgrazing (Uncontrolled grazing), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Loss of green water through unproductive evaporation and blue water through ruoff as well as evaporation), population pressure (Exessive eploitation of the grassland and forests in the riverine ecosystem), poverty / wealth (Reliance on wood as the sole source of fuel), education, access to knowledge and support services (Inadequate acess to extension service due to shortage of extension staff), governance / institutional (Weak and inactive institutions to deal with environmental issues)
Secondary causes of degradation: change in temperature (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), change of seasonal rainfall (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), droughts (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
- restaurar/ rehabilitar tierra severamente degradada
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Is simply retraining on some principles of sustainable land management, law and rules guiding the fragile ecosystems, participatory training skills and grassroots facilitation skills.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Largely exposure to act and policies guiding the fragile ecosystems and learning by doing on the job,)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): various
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Trees/ shrubs species: ficus thonigii planted arround the boundary and leguminous pasture shrubs planted within the area (stlothensis, lucaena spps)
Grass species: Randomly planted (chloris gayana, desmodium spp and Calliandra)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2 - 5%%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 2 - 5%%
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Introduction of organized cut and carry exploitation of mulching and pasture materials
Other type of management: Boundary enclosure, law enforcement
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
otra / moneda nacional (especifique):
Tanzanian shillings
Indique la tasa de cambio de USD a la moneda local (si fuese relevante): 1 USD =:
1700,0
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
1.12
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site/boundary identification | Vegetativas | October |
| 2. | Site preparation for reseeding and demarcation (slashing, selective tilling, hole digging) | Vegetativas | October |
| 3. | Planting of demarcation trees, leguminous shrubs and grass pasture | Vegetativas | November |
| 4. | Fertilizer application (DAP) | Vegetativas | Once |
| 5. | Meeting on awareness creation and formalization of the practice (change of resource use practice) | Manejo | once |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Site/boundary identification | Mandays | 15,0 | 1,13333 | 17,0 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Site preparation for reseeding and demarcation (slashing, selective tilling, hole digging) | Mandays | 15,0 | 3,9213 | 58,82 | |
| Mano de obra | Planting of demarcation trees, leguminous shrubs and grass pasture | Mandays | 15,0 | 3,9213 | 58,82 | |
| Mano de obra | Fertilizer application (DAP) | Mandays | 15,0 | 1,13333 | 17,0 | |
| Equipo | Tools | Number | 5,0 | 3,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Material para plantas | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 235,29 | 235,29 | |
| Material para plantas | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 117,65 | 117,65 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Fertilizer | kg | 125,0 | 0,588 | 73,5 | |
| Otros | Meeting on awareness creation and formalization of the practice (change of resource use practice) | Mandays | 15,0 | 3,9213 | 58,82 | 100,0 |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 651,9 | |||||
Comentarios:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selective weeding and gap filling | Vegetativas | Once |
| 2. | Supervision and monitoring | Vegetativas | monthly |
| 3. | Organized cut and carry of Mulching and pasture materials | Manejo | Weekly |
| 4. | monitoring area closure and organized cut and carry | Manejo | Weekly |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Selective weeding and gap filling | Mandays | 15,0 | 1,76466 | 26,47 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Supervision and monitoring | Mandays | 15,0 | 3,53 | 52,95 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | Organized cut and carry of Mulching and pasture materials | Mandays | 10,0 | 17,647 | 176,47 | 100,0 |
| Mano de obra | monitoring area closure and organized cut and carry | Mandays | 10,0 | 17,647 | 176,47 | 100,0 |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 432,36 | |||||
Comentarios:
Machinery/ tools: machete and sickles.
The costs were calculated per unit of ha as per 13/06/2014.
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
labour is the most determinant factor.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Especificaciones/ comentarios sobre la cantidad de lluvia:
Short rains (september to December), March to May long rains. Length of dry periods January, February, June, July and August.
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Thermal climate class: tropics. Temperature grater than 20°C, LGP is 210 days
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre topografía :
Landforms: Plateau/plains (ranked 1, is largely applied in extended cancave lower range land pouring water to the river) and footslopes (ranked 2, partly includes the convex the convex hill slopes)
Slopes on average: Gentle (The area is largely extended gentle sloppy lower range land plateau receiving water from the the upper landscape and draining into the lower Ngono river which drains into Kagera river)
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- áspera/ ligera (arenosa)
- fina/ pesada (arcilla)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- baja (<1%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (ranked 1, The lower range land is moderately deep it receives eroded soil from the upper and mid sloppy landscape) and shallow (ranked 2, largely include the the area between the upper and lower mid landscape)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked 1, the lower side is largely light sandy soil) and fine/heavy (ranked 2, some patches fine clay soil)
Soil fertility: Low (Nutrient eroded by runoff into the river)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (top soil eroded by runoff into the river)
Soil drainage / infiltration: Medium (ranked 1, caused by the dominance of sand soil) and poor (ranked 2, due to trampling by animals)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (due to the dominance of sand soil)
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
en superficie
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
mediana
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de mala calidad (requiere tratamiento)
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Ground water table: On surface (ranked 1, along the flowing river Ngono) and <5m (ranked 2, the area is within the riverine ecosystem)
Availability of surface water: Medium (The main water source is Kagera river with water flows all year round)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, Kagera river receives partly receives water drained from the upper kibanja, Kikamba and other distant places. Kagera river water therefore is contaminated can not be consumed untreated)
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- baja
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
Overgrazing has left the area with disappearance of some palatable and nutritious pastures, bushfire and deforestation also has disturbed tree and shrub composition and the soil microbiology.
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- menos del 10% de todos los ingresos
Individuos o grupos:
- individual/ doméstico
Género:
- mujeres
- hombres
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
30% of the land users are very rich and own 35% of the land.
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor.
and own 15% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Generally 90% relies on agriculture as their main source of livelihood. Only a few are engaged in off-farm activities like petty trading, kiosk, brick making e.t.c.
Market orientation: Mixed (Livestock are largely kept for domestic use e.g. milk, meat and manure and parlty for commercial purposes)
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
¿Esto se considera de pequeña, mediana o gran escala (refiriéndose al contexto local)?
- pequeña escala
Comentarios:
There is shortage of grazing land. People with large animal herd move with their animals in search of better pasture.
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- individual, sin título
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- acceso abierto (no organizado)
Comentarios:
In Tanzania land is a state property. Land use right is largely individual not titled and is acquired through inheritance or purchase through traditional or customary procedures.
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
salud:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
educación:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
asistencia técnica:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
empleo (ej. fuera de la granja):
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
mercados:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
agua potable y saneamiento:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
servicios financieros:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Producción
producción de cultivo
Cantidad antes de MST:
5.0 ton/ha
Cantidad luego de MST:
6-7.0 ton/ha
Comentarios/ especifique:
due to the availability and use of mulching by some farmersmaterials
producción de forraje
Cantidad antes de MST:
2 acres/annum
Cantidad luego de MST:
10 acre/annum
Comentarios/ especifique:
area enclosure and decline of forest fire
calidad de forraje
Cantidad antes de MST:
3
Cantidad luego de MST:
8
Comentarios/ especifique:
increase in the number of nutritiuos pasture species due to reseeding
producción animal
Cantidad antes de MST:
1200litres/cow/yeer
Cantidad luego de MST:
2000litres/cow/year
Comentarios/ especifique:
Contribution of nutritious cut and carry pastures
Ingreso y costos
gastos en insumos agrícolas
Cantidad antes de MST:
high
Cantidad luego de MST:
low
Comentarios/ especifique:
availability of manure from animal kept under zore grazing
diversidad de fuentes de ingreso
Cantidad antes de MST:
low
Cantidad luego de MST:
high
Comentarios/ especifique:
Income accrued from sell of mulching and pasture materials.
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Cantidad antes de MST:
low
Cantidad luego de MST:
high
Comentarios/ especifique:
improved diet due to varied food availability (avalability of milk)
instituciones comunitarias
Cantidad antes de MST:
weak
Cantidad luego de MST:
strong
Comentarios/ especifique:
empowerment and capacity building of environmental committee.
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
Cantidad antes de MST:
low
Cantidad luego de MST:
high
Comentarios/ especifique:
Knoledge over controll of riverine resources.
mitigación de conflicto
Cantidad antes de MST:
low
Cantidad luego de MST:
high
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
The technology has contributed to availability and accessibility to mulching and nutritious pasture that are need for increased crop and livestock productivity. This has both direct and indirect impact on the income of the community and hence livelihood (e.g. ability to meet education and health expenses).
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo de agua/ escurrimiento de sedimento
cantidad de agua
Cantidad antes de MST:
low
Cantidad luego de MST:
high
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduction in uproductive loss of both green and blue water.
escurrimiento superficial
Cantidad antes de MST:
high
Cantidad luego de MST:
low
Comentarios/ especifique:
Resultant of vergetation cover
evaporación
Cantidad antes de MST:
high
Cantidad luego de MST:
low
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduce uproductive evaporation due vegetation cover
Suelo
cubierta del suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
low
Cantidad luego de MST:
high
Comentarios/ especifique:
Improved vegetation cover
pérdida de suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
high
Cantidad luego de MST:
low
Comentarios/ especifique:
Cotrolled soil erosion due to runoff
encostramiento/ sellado de suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
high
Cantidad luego de MST:
low
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced overgrazing and animla trumpling
compactación de suelo
Cantidad antes de MST:
high
Cantidad luego de MST:
low
Comentarios/ especifique:
Reduced overgrazing and animla trumpling
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Cantidad antes de MST:
low
Cantidad luego de MST:
high
Comentarios/ especifique:
Controlled fire burning
Reducción de riesgos de desastres y riesgos climáticos
emisión de carbono y gases de invernadero
Cantidad antes de MST:
high
Cantidad luego de MST:
low
Comentarios/ especifique:
Controled bush fire
riesgo de incendio
Cantidad antes de MST:
high
Cantidad luego de MST:
low
Comentarios/ especifique:
harzards due to bush fire but reduced due to enclosure, fire break and use of bylaws.
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
colmatación río abajo
Cantidad antes de MST:
high
Cantidad luego de MST:
low
Comentarios/ especifique:
Resultant of improved vegetation cover and controlled erosion
contaminación de aguas subterráneas/ de ríos
Cantidad antes de MST:
high
Cantidad luego de MST:
low
Comentarios/ especifique:
Resultant of improved vegetation cover and controlled erosion
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Cambio climático gradual
Cambio climático gradual
| Estación | tipo de cambios climáticos/ climas extremos | ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| temperatura anual | incrementó | bien |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | no se sabe |
| tormenta de viento | no se sabe |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | no muy bien |
Desastres hidrológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| inundación general (río) | no se sabe |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| periodo reducido de crecimiento | no muy bien |
Comentarios:
The technology was modified to become more tolerant through organized cut and carry of mulching and pasture materials.
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
positivo
Comentarios:
Mulching and pasture have short maturing period and this causes land users to realize rewards right from the beginning of the technology and the benefit increases more with time.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
Comentarios:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The technology is applied only on communally owned area nearby the fragile reverine ecosystem. Implementation is done by empowered community based on and guided with decision reached by the whole community and law reinforcement. Is not based on individual voluntarism and option.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The technology is applied only on communally owned area nearby the fragile reverine ecosystem. Implementation is done by empowered community based on and guided with decision reached by the whole community and law reinforcement. Is not based on individual voluntarism and option.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: As a result of benefit realization of the use of technology, there a growing acceptance and spontaneous adoption by the whole community
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra |
|---|
| The technology prevent degradation of the river bank and disappearance of palatable and nutritious pasture |
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
| Area enclosure complimented with reinforcement of bylaws reduce fire incidences and helps in sequestration of carbon both above and below the ground and reduce the effect of green gas emission. |
| Area enclosure and organized cut and carry feeding ensure availability of feed to animals kept in farm under zero grazing (e.g. dairy goats and cattle) and control unproductive loss of manure. |
| Area enclosure and organized cut and carry feeding ensure availability of mulching materials needed in production of banana and other crops. |
| Promote direct and indirect diversification of income sources to the rural poor. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del usuario de la tierra | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Time consuming and labour heavy especially to environmental committee members. | Device motivation and incentive system at the grassroots. |
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| Emergency and dominance of invasive species | Liaise with research to find alternative and beneficial use of invasive species. |
| Needs committed people who can spend their valuable time in promotion of the technology. | Use SLM related incentives and promotion e.g. support with dairy goat to people who actively participate in promotion of the technology (as part of crop livestock integration) . |
| Takes time to inculcate self initiatives and ownership | Systematize and Operationalize into existing systems |
| Needs attitude and behavioral change (is not normal traditional for rural people to cultivate grass). | Encourage change of mindset by enabling farmers understanding of the principle behind pasture establishment. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.1 Métodos/ fuentes de información
- visitas de campo, encuestas de campo
- entrevistas con usuarios de tierras
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos

Active participation of herder leader (WAKONDO) in management … [Tanzania, República Unida de]
Prevention and mitigation of the grazing land and riverine ecosystems through mandatory grassroots meetings, law enforcement and active participation and empowerment of herder leaders’ (masters of the most resource destructive group)
- Compilador: ALLAN BUBELWA
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos