Kiwi fruit cultivation [Nepal]
- Creación:
- Actualización:
- Compilador: Shreedip Sigdel
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
kiwi (theki) fal kheti (Main Contributor: Samden Sherpa, ICIMOD)
technologies_1686 - Nepal
Visualizar secciones
Expandir todo Colapsar todos1. Información general
1.2 Detalles de contacto de las personas de referencia e instituciones involucradas en la evaluación y la documentación de la Tecnología
Especialista MST:
Sherpa Samden Lama
+977 1 5003222
ssherpa@icimod.org
ICIMOD
P.O.Box 3226, Kathmandu, Nepal
Nepal
Nombre de la(s) institución(es) que facilitaron la documentación/ evaluación de la Tecnología (si fuera relevante)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Nepal1.3 Condiciones referidas al uso de datos documentados mediante WOCAT
¿Cuándo se compilaron los datos (en el campo)?
01/04/2011
El compilador y la/s persona(s) de referencia claves aceptan las condiciones acerca del uso de los datos documentados mediante WOCAT:
Sí
2. Descripción de la Tecnología MST
2.1 Breve descripción de la Tecnología
Definición de la Tecnología:
Kiwi fruit cultivation on sloping land in the mid-hill areas of Nepal can help prevent soil erosion and is a sustainable land management practice. This high value crop introduces biodiversity and improves livelihoods by providing a source of cash income.
2.2 Descripción detallada de la Tecnología
Descripción:
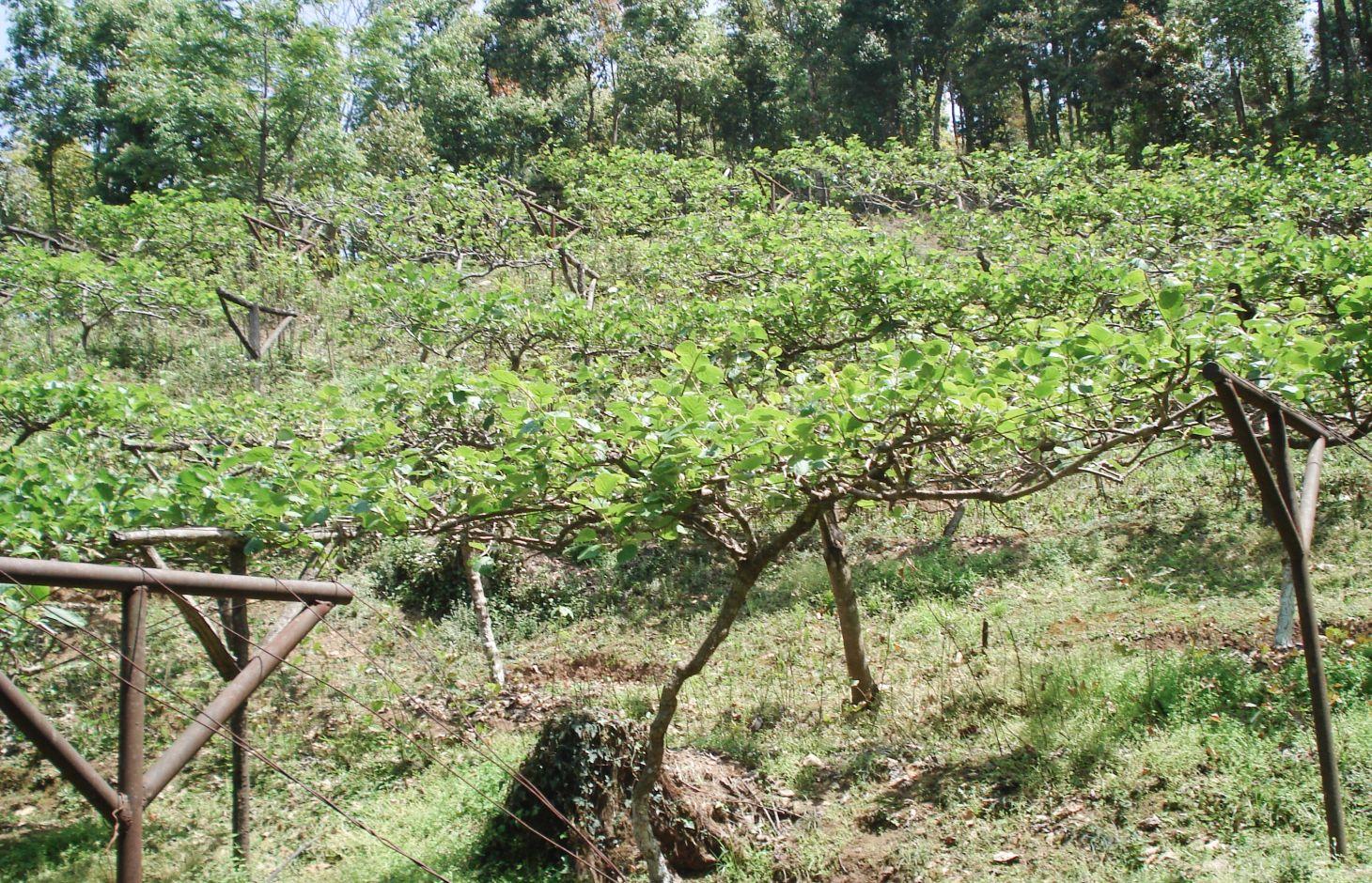
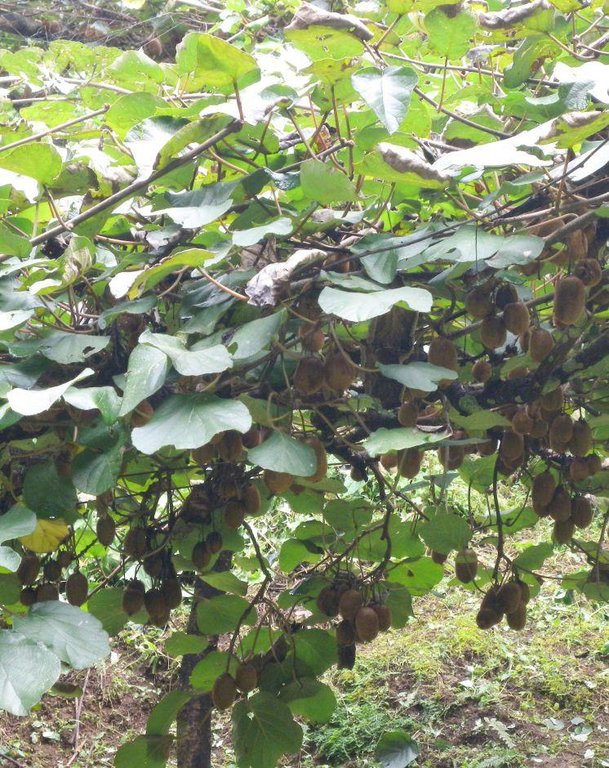
The kiwi fruit is native to China. Previously called Chinese gooseberry, it is now more commonly known by its marketing name of kiwi fruit. Kiwi fruits grow on large vines that are similar to grapevines in their general growth and fruiting habits as well as their training and trellising requirements. The fruit normally ripens within 25 weeks after the flowers first appear. The fruits range in weight from 40 to 90 g and can be picked shortly after the first frost in autumn; after that, they can be kept in cold storage for 4–6 months at oC. Kiwi vines can be grown on a wide range of soil types at elevations ranging from 1000 m to 2500 m. The kiwi plant is dioecious, meaning individual plants are either male or female. Only female plants bear fruit, but only when pollinated by a male plant. Vines of both sexes are essential for fruit production, and they must flower at the same time to ensure pollination. One male pollinator vine is required for eight female vines. The vines are commonly supported on sturdy structures strong enough to bear the heavy fruit, which might otherwise break the rather weak vines. T-bars or hitching post trellises are recommended to support the large fruiting area in the form of a canopy and provide easy access to the fruit.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Seedlings can be planted in the spring as soon as there is little chance of frost. Vines need to be pruned both in summer and in winter to maintain a balance between kiwi plant growth and profitable fruit production. Excessive plant growth is removed during the growing season to keep the kiwi canopy open and to remove non-fruiting wood. Harvesting can begin from the end of November. Frequent weeding is required to reduce competition for moisture and fertilizer. Kiwi fruit requires abundant water; during the dry season the newly planted kiwi vines need deep watering once a week.
2.3 Fotografías de la Tecnología
2.5 País/ región/ lugares donde la Tecnología fue aplicada y que se hallan comprendidos por esta evaluación
País:
Nepal
Especifique más el lugar :
Lalitpur District
2.7 Introducción de la Tecnología
Especifique cómo se introdujo la Tecnología:
- durante experimentos/ investigación
3. Clasificación de la Tecnología MST
3.1 Propósito(s) principal(es) de la Tecnología MST
- reducir, prevenir, restaurar la degradación de la tierra
- crear impacto económico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) actuales de uso de la tierra donde se aplica la Tecnología

Tierras cultivadas
- Cultivos perennes (no leñosos)
Comentarios:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): When sloping land is not used for agricultural production and not planted with ground cover or other vegetation (such as contour hedgerows), the fertile soil can be eroded and washed away by heavy monsoon rains.
3.3 Información adicional sobre el uso de tierras
Número de temporadas de cultivo por año:
- 2
3.4 Grupo MST al que pertenece la Tecnología
- variedades vegetales/ razas animales mejoradas
3.5 Difusión de la Tecnología
Comentarios:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 m2.
3.6 Medidas MST que componen la Tecnología

medidas vegetativas
- V1: Cubierta de árboles y arbustos
3.7 Principales tipos de degradación de la tierra encarados con la Tecnología

erosión de suelos por agua
- Wt: pérdida de capa arable/ erosión de la superficie

deterioro químico del suelo
- Cn: reducción de la fertilidad y contenido reducido de la materia orgánica del suelo (no ocasionados por la erosión)
Comentarios:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires)
3.8 Prevención, reducción o restauración de la degradación de la tierra
Especifique la meta de la Tecnología con relación a la degradación de la tierra:
- reducir la degradación de la tierra
4. Especificaciones técnicas, actividades de implementación, insumos y costos
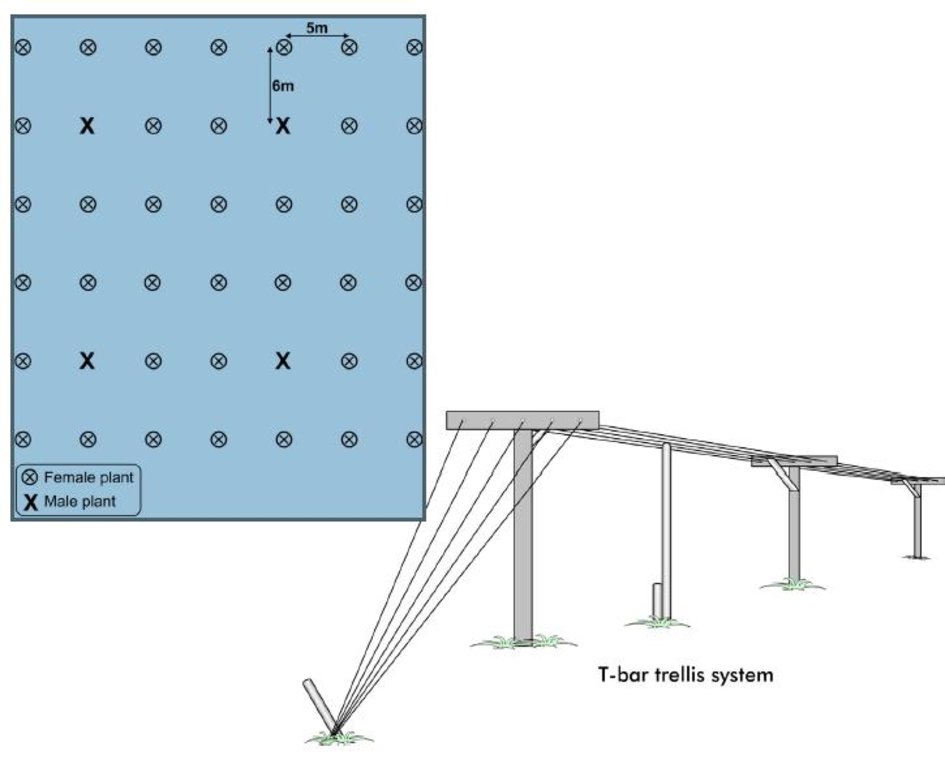
4.1 Dibujo técnico de la Tecnología
4.2 Especificaciones técnicas/ explicaciones del dibujo técnico
Above: Layout of a kiwi orchard. The ideal density of kiwi plants in an orchard is 300 per ha, or in terms of the units of measure commonly used in Nepal, 15 plants per ropani. The plants are spaced 6 m apart and the distance between the rows is 5 m, with a male to female plant ratio of 1:8.
Below: T-bars are used as trellis supports for the kiwi vines. The T-bars are 2.5–3 m long iron posts that are anchored into the ground; they extend approximately 1.8 m above the ground and 60–70 cm deep into the soil. The arms of the T-bar extend 1–1.2 m. The bars are spaced approximately 4.5 m apart with galvanized wire strung between them and pulled taught to form the trellis itself. The end posts are braced by 4–5 wires that are secured into the ground (as shown).
The kiwi plants should be at least
0.6 m away from the T-bars. The centre wire supports the main cordons, and the outer wires support the fruiting lateral parts.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of biomass (quantity), Reduce soil erosion
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle
4.3 Información general sobre el cálculo de insumos y costos
Especifique cómo se calcularon los costos e insumos:
- por área de Tecnología
Indique tamaño y unidad de área:
ha
Especifique la moneda usada para calcular costos:
- dólares americanos
Indique el costo promedio del salario de trabajo contratado por día:
3.7
4.4 Actividades de establecimiento
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | • The plot where the vines are to be planted is prepared by clearing and weeding.• The seedling pits are prepared at least 2 months before planting. Typically the pits are 1 m x 1 m and 1 m deep. The pits are filled with compost (30 kg per pit ) and covered with soil to a height of 0.3 m above the ground. | Vegetativas | 2 months |
| 2. | • Seedlings are planted in the winter to the same depth as in the nursery; they are planted 6 m apart in rows spaced 5 m apart.• The plants are pruned back to single, healthy shoots 15–30 cm high. | Vegetativas |
4.5 Costos e insumos necesarios para el establecimiento
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Prepare pits and seedlings | persons/day/ha | 136,0 | 3,6765 | 500,0 | |
| Material para plantas | Planting material | ha | 1,0 | 1500,0 | 1500,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Compost / manure | ha | 1,0 | 150,0 | 150,0 | |
| Material de construcción | Iron pole | ha | 1,0 | 3500,0 | 3500,0 | |
| Costos totales para establecer la Tecnología | 5650,0 | |||||
4.6 Actividades de establecimiento/ recurrentes
| Actividad | Tipo de medida | Momento/ frequencia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Permanent sod is maintained between the plant rows. Frequent weeding is required especially during the rainy season.• Both summer and winter pruning is required. | Vegetativas | |
| 2. | • Cuttings from branches that fruited during the previous season (typically less than a pencil width in thickness) are collected during the winter pruning for propagation.• Overhead sprinkler irrigation is used for commercial kiwi production.• Kiwi vines are fertilized with manure in the early spring | Vegetativas |
4.7 Costos e insumos necesarios para actividades de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (por año)
| Especifique insumo | Unidad | Cantidad | Costos por unidad | Costos totales por insumo | % de los costos cubiertos por los usuarios de las tierras | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mano de obra | Maintenance and prunning | persons/day/ha | 122,0 | 3,6885 | 450,0 | |
| Equipo | Secateurs | ha | 1,0 | 50,0 | 50,0 | |
| Equipo | Binding wire | ha | 1,0 | 650,0 | 650,0 | |
| Fertilizantes y biocidas | Compost / manure | ha | 1,0 | 150,0 | 150,0 | |
| Indique los costos totales para mantenecer la Tecnología | 1300,0 | |||||
4.8 Factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
Describa los factores más determinantes que afectan los costos:
The above establishment cost is for a plantation of 300 plants on one hectare; the recurrent annual maintenance cost has been calculated for a plantation of 300 plants per ha per year. All costs are estimated based on experience gained at the ICIMOD Knowledge Park at Godavari.
5. Entorno natural y humano
5.1 Clima
Lluvia anual
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Sub-húmeda
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografía
Pendientes en promedio:
- plana (0-2 %)
- ligera (3-5%)
- moderada (6-10%)
- ondulada (11-15%)
- accidentada (16-30%)
- empinada (31-60%)
- muy empinada (>60%)
Formaciones telúricas:
- meseta/ planicies
- cordilleras
- laderas montañosas
- laderas de cerro
- pies de monte
- fondo del valle
Zona altitudinal:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1,000 m s.n.m
- 1,001-1,500 m s.n.m
- 1,501-2,000 m s.n.m
- 2,001-2,500 m s.n.m
- 2,501-3,000 m s.n.m
- 3,001-4,000 m s.n.m
- > 4,000 m s.n.m
5.3 Suelos
Profundidad promedio del suelo:
- muy superficial (0-20 cm)
- superficial (21-50 cm)
- moderadamente profunda (51-80 cm)
- profunda (81-120 cm)
- muy profunda (>120 cm)
Textura del suelo (capa arable):
- mediana (limosa)
Materia orgánica de capa arable:
- elevada (>3%)
Si se halla disponible, adjunte una descripción completa de los suelos o especifique la información disponible, por ej., tipo de suelo, pH/ acidez de suelo, capacidad de intercambio catiónico, nitrógeno, salinidad, etc. :
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
Agua subterránea:
< 5 m
Disponibilidad de aguas superficiales:
bueno
Calidad de agua (sin tratar):
agua potable de buena calidad
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre calidad y cantidad de agua:
Water quality (untreated): Also for agricultural use (irrigation)
5.5 Biodiversidad
Diversidad de especies:
- elevada
Comentarios y especificaciones adicionales sobre biodiversidad:
695 species of flora and 230 species of fauna have been documented within the Knowledge Park's 30 ha area
5.6 Las características de los usuarios de la tierra que aplican la Tecnología
Orientación del mercado del sistema de producción:
- mixta (subsistencia/ comercial)
Ingresos no agrarios:
- > 50% de todo el ingreso
Nivel de mecanización:
- trabajo manual
- tracción animal
Indique otras características relevantes de los usuarios de las tierras:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
5.7 Área promedio de la tierra que pertenece a o es arrendada por usuarios de tierra que aplican la Tecnología
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
5.8 Tenencia de tierra, uso de tierra y derechos de uso de agua
Tenencia de tierra:
- estado
Derechos de uso de tierra:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
Derechos de uso de agua:
- comunitarios (organizado)
- individual
5.9 Acceso a servicios e infraestructura
caminos y transporte:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
Labour:
- pobre
- moderado
- bueno
6. Impactos y comentarios para concluir
6.1 Impactos in situ demostrados por la Tecnología
Impactos socioeconómicos
Disponibilidad y calidad de agua
demanda de agua para irrigar
Impactos socioculturales
seguridad alimentaria/ autosuficiencia
Comentarios/ especifique:
Kiwi is considered an elite fruit and it is usually too expensive for local consumption
instituciones comunitarias
MST/ conocimiento de la degradación de la tierra
livelihood and human well-being
Comentarios/ especifique:
Kiwi production can be a good source of cash income as it is a high value crop. Kiwi fruit is high in nutrients, eating kiwis has been show to boost the immune system, to help regulate blood pressure, and to be beneficial for cardiac patients
Impactos ecológicos
Suelo
cubierta del suelo
pérdida de suelo
Biodiversidad: vegetación, animales
biomasa/ sobre suelo C
Otros impactos ecológicos
Pollen for bees
biodiversity
efficient use of land
competition with other plants for water, nutrients, and sunlight when intercropping
6.2 Impactos fuera del sitio demostrados por la Tecnología
inundaciones río abajo
capacidad de amortiguación/ filtrado
6.3 Exposición y sensibilidad de la Tecnología al cambio climático gradual y a extremos relacionados al clima/ desastres (desde la percepción de los usuarios de tierras)
Extremos (desastres) relacionados al clima
Desastres climatológicos:
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| tormenta de lluvia local | bien |
| tormenta de viento | no muy bien |
Desastres climatológicos
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| sequía | no muy bien |
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
Otras consecuencias relacionadas al clima
| ¿Cómo es que la tecnología soporta esto? | |
|---|---|
| Mild winter frost | bien |
Comentarios:
A net canopy can be used to protect the vines from hail storms and help prevent fruit from dropping prematurely
6.4 Análisis costo-beneficio
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de establecimiento (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
¿Cómo se comparan los beneficios con los costos de mantenimiento/ recurrentes (desde la perspectiva de los usuarios de tierra)?
Ingresos a corto plazo:
ligeramente positivo
Ingresos a largo plazo:
muy positivo
Comentarios:
The approximate annual income from kiwi production is USD 11,765/ha/year. The technology provides on-farm employment opportunities for both men and women.
6.5 Adopción de la Tecnología
- casos individuales / experimentales
Comentarios:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Kiwi fruit is gaining in popularity in Nepal; at present it is cultivated commercially by farmers in Kavre, Lalitpur, Dolakha, and Ilam Districts as well as in the Kathmandu Valley. The technology is widely accepted. Kiwi saplings were initially supplied by ICIMOD and by a private nursery in Kavre District.
Driver for adoption:
• Increased market demand for kiwi fruit
• A good alternative for sloping land management
• Kiwi cultivation is a source of income generation
Constraints
• It has been difficult to meet the high demand for kiwi seedlings. The scarcity of seedlings is the main bottleneck limiting the uptake of kiwi production.
6.7 Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades de la Tecnología
| Fuerzas/ ventajas/ oportunidades desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave |
|---|
|
Orchards are easy to establish and farmers can readily learn what is needed for kiwi cultivation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Awareness and training programmes can help farmers quickly learn what is needed for kiwi cultivation. |
|
The benefits of the technology are easy to observe; farmers generate cash income from selling kiwi fruit, juice, and jam. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Awareness and training programmes can help farmers quickly learn what is needed for kiwi cultivation and postharvest processing. |
|
Soil erosion is decreased due to increased groundcover. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Awareness and training programmes can help farmers quickly learn what is needed for kiwi cultivation. |
|
Kiwi cultivation provides on-farm employment opportunities. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Awareness and training programmes can help farmers quickly learn what is needed for kiwi cultivation. |
6.8 Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos de la Tecnología y formas de sobreponerse a ellos
| Debilidades/ desventajas/ riesgos desde la perspectiva del compilador o de otra persona de referencia clave | ¿Cómo sobreponerse a ellas? |
|---|---|
| The initial costs associated with establishing the orchard may be a little expensive for many farmers, these include the purchase of: T-bar trellises, seedlings, iron rods, and wire. | Begin by using locally available materials such as bamboo poles to make T-bar trellis. |
7. Referencias y vínculos
7.3 Vínculos a la información relevante disponible en línea
Título/ descripción:
Kiwi fruit production guide. Tuscaloosa, Alabama, United States: Alabama University, Himelrick, DG; Powell, A (1998)
URL:
http://www.aces.edu/pubs/docs/A/ANR-1084/ANR-1084.pdf
Vínculos y módulos
Expandir todo Colapsar todosVínculos
No hay vínculos
Módulos
No se hallaron módulos